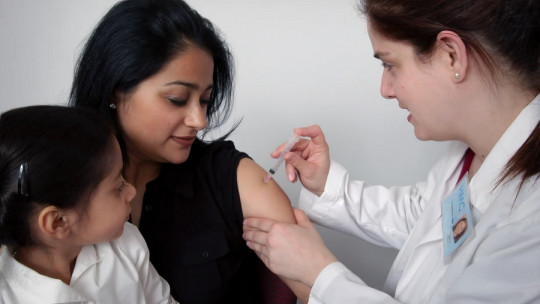
One of the main reasons for attending psychological therapy is phobic disorders, and, among these, one of the most common fears of needles In fact, some studies claim that up to 10% of the population suffers from this phobia.
While it is true that needles can cause pain if they are used violently, Needle phobia or belonephobia is characterized by the person suffering from irrational terror and great anxiety that can become disabling.
Belonephobia causes, for example, an individual to be unable to go to a health center due to the unreal fear they feel towards these objects. One of the characteristic symptoms of phobias is that the phobic individual tries avoid the stimulus that causes this discomfort reaction
In this article we will delve into the characteristics of fear of needles and find out what its causes, symptoms and consequences are.
What is fear of needles
For many people, the fear of needles only manifests itself at specific moments, for example, when one must get vaccinated. However, for other individuals, it may appear more frequently, let’s imagine when someone is diabetic and must inject insulin.
The fear of needles is a phobia, and therefore belongs to the group of anxiety disorders It is an intense, irrational and persistent fear towards some situations in which the phobic stimulus may be present, that is, needles, but also towards syringes and the possibility of receiving injections, just like trypanophobia or fear of injections.
Belonephobia is also often associated and often confused with the fear of blood (hematophobia) or the fear of sharp objects (aichmophobia). Of course, these people do not necessarily experience fear of blood and other sharp objects, which serves to distinguish between belonephobia, aichmophobia and hematophobia
This type of phobia belongs to specific phobic disorders that are generally fears of certain objects or situations. For example: cats, spiders, snakes or the fear of flying.
Causes
Phobias are usually learned fears. These fears develop through a type of associative learning called classical conditioning, after a traumatic event. For example, after having a bad experience with needles.
In fact, the scientific community is in favor of the idea that phobias are learned, and one of the figures who has contributed the most in this sense is John Watson an American psychologist who in the 1920s caused a boy named Albert to develop an irrational fear of a white rat whom he previously adored.
The experiment aimed to observe the emotional reactions of the child, who at first played with the animal completely normally. However, throughout the sessions, the rat was presented along with a loud noise that scared the little one. After several presentations of both stimuli together, little Albert developed fear of the rat even without the presence of the loud noise.
If you want to know more about this type of learning, you can read this article: “Classical conditioning and its most important experiments.”
Other causes of this phobia
But the phobias can also be learned by observation , in what is known as vicarious conditioning. That is, the person can see how an individual screams when they are going to give him an injection and can develop a strong fear of needles.
Other authors affirm that human beings are biologically predisposed to suffer phobias, since fear is an adaptive emotion that has been key to our survival because triggers a fight or flight response That is why fear has to do with the primitive areas of the brain and develops through primitive and non-cognitive associations. In other words, they are not modifiable by logical arguments.
Symptoms and signs
This type of phobia can appear in different situations. For example:
When the person who suffers from this phobia is in any of these situations, they experience a series of cognitive, behavioral and physical symptoms. They are the following:
Treatment of belonephobia
Although this type of phobia is very common, it also has a high success rate in terms of treatment, according to scientific studies. There are different psychological therapies that work, but the most used is cognitive behavioral therapy.
This form of therapy uses different techniques, and to treat phobias, the most effective are relaxation techniques and exposure techniques A technique that combines both is systematic desensitization, which consists of gradually exposing the patient to the phobic stimulus, but first they must have learned different coping strategies, such as the aforementioned relaxation techniques.
Other very effective types of therapy They are cognitive therapy based on Mindfulness or acceptance and commitment therapy, which belong to third generation therapies. If you want to know more about these therapeutic methods, you can read the article “What are third generation therapies?”
New technologies and phobias
New technologies are also used to improve the quality of life of people with phobias. Online therapy is increasingly used , and virtual reality has proven to be very effective as an exhibition method. In fact, there are even different mobile apps that are designed to help people who suffer from a phobic disorder.
You can learn more in the article “8 apps to treat phobias and fears from your smartphone”.