Let’s imagine that we wake up one morning, or after suffering an accident, and suddenly we find that everyone starts speaking in a strange language. The worst of all is that it seems familiar to us, but we don’t understand what they want to tell us.
We try to communicate, but we realize that we are not saying what we intend. The others insist, look at us and continue talking to us even though we do not understand what they are trying to communicate to us. And we can’t make ourselves understood either. Although it may seem like a science fiction movie, This is what people who suffer from global aphasia experience.
The concept of aphasia
Aphasias are a group of speech and language disorders caused by a brain injury which occur in adults with a language that had already been previously consolidated.
These types of disorders can affect very different aspects of language, among which we can find verbal fluency, articulation capacity, language comprehension, repetition, grammar, reading and writing or naming. The different aspects affected will depend on the injured area.
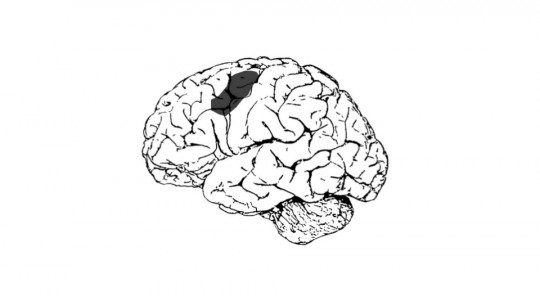
Broadly speaking, one of the main classifications of these disorders is the one proposed by Goodglas and Kaplan, in which they are divided into different typologies depending on whether or not they present a good level of verbal fluency, comprehension and repetition capacity. The best known are Broca’s aphasia and Wernicke’s aphasia, each with its own damaged and preserved aspects. However, There is a type of aphasia in which alterations occur in all areas of language, known as global aphasia.
Global aphasia: main characteristics
Global aphasia is the most severe form of aphasia because all or a large part of the different aspects of language are affected and altered by a brain injury.
People who suffer from it have severe difficulties in both comprehension and oral and generally written expression. Likewise, subjects affected by global aphasia have poor imitation abilities. If they are capable of uttering oral language, it is common for them to use telegraphic and stereotyped areas, with little chance of establishing communication through verbal language. They can also understand certain words or verbs.
In addition, they tend to be incapable of writing or limited to an automatism such as the ability to sign. Reading is also affected. It is possible that at a written level they can reproduce a text by copying it, although guided by the forms and not by its content. Articulation capacity, verbal fluency, and the use of lexicon and grammar are severely diminished and impaired.
Because the lesion that causes global aphasia is massive, other symptoms usually appear such as ideomotor apraxia (they do not know how to use objects for their true purpose) and ideatory apraxia (they have an inability to follow action sequences in the correct order), hemiplegia or paralysis. half body Global aphasia per se does not cause any cognitive difficulties, with intelligence and most executive functions being preserved. However, it is possible that they present cognitive and intellectual difficulties due to neuronal damage, limiting them even more.
Causes
The causes of aphasia, as we have commented previously, are due to the presence of lesions in the areas that control language their connections among themselves or the connections with other brain nuclei that allow linguistic information to be integrated with motor information, or that have been destroyed.
In the case of global aphasia, it is necessary that there be significant damage to the entire left hemisphere, which contains the areas that process language, or to the area surrounding the perisylvian cortex. Both Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas, their connections with each other, or the connections with other areas that allow the processing or execution of speech, are damaged or disconnected from the rest of the brain.
What exactly causes these injuries can vary greatly, ranging from head trauma or lacerations to strokes, brain tumors or neurodegenerative diseases.
Difficulties caused by this disorder
The consequences of global aphasia and the symptoms it causes are very limiting for the person who suffers from it. As social beings that we are, our lives are structured based on the assumption that we are capable of communicating. That is why not being able to express oneself can cause
On a social level, global aphasia greatly hinders the possibility of establishing emotional relationships with our peers. Although his social skills and interest in establishing contact with others are preserved, the patient has severe difficulties in making himself understood unless he has alternative methods. It is common that, given that before the injury he could communicate orally correctly, the environment begins to try to communicate by shouting (interpreting that he has lost hearing ability) or interprets the lack of communication on the part of the subject as a lack of interest. It is important to understand that the subject hears perfectly, his difficulty being that of interpreting language.
This problem also generates difficulties at work, as well as academically. Learning, at least by usual means, is difficult unless adapted strategies such as the use of pictograms or through the use of physical procedures are used.
At the level of the individual himself, This disorder can be experienced with real terror. After all, the subject is suddenly unable to understand what they are trying to say or make themselves understood through the usual mechanisms, and the unsuccessful attempts on the part of the subject and the environment to reestablish oral communication can end up causing high anxiety. and depression to the individual. The subject may feel isolated, closed within himself, until the treatment begins to be effective or alternative forms of communication are found.
Possible treatments
The treatment to be used in case of global aphasia focuses on the recovery of the functions altered by the brain injury and/or adopting or learning alternative communication methods. Psychological and social support is also essential to allow the patient and those around them to understand and accompany the patient in the process they are suffering.
It is important to keep in mind that many brain injuries can evolve in ways that reduce damage. This is what happens, for example, in the event of a trauma or a stroke, in which the blood can drown part of the brain connections but leaves a zone of ischemic twilight that can be recovered from the accident. In this way, many patients can see how the effects of the injury progressively diminish. In some cases this can cause a change from a global aphasia to a more localized one.
The use of language therapy and speech therapy is common, used to improve and optimize the linguistic competence that the affected person may maintain. The use of augmentative language techniques is also common, or the use of visual material such as pictograms with which the patient can communicate in an alternative way.
It is important to stimulate the patient without overloading him, so that he can gradually relearn and polishing skills without becoming saturated. Psychoeducation is very important for both the patient and the environment, since it is necessary to understand that cognitive abilities are preserved (unless there are other impairments beyond global aphasia) and the difficulties that aphasia poses for the subject.