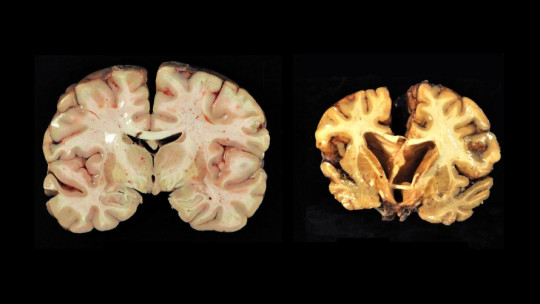
The brain is the most important set of organs in our body, but it is also one of the most delicate. A small malformation or alteration in its functioning can totally affect its performance, and although thanks to neuroplasticity it can overcome a large number of injuries, this does not always happen.
Hypoxic encephalopathy Specifically, it is one of the most serious situations that the brain can suffer and, in fact, it is the main cause of brain death. Below we will see what it is, why it occurs and what is usually done to try to reverse this condition.
What is hypoxic encephalopathy?
Encephalopathies are a category used in medicine to generally refer to diseases of the brain, and this case is no exception. In hypoxic encephalopathy, there is a lack of oxygen in this set of organs due to which the tissue formed by neurons and glial cells begins to die, producing a risk of serious sequelae or even death.
This is what can happen, for example, in cerebral ischemia: blood flow is interrupted, and as a consequence there are cells that cannot stay alive and begin to be rapidly destroyed.
It must be taken into account that When talking about hypoxic encephalopathy we are not simply talking about a lack of oxygen in the brain, but rather the damage to brain tissues caused by it. It is the disease, and not the cause of cell death.
On the other hand, hypoxic encephalopathy is relatively common, estimated to cause around 25% of infant deaths worldwide. It is also one of the main causes of mortality in boys and girls going through early childhood.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease depend largely on the area of the brain that is affected, and depending on its severity.
Mild hypoxic encephalopathy
In this situation, Typical symptoms in hypooxic encephalopathy are these:
Moderate hypoxic encephalopathy
The associated symptoms are:
Severe hypoxic encephalopathy
In these cases, the following are common:
Forecast
The prognosis made from hypoxic encephalopathy can be very variable, and improves in cases in which the initial symptoms improve during the first week. However, as a guide, It is estimated that the main consequences of the disease are the following:
-
Epileptic seizures.
- Cognitive impairment.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Difficulties when controlling movements.
Stages of this disease
Hypoxic encephalopathy has two phases, each with its risks and possible consequences. The first of them consists of the damage caused by the deprivation of oxygen itself, while the second It is called reperfusion injury.
In this second phase, the reestablishment of blood flow to the brain is capable of damaging tissues due to the accumulation of substances that had occurred during the previous stage in a certain section of the circulatory system. In this way, everything that has been accumulated passes through an area of the nervous system that is vulnerable at the same time.
Risk factor’s
It is estimated that the main associated risk factors to the appearance of hypoxic encephalopathy are the following:
-
Meningitis and encephalitis.
- Congenital malformations of the skull, such as microcephaly.
- Craniocerebral trauma.
- Low blood pressure.
- Having had a premature birth.
- During pregnancy, the risk factors related to the possible development of the disease in the baby are these:
- Knots in the umbilical cord.
- Placenta rupture.
- Elevated pressure inside the skull of the fetus.
- Drug use during pregnancy.
Treatment
In cases of hypoxic encephalopathy, it is important to act as soon as possible to prevent areas crucial for the functioning of the nervous system and the general survival of the body from being damaged. One of the first measures is use assisted breathing to respond to immediate needs of the body while trying to restore blood flow.
What follows from this has to do with the supply of medications to treat possible seizures. Sometimes treatments are also used to reduce the temperature of the affected area of the brain, with the aim of varying the pressure in that area and causing the irrigation to pass through there again.
On the other hand, as the lack of oxygen in the central nervous system may have affected the functioning of all types of organs in the body, it is also necessary to treat these effects in parallel. If the disease occurs in a newborn baby, these techniques should be as least invasive as possible.
In cases where flow has already been restored but significant sequelae remain, occupation therapy is highly recommended since it helps the person to integrate better and gain autonomy over their own life.