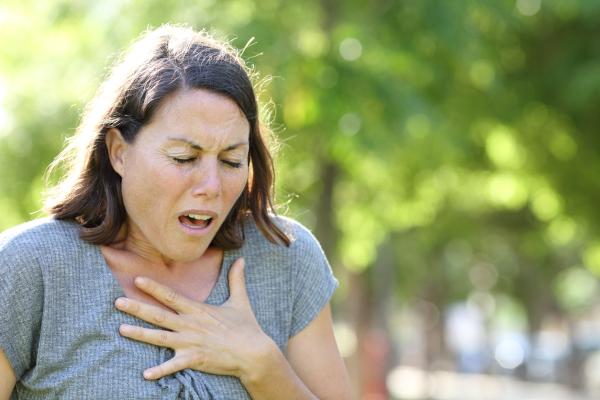
Anxiety is an emotional reaction that arises in response to alarming situations. An individual becomes anxious when he fears something, when he experiences a difficult situation and feels insecure, it is a reaction to stress. Can you have muscle spasms due to nerves? What are the physical symptoms of anxiety? How does anxiety affect muscles? In this PsychologyFor article, we are going to explain to you why anxiety can cause muscle spasms, cramps and other symptoms.
Physical symptoms of anxiety
Anxiety presents not only with psychological symptoms, but also with physical ones, in this way the individual can experience:
- Tachycardia
- Muscle tension
- Shaking
- Punctures
- Difficulty breathing
- Tingling and numbness
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
It is common for the individual to interpret these physical symptoms as some organic problem, therefore, it is advisable to seek a doctor in order to exclude any possibility of physical illnesses. Knowing that the symptoms come from anxiety, the person has other means to seek help, such as, for example, going to a psychiatrist and also a psychologist.
Effects of anxiety on the body
When the individual feels tachycardia, most likely their first thought is that they are having a heart attack. It is common for people to have erroneous thoughts regarding the symptoms of anxiety. In this article we explain the Differences between anxiety and heart attack.
Another example of physical pain caused by anxiety is pain in the chest. They can occur throughout the day and are very unpleasant. Obviously, they also cause the person great uncertainty about their state of health, especially cardiac health.
Muscle tension
Anxiety can also cause muscle tension. When the individual feels fear, the body responds to the emotions, muscles shrink as a defense mechanism and right from there it develops muscle tensions. Muscle stiffness due to anxiety is common, and anxiety can even lead to muscle stiffness.
Punctures
Altered breathing, described by those suffering from anxiety as difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, is a symptom that can produce gases and those in turn cause stomach cramps. Even referring to breathing alterations, breathing with an agitated or shallow pattern causes alterations in the muscles around the chest and intercostal muscles, causing punctures in the individual. Anxiety costochondritis, pain in the sternum caused by anxiety, can also occur.
Spasms
Anxiety also causes muscle spasms. What is a muscle spasm and why does it happen? Spasms are rapid, involuntary muscle movements. The most common ones occur on the eyelids, tongue, arms, fingers, legs and feet. That sudden muscle contraction It can also occur as a nervous tic, producing involuntary movements, over time, depending on daily repetition, it can cause muscle pain.
Therefore, the answer is yes: both twinges and muscle spasms can be caused by anxiety.
Tingle
Another physical symptom that anxiety causes is numbness and tingling sensations in some parts of the body. They are most common on the face, hands, arms, legs and feet. That happens because blood speeds up due to the body’s response reaction to imagined or unreal dangerous situations allowing the body to be ready to flee and leaving those less important parts tingling and feeling weaker.
Dizziness
Regarding dizziness caused by anxiety, in certain situations due to the heart beating faster, blood pressure increases and this increase causes feelings of dizziness in the individual.
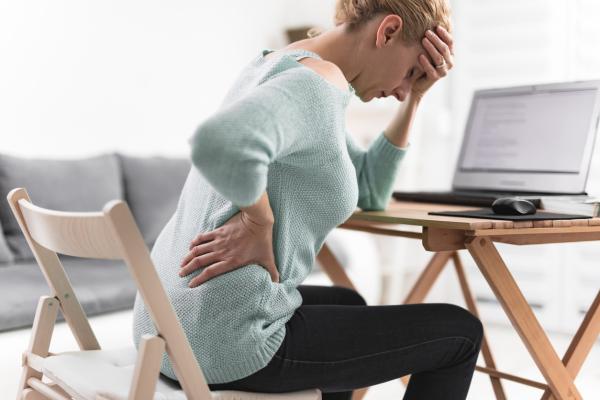

How to relieve muscle pain due to anxiety?
As we have seen previously, anxiety can produce muscle tension and, consequently, pain arises.
To relieve these muscle pains, caused by contraction at the time of anxiety or in the long term due to stress, it is indicated to perform deep breaths through the nose and exhaling through the mouth, while feeling the muscles contracting and relaxing. Why should the individual start with breathing exercises? This is justified by the nervous system, since at the time of breathing it will be stimulated.
It is indicated that the individual sits or lies down and puts his hands on his abdomen to control the execution and begins by performing slow, deep breaths through the nose, holding the air for a couple of seconds and then expelling it through the mouth. In this article, we explain Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercises.
In the sequence of the breathing exercises, it is indicated exercises to relax the jaw opening and closing the mouth slowly. Neck exercises moving it from one side to the other. with the shoulders rising up and down.
It is important that the individual has the habit of doing some activity that helps relieve your tension.
In cases where the individual feels too much muscle pain, it is recommended that they go to the physiotherapy.
And, finally, you can seek help with drugs, both anxiolytics such as muscle relaxants, as long as the individual consults a doctor to prescribe them according to their need.
Below you will find a guided video so you can start practicing relaxation.
This article is merely informative, at PsychologyFor we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Does anxiety cause muscle spasms and cramps? we recommend that you enter our Clinical Psychology category.
Bibliography
- Neurocenter. (2020). Anxiety and muscle spasms. How can physical therapy help? Retrieved from: https://www.neuro-centro.com/ansiedad-y-espasmos-musculares-como- may-ayudar-la-fisioterapia
- Anxiety clinic. (2021). Anxiety: the reason for the symptoms. Retrieved from: https://clinicadeansiedad.com/problemas/introduccion/ansiedad-el-por-que-de-los-sintomas/
- Take care Plus. (2020). Tips to relax stress contracture. R//cuidateplus.marca.com/bienestar/2020/09/19/consejos-relajar-contracturas-estres-174882.html