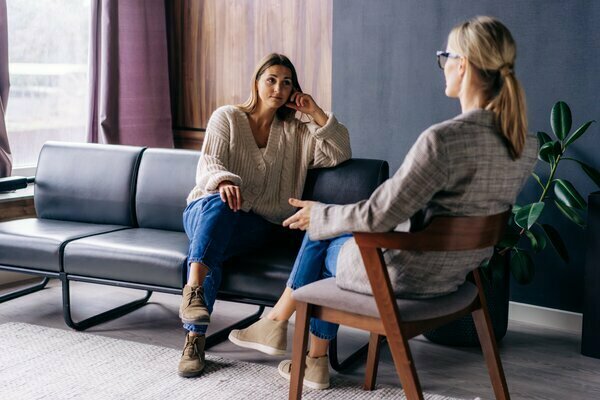
Although Physiological Psychology was developed strictly at the end of the 19th century Based on a text by Wilhelm Wundt titled Principles of Physiological Psychology, this field of study has its roots with the ancient Greeks, who were already seeking to elucidate what makes us so unique.
Although philosophers such as Aristotle thought that the brain served only to cool the blood, thus maintaining that the mind resided in the heart, figures such as Hippocrates and Galen offered clearer views on the importance of the brain on behavior.
Galen, a Greek physician (129 – 200 AD) would consider the brain such an important organ that he dissected cows, sheep, pigs, cats and dogs just to study it.
Physiological Psychology after the Scientific Revolution
Closer in time, in the 17th and 18th centuries, intellectual positions related to physics and mathematics maintained a central axis in the study of behavior A young René Descartes, fascinated by the hidden mechanisms that made the statues in the Royal Gardens in Western Paris move, traced his theory of the functioning of the body around these technological devices.
In his mind, the pressurized water that made the moving statues move was replaced by cerebrospinal fluid, the cylinders by muscles, and the valve by the pineal gland. This would cause more men of his time to postulate new models regarding the functioning of the human body.
Galvani’s discoveries
The Italian physiologist Luigi Galvani dealt a blow to the way in which the system proposed by Descartes had been understood discovering that stimulating a frog’s nerve caused the muscle to which it was attached to contract.
He observed that the brain does not inflate the muscles by sending fluid under pressure through the nerves ; The functioning of the nervous system was not so simple and mechanical. This was a vital contribution to the state of knowledge regarding the physiology of behavior.
Johannes Müller
Johannes Müller was another key figure for the birth of physiological psychology; His work through experimentation, removing and isolating organs from animals on which he carried out a thorough analysis of their responses when exposing them to various chemical substances, would lead to explain that nerves are not only motors, but also parts of a sensor system
His greatest contribution was precisely his doctrine of specific nervous energies: the quality of the sensation does not depend on the stimulus that affects the senses but on the type of nerve fiber that intervenes in perception.
An example of this is that electrical stimuli applied to the optic nerves will only cause light sensations.
Pierre Florens and Paul Broca
Müller’s mode was also shared by Pierre Flourens and Paul Broca who experimented directly on the organ through different techniques.
Flourens, a 19th-century French physiologist considered the founder of experimental brain science, examined the behavior of various animals after removing various parts of the brain and demonstrated conclusively that those parts of the organ removed were responsible for the affected function; In this way, an animal that has its cerebellum removed will have problems with motor coordination.
Years later, Paul Broca used principles similar to those of Flourens, but with specific patients, those with speech problems. Thus he discovered in postmortem studies that most of his patients (except for one) had damage to the left third frontal gyrus.
Broca reported 25 cases with these alterations that had the left hemisphere affected. Broca’s successes were a great impetus for other characters like Wernicke studied the neuroanatomical bases related to language, and the contributions related to the study of behavior were maintained. Thanks to these contributions, among other things, we know what logic lies behind aphasias.
Physiological Psychology today
Currently, physiological psychologists are based on experimentation, and use both generalization and reduction to explain behavior.
Physiological Psychology It has a multidisciplinary character and is strengthened by sources such as medicine, biology, chemistry, etc Finally, mention should also be made of contributions such as those of Ramón y Cajal, Francisco Varela, Mark Rosenzweig, Arnold Leiman, among others. Together, they created the fundamental bases for the development of this science.