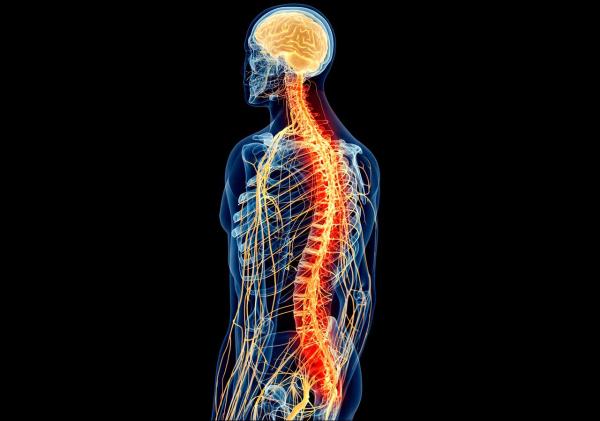
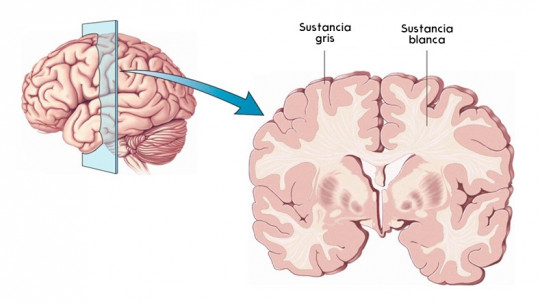
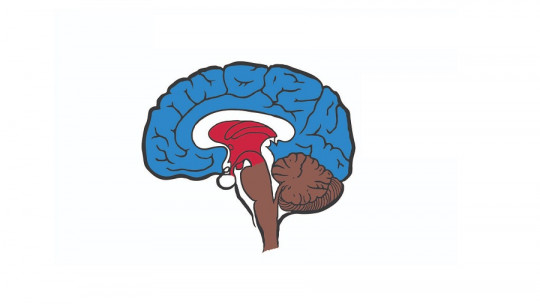
The brain is made up of different structures and layers, however, when we look at the brain, the first thing we see is a grayish mass, with some areas darker than others. Well, these darker areas are what we call gray matter.
Furthermore, this gray matter does not seem to be located only in the brain, but we can find it in other areas of the nervous system, such as the spinal cord or the cerebellum. If you want to know more, keep reading! In the following PsychologyFor article we will talk about gray matter of the brain: what it is, its location, its functions and how to increase it
What is the gray matter of the brain
The gray matter of the brain is a primary component of the Central Nervous System. This fabric is formed by neuronal bodies and neuropils , the region between several cell bodies or somata of neurons in the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord. The gray matter of the brain is named for its characteristic darker color, the result of the nuclei that make up the cells.
Specifically, gray matter is composed of axon terminals, dendritic cells, and glial cells. It should be noted that it differs from white matter by the absence of a myelin layer in the neurons that form it and, in addition, it is made up of a large number of cell bodies. In this article you will find more information about the difference between gray and white matter in the brain.
Location of the gray matter of the brain
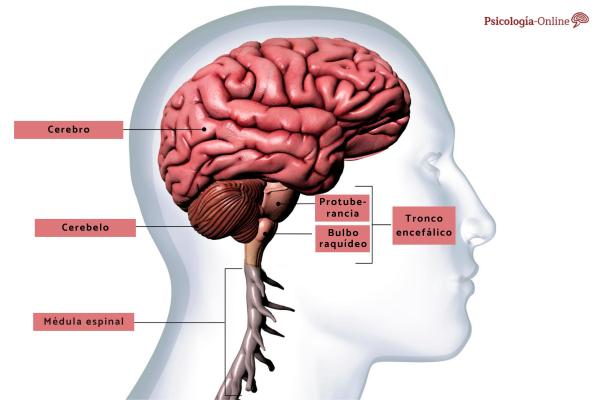
Gray matter occupies 40% of the entire brain and consumes 94% of oxygen. Specifically, it is found, mostly in the cerebral cortex Even so, we can also observe gray matter in the spinal cord and around the cerebral aqueduct in the midbrain and in the brainstem and cerebellum.
If you want to solve your doubt about where the gray matter of the brain is located, you should know that it is distributed on the surface and depths of the two cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum Let’s see in which areas exactly:
- Thalamus.
- Hypothalamus.
- Subthalamus.
- basal ganglia.
- Putamen.
- Pale globe.
- Nucleus accumbens.
- Septal nuclei.
- Cerebellar nuclei.
- Brainstem.
Although the gray matter is found in both hemispheres , that of the right hemisphere is a little larger and is heavier compared to the left hemisphere. However, the left contains a greater amount of gray matter in relation to white matter.
It should be noted that we also found differences between sexes. While men have a greater volume of white matter, Women tend to have more gray matter in the brain especially in the temporal lobes, the entorhinal cortex and the anterior lobes of the cerebellum.
Layers of gray matter
The gray matter of the spinal cord formed by interneurons and the cell bodies of projection neurons, is located in the center of is and is distributed, in turn, in three gray columns that are presented in the shape of an “H”: the anterior gray column, the posterior gray column and the lateral gray column.
In turn, these three columns are divided into different layers called rexed blades which are distributed as follows:
- In the posterior horn : laminae I to VI are found, the access point for afferent information from the dorsal roots
- In the intermediate zone : Plates VII and X are found.
- In the anterior horn : there are plates VIII and IX. These contain the body of the lower motor neurons.
Let’s see what the functions of each of the sheets of the gray matter of the brain are:
- Plate I : place of entry of the posterior root and contains some cells of the spinothalamic tract.
- Plate II : involved in spinal pain modulation.
- Plates III to VI : They are responsible for the processing of afferent somatosensory information.
- Plate VII : It is formed mainly by interneurons and the soma of preganglionic autonomic neurons.
- Plates VIII and IX : They are responsible for motor output. It contains the alpha motor neurons, which innervate the extrafusal striated muscle fibers responsible for the motor act itself, and the gamma motor neurons, which innervate the intrafusal muscle fibers, which is why they are important in maintaining tone and posture.
- Plate X : It is arranged around the central spinal canal and its function is unknown.
Functions of the gray matter of the brain
If you wonder what the function of the gray matter of the brain is, you should know that it is related to muscle control and sensory perception Let’s see what it interferes with:
- Sight and hearing.
- The memory.
- The emotions.
- He speaks.
- Decision making.
- Self-control.
As we see, the gray matter controls muscular and sensory activity, as well as information processing. Let’s see what processes it participates in depending on its location:
- Gray matter located in the cerebral cortex : It is considered essential for higher learning and to carry out psychological processes that involve attention, memory and thinking.
- Gray matter located in the cerebellum : It is related to motor control, coordination and precision functions.
- Gray matter of the spinal cord : divides its functions according to the three columns that compose it. The anterior gray column is involved in movement, the posterior gray column receives sensory information from the body, including fine touch, proprioception and vibration, and the lateral gray column functions as the third column of the spinal cord.
How to increase the gray matter of the brain
According to a study by West, G and Rich B., (2017), one way to increase the gray matter of the brain is through video games It seems that these cause an increase in the gray matter of the brain in the hippocampal area in young and old adults, which produces a decrease in cognitive decline.
In this same study, increases in the gray matter of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex were found after musical activities how to play the piano. In this article on music and children’s brain development you will find more information about this aspect.
Furthermore, it seems that sport and physical activity aerobics It also causes an increase in the gray matter of the brain and positively influences cognitive functioning.
This article is merely informative, at PsychologyFor we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Gray matter of the brain: what it is: location, functions and how to increase it we recommend that you enter our Neurosciences category.
Bibliography
- Carlson, N. R. (2014). Behavioral physiology. Madrid. Pearson Education, S.A.
- Herranz Gómez, A. (2021). The use of video games in the prevention of cognitive deterioration in older people. NeuroRehabNews, (October). https://doi.org/10.37382/nrn.Octubre.2020.552
- Micaela (sf). Understanding the brain, what is gray matter? Dacer. Retrieved from: Understanding the brain: what is gray matter? Dacer neurorehabilitation and brain damage center
- Muñoz, S., (September 2021). The white matter and gray matter of the brain. Psychoactive. Recovered from: The white matter and gray matter of the brain (psicoactiva.com)
- Neurowikia. (sf). Functional anatomy of the spinal cord: Medullary laminae. Recovered from: Functional anatomy of the spinal cord: Medullary laminae | NeuroWikia