The thinking organ. Our brain is one of the most important areas of the body, since it regulates the different vital functions that allow our survival. Furthermore, it allows us to be who we are.
Reason, emotion, motivation…all of this originates in the nervous system and especially in the brain. But this organ is not something homogeneous, but is structured in different areas. That is why in this article we are going to mention the different structures of the brain
What do we understand by brain?
We call brain to the functional center of the nervous system, located at the upper end of the neural tube. Located inside the skull and protected by it and the meninges against external damage and aggression, it is the most important organ as it regulates and controls all the functions of the organism, allowing the life and survival of the human being. Furthermore, thanks to it we are able to think, reflect, have feelings and emotions, identify with something or someone and, in general, even be aware of ourselves.
It is considered that the brain itself is mainly configured by the cortex and subcortex, with the brainstem or cerebellum not entering into it. Nonetheless, cerebrum and encephalon are often used synonymously and generally when we talk about the brain we will be referring to the entire brain.
Main brain structures
The brain is made up of a large number of structures, the brain can be divided into different parts During our development we can find three main areas of the brain, the hindbrain or rhombencephalon, the middle brain or mesencephalon and the forebrain or forebrain (which is later divided into diencephalon and telencephalon), each with various brain structures.
1. Hindbrain
Located in the lower part of the brain, the hindbrain is the part of the brain where the most primitive structures are located of this one. This is the part of the brain that contacts the spinal cord and regulates the most basic vital functions.
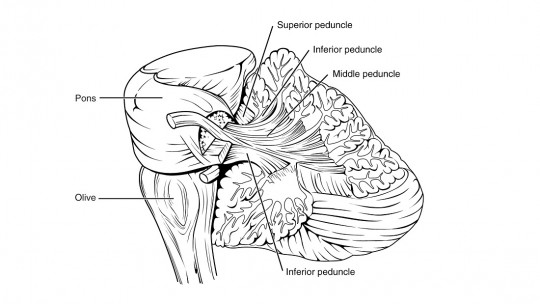
In this division of the brain we can observe two subdivisions, each of them being located in different brain structures. Along with the midbrain, It is part of the brainstem, also known as the brainstem or brain stem.
medulla oblongata
It is one of the brain structures that are part of the hindbrain, derived from the myelencephalon. The medulla oblongata It is the connection point between the spinal cord and the brain being an essential part of the brain for survival since it is responsible for managing processes such as heart rate, motor skills and digestion.
Pons or pons
The pons is another of the brain structures most vital for mere survival, your injury could cause death It is responsible for the movement of the viscera, homeostatic processes such as maintaining temperature, and participates in the regulation of consciousness and breathing.
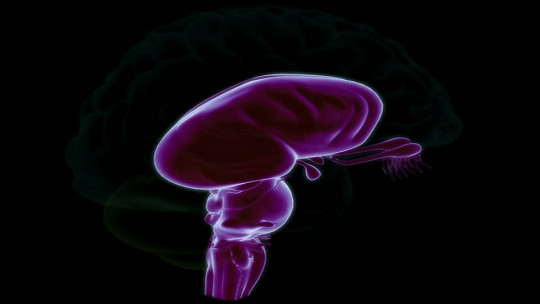
Cerebellum
This part of the brain is known for its involvement in a large number of processes and functions of the body. Especially recognized for his role in the control of muscle movement also participates in aspects such as emotional regulation or cognitive processes such as memory and intelligence.
2. Midbrain
The midbrain or midbrain is the part of the brain located between the forebrain and the hindbrain. It unites both regions and allows communication between them, also having great importance for the control of vital processes. Like the hindbrain, it is part of the brainstem or brainstem. Contributes to integrating information from different channels and it is linked to the level of consciousness. In this region we can fundamentally find two structures of the brain.
tectum
Lying in the most dorsal part of the midbrain this structure is linked to the reaction to sound stimuli and the reflex control of eye movements.
Tegmentum
Formed in turn by structures such as the substantia nigra, the red nucleus or the periaqueductal gray matter, this structure of the brain involved in functions such as movement, pain management and fight or flight reactions.
3. Prosencephalon
It is the most developed part of the brain and has the most structures, taking care of higher mental functions We can differentiate two large areas, diencephalon and telencephalon.
3.1. diencephalon
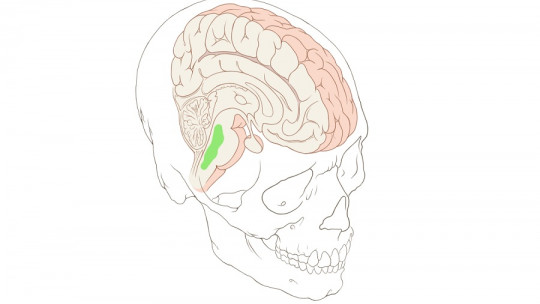
Located deep in the brain, the diencephalon is an internal part of the forebrain that is mainly made up of two large structures of the brain, thalamus and hypothalamus
Thalamus
This brain region It is the main nucleus for the integration of sensitive information, allowing to maintain a coordinated perception regarding the external stimulation before being able to send it to other brain areas in which the information is processed. In addition, thanks to its connection with the limbic system, it allows perception and emotion to be linked.
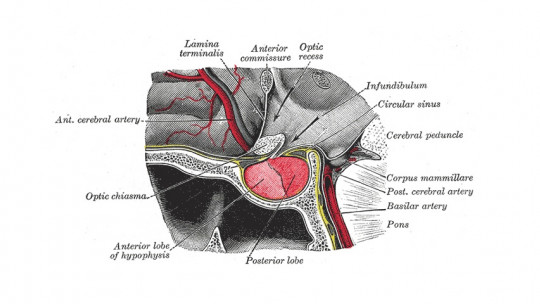
hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is one of the structures of the brain linked to the regulation of different hormones that allow the management of the organization. Connected to the pituitary gland, it participates in a large number of processes coordinated together with the autonomic nervous system, such as wakefulness, sexual behavior, hunger and thirst or affectivity. It is essential in the control of body homeostasis.
3.2. Telencephalon
If we consider the brain as a part of the brain and not as synonymous with it, the cerebrum would be the part of the brain equivalent to the telencephalon. Within it we can find different systems that in turn are made up of different structures.
Cerebral cortex
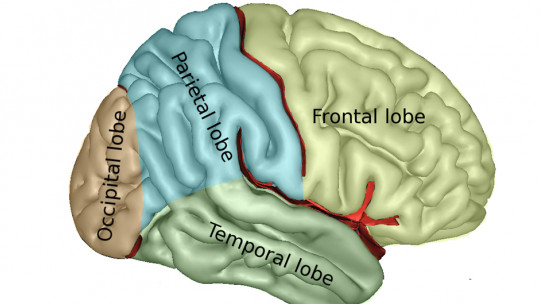
The most visible and recognizable part of the brain, the cerebral cortex is the area of the brain where the integration and processing of information and thanks to which the most complex functions are carried out allowing aspects such as reasoning, speech, executive functions or fine motor skills.
The bark is divided into two cerebral hemispheres In addition to this, we can establish five differentiated lobes specialized in various functions, the frontal, occipital, temporal and parietal lobes, in addition to the insula.
basal ganglia
A small group of brain structures that They are located below the crust, the basal ganglia are of great importance when it comes to controlling functions automatically. They are related to learning and task automation, as well as memory or movement. Putamen, globus pallidus and caudate nucleus are its main components.
Limbic system
The limbic system is a system of different brain structures which They are responsible for managing emotions, learning and memory. Some of its main components are the amygdala, the hippocampus, the hypothalamus or the mammillary bodies.