Howard Gardner revolutionized the concept of intelligence in the 1980s. His theory of multiple intelligences broke with the academic approach to intelligence and shows that the IQ is made up of various factors or types of intelligence. This theory includes the intelligence to understand and relate to ourselves, the so-called intrapersonal intelligence, closely linked to emotions and whose development is related to our well-being.
If you want to know more about this type of intelligence, don’t miss this PsychologyFor article about intrapersonal intelligence: what it is, examples and activities to improve it<
What is intrapersonal intelligence
Intrapersonal intelligence is one of the types of intelligence recognized by the psychologist Gardner in his Theory of Multiple Intelligences. This intelligence is related to the quality of the relationship we have with ourselves.
Specifically, intrapersonal intelligence refers to the capacity and degree of self-knowledge, as well as the ability to perceive and form a true individual image, as objective as possible and adjusted to reality. This intelligence involves awareness and knowledge of one’s own intentions, motivations, desires, moods, emotions, abilities, etc.
In short, intrapersonal intelligence is having self-knowledge about how we are and what we want and be able to use this information develop accordingly. Additionally, this capability allows analyze your own thoughts and feelings as well as assessing the best way to address the emotional needs of each person.
The intrapersonal intelligence described by Howard Gardner is related to the following abilities:
- Self-awareness or self-knowledge: involves recognizing one’s own feelings, thoughts and reactions, how they affect, as well as the cause of them. It includes emotional awareness, self-assessment of strengths and weaknesses, and self-confidence.
- Self-regulation: ability to act based on prior knowledge of our emotions. It also includes the ability to reflect on the emotions we are experiencing, their causes and how to act based on them. It is based on the skills of self-control, reliability, adaptability and innovation.
- Self motivation: It is the capacity by which we are able to establish, meet our own goals and objectives and make efforts based on what we want to achieve. Self-motivation is related to the ability to achieve, commitment, initiative and optimism.
Regarding the cerebral location of intrapersonal intelligence, it is mostly located in the frontal lobes which are responsible for executive functions and regulating behavior, and the parietal lobes, are responsible for integrating the information. This type of intelligence is also linked to the limbic system, which is known as the emotional part of the brain.
How to recognize a person with intrapersonal intelligence
People with this type of intelligence have defined traits. Specifically, the main characteristics of intrapersonal intelligence are:
- Ability to transmit one’s own emotions accurately and in detail. People with intrapersonal intelligence are able to identify them easily, since they pay attention to their physical and emotional state and reflect on it.
- High introspection capacity, so it is reflected with the aim of knowing oneself better and having greater awareness of oneself. People with this intrapersonal intelligence spend time and enjoy this internal reflection. In the following article you will see how to do an introspection exercise.
- Analyze your own actions: If you have this intelligence developed, it is common to do an analysis to try to understand them, value them and learn from mistakes for future occasions.
- Promotes a self-concept adjusted to reality about your personality, strengths and limitations. This knowledge favors the ability to make decisions that have a beneficial impact on the person themselves more easily and to achieve the proposed objectives.
- Promotes self-compassion: feeling through which people understand themselves, their own mistakes and have the ability to forgive themselves. Being aware of one’s own limitations and circumstances means that, if they make a mistake, the person does not punish themselves, but rather treats themselves with kindness and understanding.
- Knowledge of one’s own emotional needs and how to address them: refers to the ability to set realistic goals and objectives based on personal motivations and knowledge of your abilities and circumstances. In turn, defining realistic objectives enhances commitment and effort.
- Practice emotional self-care: oneself is aware of what one needs and how to address these needs.
- They have a wide emotional vocabulary: They are able to understand and capture small nuances of emotions.
Furthermore, it should be noted that people with high interpersonal intelligence tend to be attracted to professions such as psychology, psychiatry, sociology, philosophy writing, anatomy or others that involve analytical skills.
Examples of interpersonal intelligence
We can find different examples of intrapersonal intelligence in daily life such as the following:
- Postpone decisions: a person who pays attention to his own circumstances, his emotional and physical state and realizes that he is beginning to feel sad. She is aware that when she is sad she is not able to make good decisions and she finds it positive for her mood to talk to her friends and take walks. Based on this knowledge, she chooses to postpone an important decision that she had pending until she is emotionally better. Likewise, she decides to go for a walk and call her best friend with the aim of improving her emotional state.
- Decline a job: saying no to a job offer in which one of the conditions is having to deal with difficult social situations, since you are aware that you are an extremely sensitive and apprehensive person. Based on his own knowledge of his personality and competencies, he concludes that he could not cope competently and without suffering excessively. Therefore, he decides to wait for another job offer.
Celebrities with emotional intelligence
Among the world of celebrities, there are those who stand out for having cultivated intrapersonal intelligence. Some examples of people with a high development of intrapersonal intelligence are Virginia Woolf and Carl Jung:
- Virginia Woolf was a British writer of the 20th century. In her writings and essays she stands out for the analysis she carries out about her feelings and emotions, both in the present and in the past. Virginia made dives into her own inner world with the aim of better understanding herself and, subsequently, she reflected her reflections and conclusions in her writing.
- Carl Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist born at the end of the 19th century. Jung had a high capacity to pay attention to and analyze his own feelings and emotions, which led him to investigate them in depth and ultimately develop theories. Part of his method was based on self-knowledge and exhaustive analysis of his own person. He founded the school of analytical psychology and made great contributions to the field of psychology that continue to exist.
Differences between interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligence
Both intelligences are part of Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences and interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligences are social and emotional. However, they encompass different capabilities and objectives.
On the one hand, intrapersonal intelligence refers to the capabilities and abilities to relate to oneself< On the other hand, interpersonal intelligence refers to the abilities and skills in social interactions with other people<
Therefore, intrapersonal intelligence is the ability to understand and listen to oneself, know one’s own weaknesses and strengths and act accordingly, while interpersonal intelligence is the ability to understand other people. and act consistently. Both intelligences are necessary and important for a quality and more satisfying emotional life.

Activities to develop intrapersonal intelligence
Intrapersonal intelligence is the capacity for realistic self-knowledge and self-reflection. This intelligence has a positive impact on our well-being and emotional awareness, decision making and self-care. For all these reasons, it is important to cultivate and stimulate this capacity, but how to promote it? Below we show you a series of activities to develop intrapersonal intelligence:
- Analyze your emotions: Spend time thinking about how you feel, naming those emotions, and trying to verbalize them with other people. You can rely on this list of emotions with their meaning. This analysis favors both the early identification of possible emotions and the understanding of them based on the circumstances or situations. Understanding yourself and your emotions empowers you when making decisions based on realistic knowledge and promotes your ability to know what you should avoid.
- Record your emotions and feelings: write down how you feel or what you think has affected your emotions. Describing them in detail encourages self-awareness. Writing and recording our thoughts and feelings helps us reflect on them. The records and their analysis make it easy to discover, for example, that performing a certain action makes you feel good or bad.
- Take some time to examine yourself: It is necessary to leave space to reflect on yourself, your strengths and weaknesses, to recognize your virtues and think about how you can improve. Carrying out this task in writing can facilitate the process of self-knowledge.
- Review your values, priorities and goals: Goals in life change. Therefore, it is necessary to look for and create moments of reflection about what you want, what your needs are and how they have evolved over time. Create a hierarchy of objectives, assess what you need to achieve them and what you could do about it. It is also important to value those past goals that you have already achieved, value the learning, how they made you feel, etc.
- Adapt to possible difficult situations: Use your strengths and limitations to face future situations. In this sense, visualization and imagination allow you to generate an idea of the situation and analyze in which aspects you perform well and which ones cost you more in order to work on them and improve them.
- Find activities that encourage your introspection: It is important that you also know what type of stimuli promote internal reflection and contact with your emotions. People are different, so what someone else finds beneficial may not be beneficial to you and vice versa. In the process of self-knowledge it is important that you get to know what favors your internal dialogue. Some of these activities can be listening to music and being alone, practicing yoga, practicing meditation, painting, playing an instrument, playing sports, walking, talking to other people about yourself and your emotions, writing about your emotions, going to a expert in psychology, etc.

Intrapersonal intelligence test
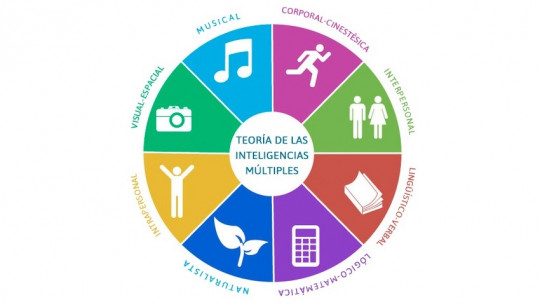
If you want to know if your intrapersonal intelligence stands out, we recommend taking this multiple intelligences test. With the result, you will be able to know which of the 8 intelligences proposed by Howard Gardner is the one that predominates in you:
- Linguistic Intelligence.
- Logical Intelligence – Mathematical.
- Visual – Spatial Intelligence.
- Kinesthetic or Body-Kinetic Intelligence.
- Musical intelligence.
- Interpersonal intelligence.
- Intrapersonal intelligence.
- Naturalistic Intelligence.
This article is merely informative, at PsychologyFor we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Intrapersonal intelligence: what it is, examples and activities to improve it we recommend that you enter our Cognitive Psychology category.
Bibliography
- Ernst-Slavit, G. (2001). Education for all: Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences. Psychology Magazine19(2), 319-332.
- Gardner, H. (2003). Intelligence in seven steps. New Horizons For Learning, Creating the Future. Report retrieved December, 21, 2005
- Shepard, R., Fasko, D.J., & Osborne, F.H. (1999). Intrapersonal intelligence: Affective factors in thinking. Education119(4), 633.