These types of hallucinations are visual, auditory, or other sensation experiences that can occur in the transition between being awake and falling asleep (hypnagogic) or between being asleep and waking up (hypnopompic). These experiences can be vivid and are often perceived as real, even though they are not related to external stimuli.
In this PsychologyFor article, we will provide you with information about the hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations: what they are, causes, symptoms and treatment We explore this phenomenon to uncover the fascinating intersection between the conscious mind and the mysteries of dream, shedding light on the complexities of the transition between the real world and the limitless landscape of the imagination.
What are hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations?
Hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations are sensory phenomena that occur on the border between wakefulness and sleep. That said, let’s look at the characteristics of each one:
- Hypnagogic hallucinations: These hallucinations are experienced just before falling asleep. They can manifest as images, sounds or tactile sensations, creating a bridge between reality and the beginning of the dream. In other words, the person is sure of having seen, heard or listened to something, although he does not know if it was real. Often associated with sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations can be experienced as very vivid and surreal.
- Hypnopompic hallucinations: These hallucinations occur upon waking up or during the transition from sleep to wakefulness. Like hypnagogics, they can encompass various senses and generate intense perceptual experiences. As an example, it is possible to hear voices that are confused with sleep. Specifically, hypnopompic hallucinations can influence the way we perceive awakening, merging elements of the dream with momentary reality.
Both types of hallucinations provide a fascinating window into mental processes at the borders of consciousness and sleep, highlighting the intricate relationship between the mind and the phases of the sleep-wake cycle.
Symptoms of hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations
The symptoms of hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations can vary, but generally involve sensory experiences that can be intense and vivid. Below we describe the common symptoms associated with these hallucinations:
- Visual disturbances: In hypnagogics, before falling asleep, people may experience clear, colorful images, often surreal in nature. In hypnopompic hallucinations, upon awakening, images may persist, creating a gradual transition between the dream world and reality.
- Auditory perceptions: the perception of sounds, such as voices, laughter, or humming, that have no external source. The persistence of dream sounds in the waking state sometimes generates an amalgamation of auditory experiences.
- Sensitive alterations: In hypnagogic hallucinations, the perception of tactile sensations, such as the sensation of floating or pressure on the body, often associated with sleep paralysis. In hypnopompic, the continuity of tactile sensations from the dream upon waking, creating a connection between the dream world and physical reality.
It is essential to note that hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations are common phenomena and, in most cases, do not indicate a mental health problem However, if these experiences are frequent, disruptive, or cause significant distress, it is recommended that you seek the guidance from a health professional
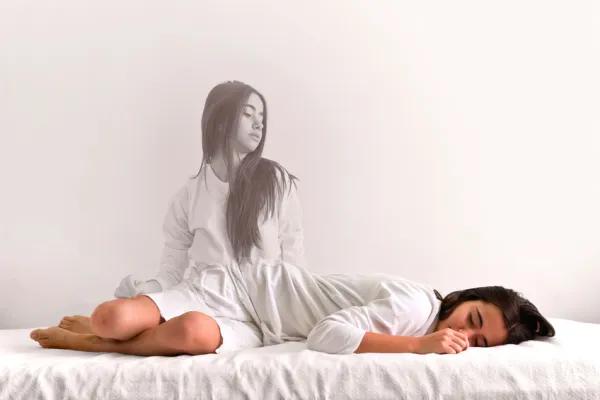

Causes of hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations
Hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations can have various causes, and are often related to normal sleep-wake processes. Let’s see then what are the possible causes of these hallucinations.
- Transition between states of consciousness: Hypnagogics occur during the transition from wakefulness to sleep, when the brain goes from a state of active consciousness to a more relaxed state. Instead, hypnopompic symptoms occur during the transition from sleep to wakefulness, when the brain is gradually waking up.
- Sleep paralysis: a condition in which the body is temporarily immobilized upon waking or falling asleep. It is frequently associated with hypnopompic and hypnagogic hallucinations.
- Sleep cycle imbalances: Changes in normal sleep patterns, such as interruptions or irregularities in sleep phases, can lead to the appearance of hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations.
- Stress and fatigue: Stress, anxiety, and fatigue can increase the likelihood of experiencing hallucinations during sleep transitions. These factors can affect sleep quality and the brain’s ability to regulate dream experiences.
- Sleep disorders: Some sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy, may be associated with hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations. In the case of narcolepsy, the rapid transition between wakefulness and sleep can trigger these experiences.
Treatment of hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations
Despite the difficulties caused by these clinical presentations, there are some approaches that can reduce and/or eradicate them. In the next items, we will develop the treatments for hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations:
- Improved sleep hygiene – Establishing regular sleep routines, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and creating an environment conducive to rest can help improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations.
- Stress and anxiety management: Strategies to manage stress and anxiety, such as relaxation practice, meditation, or cognitive behavioral therapy, may be beneficial in reducing disruptive experiences during sleep transitions.
- Avoid stimuli before sleeping: Limiting exposure to electronic devices and stimulating activities before bed can help facilitate a smoother transition to sleep and reduce the chances of hallucinations.
- Consult with a health professional: If hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations persist or are associated with other symptoms, it is crucial to seek help from a doctor or sleep specialist. They may conduct more in-depth evaluations and consider options such as cognitive behavioral therapy, sleep disorder treatment, or, in more severe cases, specific medications.

This article is merely informative, at PsychologyFor we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations: what they are, causes, symptoms and treatment we recommend that you enter our Clinical Psychology category.
Bibliography
- Parra, A. (2009). Nocturnal hallucinatory experiences: Relationship with schizotypy, dissociative tendencies and propensity to fantasy. International Journal of Psychology, 43 (1), 134-143.