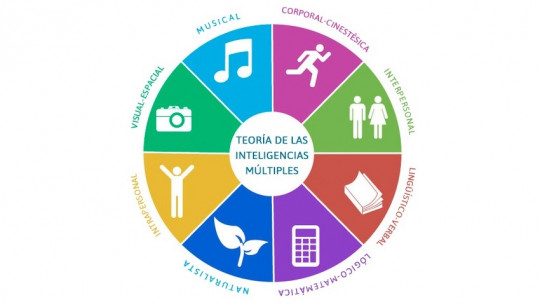
The theory of multiple intelligences made known by Howard Gardner has been, since it was disseminated in the 1980s, one of the research and intervention proposals in psychology that have generated the most interest on the street.
Initially, the types of intelligence proposed by Gardner were 7, but twelve years after the publication of the work that would make them known, the author presented another element for this list. This was naturalistic intelligence, also known as the eighth type of intelligence
What is naturalistic intelligence?
Naturalistic intelligence is the ability to categorize elements of the environment, recognizing their differences and the way in which they relate to each other and to use this information to interact with them in a beneficial way.
The paradigm of this type of intelligence are naturalists and explorers such as Charles Darwin or Alexander von Humboldt, capable of entering natural environments, identifying different animal and plant species, learning the defining characteristics of each one and using this information for their own benefit. .

Confusions around naturalistic intelligence
Naturalistic intelligence presents itself with confusion precisely because of the reference to the natural world that is made in its conceptualization.
While in the definitions of the rest of the intelligences proposed by Howard Gardner, much emphasis is placed on their capacity for mental processes, the idea of naturalistic intelligence It seems to give a lot of importance to the type of information it works with, and not only to what is done with that information The formal nature of this intelligence as a process is explained, but it also talks about the specific contents it deals with: those elements of nature that we must identify and take advantage of for our benefit, the anatomical particularities of each of the plants and animals that we examine, etc.
In other words, while we know that logical-mathematical intelligence will be activated whenever we set ourselves a logical and mathematical challenge and that spatial intelligence will play a role whenever we conceive something that can be imagined on a two-dimensional or 3D plane, it seems that Naturalistic intelligence will only work with a very specific type of content: those that would be linked to the natural environment or to all the forms of life that come from them.
Immersion in the natural vs. debate artificial
Curiously, understanding that naturalistic intelligence applies only to this type of content does not make its conceptualization clearer and more delimited, but rather the opposite occurs.
In fact, supporting this notion of what naturalistic intelligence is forces us to relate the debate about whether the theory of multiple intelligences is more or less scientifically valid with another discussion that has practically nothing to do with it: the philosophical dispute about what it is. the natural and the unnatural, and in what sense these two worlds are ontologically different from each other. For example, are different types of vegetables something natural, when they have been profoundly altered over centuries and millennia of artificial selection? Or even… are what we know today as animal species something natural, when many of these categories have been established from the genetic (and therefore “artificial”) analysis of their members and not so much from direct observation? of your anatomy?
This immersion in metaphysical waters makes it not too complicated to relate naturalistic intelligence with the personal enjoyment of environments little altered by humans or with mystical ideas such as the ability to empathize with life on the planet, sensitivity when it comes to feel one with nature, etc.
The role of the natural in the eighth intelligence
However, contrary to what is often believed, Naturalistic intelligence does not refer only to flora, fauna and what we find in virgin environments Part of this confusion could come from the fact that at first Gardner explained very vaguely what this new type of intelligence consisted of, dedicating just a few lines to it, and in them he did not talk so much about naturalistic intelligence as about “the intelligence of naturalists.” .
The mentions of the natural environment served to create a powerful image that served to exemplify in a few lines what this new concept consisted of. So, although Gardner talked about the ability to get to know the natural environment well, he also He clarified that as he understood it, it was also involved in the recognition and classification of all types of objects and artifacts: cars, sneakers…
That is why naturalistic intelligence would be defined, more than by being a reflection of our ability to learn from natural environments, by being a reflection of our ability to learn about all types of environments and to interact appropriately with the elements that are available. in them.
Validity of naturalistic intelligence and criticisms
By making the concept of the natural go into the background, naturalistic intelligence is left out of the complications and turbulence of the nature-artificiality ontological dilemmas, but there is another problem from which it does not escape: it seems to overlap with the rest of the types of intelligence Or, at least, with linguistic intelligence (to conceptualize the identified elements), logical-mathematical intelligence (to understand hierarchies and categorizations) and spatial intelligence (to apply this knowledge in a specific environment and in real time).
The problem of overlap between the types of intelligence proposed by Gardner does not arise again and of course it does not concern only naturalistic intelligence, but also the core idea of the theory of multiple intelligences, according to which these are mental capacities more isolated from each other than united to form a whole. So far, due to the lack of empirical evidence in favor of multiple intelligences and the good health of the notion of a unified intelligence, the addition of this octave does not serve, for the moment, to reinforce Howard’s ideas. Gardner.