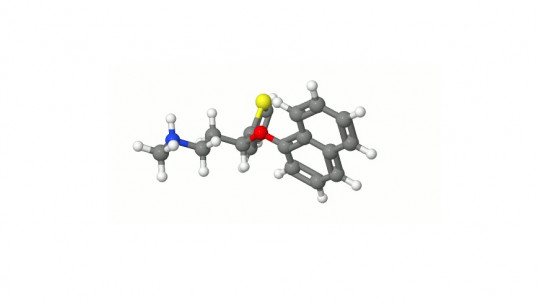
There are some drugs that are used for quite diverse disorders or pathologies. This is the case of pregabalin, an antiepileptic and analgesic drug indicated for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), neuropathic pain and seizures typical of epilepsy.
In this article we will learn about its mechanism of action, how it is administered in each case, its side effects and contraindications.
Pregabalin: what is it?
Pregabalin is an antiepileptic and analgesic drug, which is mainly used for peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults, as add-on therapy in partial seizures with or without generalization in adults and for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
Its active ingredient is an analogue of γ-aminobutyric acid (GAB)A, that is, it It is a GABA analogue drug (main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system), just like its predecessor gabapentin.
This drug is administered orally, and can be taken with or without food. The contraindication to taking pregabalin is suffering from hypersensitivity to pregabalin itself.
Regarding its dosage, the dose range is 150 to 600 mg per day, dividing its administration into two or three doses. To do it You must always follow the instructions of the medical staff who has prescribed this drug.
Pregabalin It should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age since its safety and effectiveness in these groups have not yet been established.
Indications
Pregabalin belongs to a group of medications that are mainly used for the treatment of epilepsy, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults, and neuropathic pain.
1. Epilepsy
Pregabalin is used to treat certain types of epilepsy, specifically partial seizures with or without secondary generalization, in adults. Pregabalin requires a prescription prescribed by the doctor.
It is prescribed for cases of epilepsy when current treatment is not controlling the disease. Pregabalin is usually taken in addition to the current treatment.
It should not be administered alone, but should always be used in combination with other antiepileptic treatments.
2. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
In this case, pregabalin is prescribed for symptoms of excessive and prolonged anxiety and worry typical of the TAG, which are difficult to control.
In addition, GAD can also cause restlessness or a feeling of excitement or nervousness, a feeling of fatigue and easy tiredness, as well as difficulties concentrating or easy going blank, irritability, muscle tension or sleep disturbances. Pregabalin also acts on these symptoms.
However, we must be clear that These symptoms are slightly different from stress itself, and/or to tensions typical of daily life.
3. Neuropathic pain
Pregabalin is also used to treat neuropathic pain (peripheral and central). Neuropathic pain is produced by damage or an alteration in the structures of the nervous system Therefore, this pain can be caused by damage to the peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathic pain) or by damage to the spinal cord or brain (central neuropathic pain).
Neuropathic pain is caused by abnormal functioning of the nervous system, which interprets stimuli incorrectly. It affects 7-10% of the European population.
Side effects
Pregabalin, like all medications, also has a series of adverse effects that can appear when taken (although they do not always appear). The most common side effects (which may affect more than 1 in 10 people) are dizziness, drowsiness and headache
Other slightly less common side effects (affecting more than 1 in 100 people) are: