Despite Wilhelm Wundt being recognized as the father of Psychology, there are other authors who stood out and are considered the fathers of other psychological trends. Like Sigmund Freud of psychoanalysis, John Watson of behaviorism, Ulric Neisser of cognitivism or the Perls couple of Gestalt psychology.
In this article we will talk about who was the father of Psychology and what were their contributions to this area. Finally, we will mention some psychological currents and the main representative of each of them.
Who is really considered the father of Psychology?
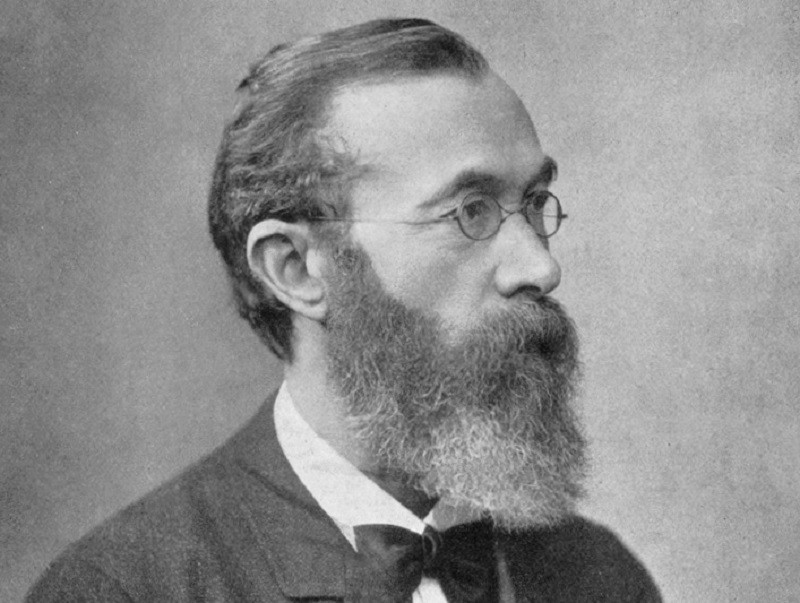
Although there have been notable figures throughout the history of Psychology, authors with great relevance and who are known not only within the field of Psychology, but also outside it, as would be the case of Sigmund Freud, who has received the title of father of psychology is German psychologist Wilhelm Wundt
Wundt’s consideration as the father of Psychology is due to the fact that he was the first to separate Psychology from Philosophy, since previously Psychology was presented as part of said field of knowledge. A relevant fact that stood out in Wundt’s career was the development of the first experimental psychology laboratory at the University of Leipzig, in 1879, thus being considered the beginning of Modern Psychology.
Who was Wihelm Wundt?
As a child, Wilhelm Wundt did not stand out for his academic performance, but this assessment would change when he began university studies, as he managed to graduate in Medicine, being the best in his course. Within the field of Medicine he was especially interested in physiology, which studies both the physical and chemical functions of the organism. He interacted and worked with important doctors specializing in physiology as Johannes Müller and later with Hermann von Helmhotz.
Wundt was Helmholtz’s assistant at the University of Heidelberg, although his experience was not very good and he ended up abandoning his work and began his studies in Philosophy at the University of Leipzig, later becoming a professor of Psychology at this University. As we mentioned before, Wundt was interested in physiology, showing an affinity for scientific study and knowledge, that is, everything that could be known through the experimental method. Likewise, he also showed interest in social sciences. In this way, the type of Psychology that he proposed tried to combine the social and physical sciences

In this way, Wundt would begin his work as a professor and professor of Philosophy, but always showing a more experimental and scientific side. It was in 1879 when the first Psychology laboratory was founded at the University of Leipzig, where Wundt taught classes. This union that the author proposes between Physics and Psychology is reflected in his work titled “Principles of Physiological Psychology”, where he pointed out the emergence of a new science. Wundt is therefore considered the father of modern Psychology among other things because developed the first scientific psychological system
The author proposes the study of the immediate experience of conscious processes, using both instruments from the experimental field and psychological knowledge when describing the immediate processes. Likewise, he studied both sensations and feelings, taking into account objective measures such as the subject’s reaction time.
The structuralist movement
Along with Edward Titchener, Wundt was a prominent author within psychological structuralism This current seeks to describe mental structures from the description of the processes of the psyche. In this way, Wundt tried to study, know, scientifically consciousness using the chemistry model, that is, look for the elements that were part of it. In the same way that the periodic table of chemical elements was proposed, the author sought to know the elements that made up people’s minds.
In order to know the elements that were part of the psyche, Wundt used the technique of experimental introspection or self-observation, which consists of making the patient reflect on their own thought processes. This strategy was carried out under strict control, previously training the subject and controlling the different variables that could influence it, so that the result was as objective as possible.
Thus, this current proposes to study the elemental structure of the process of consciousness to finally discover its last elements, which are sensations, images and feelings. Likewise, they will try to establish laws of combination between the simple elements, the last elements, to obtain the complex phenomena of the mind.
Wundt’s influence today
As we have already seen, one of the most relevant contributions that Wundt made to the field of Psychology was the inauguration of the first Experimental Psychology laboratory, supporting a more scientific and objective Psychology and thus marking the beginning of Modern Psychology, separating itself from Philosophy. and defining itself as a branch of science.
Despite the great change that Wundt made in this area, being considered the father of Psychology, currently the methods and techniques he proposed are not the most used since introspection, the main technique he used, although it tries to be as objective as possible by controlling the different variables, still involves a subjective strategy, of the subject himself, and it is difficult to scientifically assess its effectiveness.
Other relevant authors in Psychology
As we have already seen, the author considered the father of Psychology is Wilhelm Wundt. Even so, we can divide Psychology into different schools or currents, highlighting different authors in each of them. For this reason, below we will cite some of the best-known psychologists in each field, who are also of great relevance in the history of Psychology.
1. Evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is the branch of Psychology that is responsible for studying the development of human beings, from birth, through all stages of their life cycle. The study that proposes this area of Psychology It is important to know what the expected development of people is in order to know if it is necessary to intervene to avoid more serious alterations in the future.
The psychologist Jean Piaget is considered the father of this branch of Psychology, since he was the first to carry out a complete study of the psychological development of people throughout their lives.
Piaget tried to describe human development based on two concepts: cognitive functions and structures Functions are innate biological processes and are invariable; On the other hand, structures are variable and can be modified. The most characteristic structure that the author proposes are the schemes
2. Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis is the psychological current that presents the unconscious as a focus of study, the information that the subject cannot know, or that is difficult for him, but that is basic for the explanation of his behavior. Likewise, they give special importance to the study of the subject’s past, their childhood and the possible traumatic events they experienced. Despite still being in force today, this trend stands out for its little empirical basis and difficulty in verifying the effectiveness of its techniques.
The father of psychoanalysis is Sigmund Freud, who proposed concepts known as: the unconscious, already mentioned; the id, the ego and the superego; libido; psychosexual stages or drives.
3. Behavioral psychology
Behavioral psychology studies observable human behavior. In this way, the measures it uses are objective, that is, it is only interested in the variables external to the subject, which we can observe from the outside, thus avoiding the subjective assessment of the individual himself or of the professionals who measure the behavior or in any case not considering it a faithful reflection of true psychological processes.
One of the most important psychologists within this Psychological current is John Broadus Watson, known for the controversial “Albert boy” experiment where he tested the possibility of intentionally establishing a phobia.
4. Cognitive psychology
Cognitive psychology is the opposite current to behaviorism, since is interested in knowledge of people’s mental processes, how they perceive information from outside, interpret it, transform it, store it and retrieve it. Ulric Neisser is considered the father of cognitive psychology.
Currently, one of the most used currents and that has proven to be most effective in intervening in different pathologies is cognitive-behavioral therapy, which uses techniques from both schools.
5. Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt Psychology gives more importance to the whole than to the sum of things. Likewise, it highlights the relevance of the “here and now”. The founders of this psychological trend were the Perls couple, Laura and Fritz Perls.