The development of our body is something complex. From the moment the sperm fertilizes the egg until we are born, there are multiple processes that occur and are generated by our organs and body systems. The nervous system is one of the first to appear along with the heart, and will develop both during pregnancy and throughout life.
However, sometimes during pregnancy different problems occur that can cause the formation of our brain to fail. One of the many alterations that can occur is hydranencephaly, which we will discuss in this article
What is hydranencephaly?
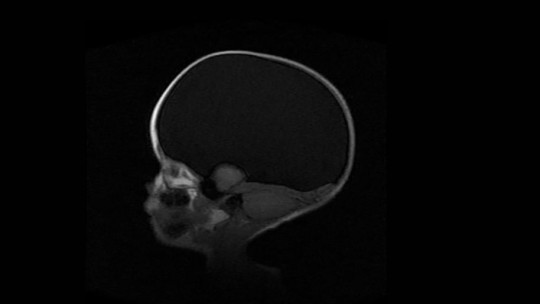
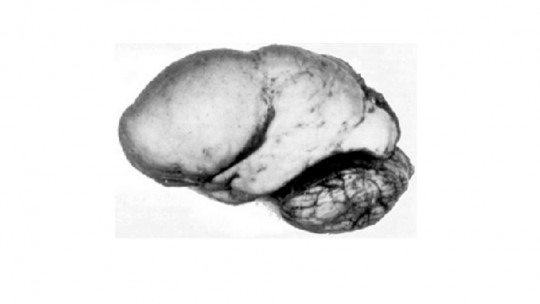
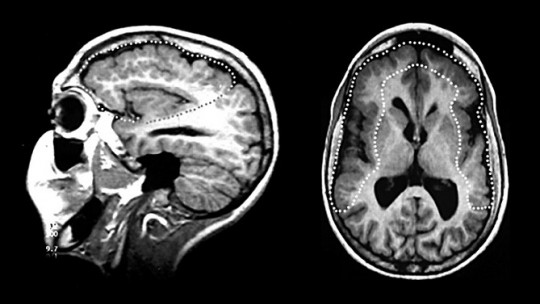
It is understood as hydranencephaly a type of congenital malformation consisting of the absence of practically the entire brain , specifically the cerebral cortex, the space generally occupied by it being replaced by cerebrospinal fluid. Despite this, the shape of the subject’s head may be normal, with the cavities and meninges surrounding the skull being preserved. The cerebellum and brainstem are usually correctly formed and functional, with basic vital functions such as breathing and heart and respiratory rhythm. Other subcortical structures may also be preserved.
The absence of a brain is due to the appearance of some type of destructive process during pregnancy, starting from the twelfth week. In most cases, this will have severe repercussions, with these children generally not being able to carry out the basic functions that said structure would perform.
Although it may seem surprising due to the total or almost total absence of the cerebral cortex, initially some of the children who are born with this problem may present appropriate behavior and way of interacting with the world, being able to feed correctly and not being diagnosed immediately. . But in general, the existence of different alterations is observed, such as seizures, paralysis or sensory disturbances such as blindness or deafness They may present absence or slowing of growth, hypotonia or high irritability. The presence of some degree of mental and physical disability is to be expected, requiring and depending on external care.
In most cases, the prognosis of children who suffer from this disorder is very negative, with the majority of those who suffer from it dying before one year of age. But there are also numerous cases in which, despite their condition, they manage to survive and even overcome adolescence and reach adulthood.
Hydranencephaly and hydrocephalus: differences
It is important to keep in mind, since they are diagnoses that can be confused, that hydranencephaly and hydrocephalus are not the same Both disorders are similar in the fact that there are large pockets of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain that occupy a large part of the skull, but while in hydrocephalus the excess fluid pushes the brain tissue and the existence of at least part of the tissue can be observed irrigated brain, in hydranencephaly this tissue does not directly exist.
Both disorders can be related, but it must be taken into account that hydranencephaly cannot be a consequence of hydrocephalus. What is possible is that hydranencephaly ends up causing hydrocephalus: the fluid that occupies the place of the brain can accumulate due to the production of more cerebrospinal fluid, causing an increase in intracranial pressure and/or protrusion of the skull.
Possible causes
Hydrocephalus is a congenital malformation whose causes can be multiple. Generally, as we have said before, it is due to a destructive process that affects brain tissue during pregnancy This destruction can be caused by different elements, the most frequent being the existence of heart attacks or strokes caused by the rupture of the internal carotid.
Other causes in addition to strokes can be found in infection by different types of viruses or intoxication resulting from alcohol or drug consumption by the mother during fetal development. Finally, can be generated by genetic diseases and disorders
Treatment
Hydranencephaly, as a congenital condition, currently has no curative treatment. This does not mean that any type of therapy cannot be used, although will tend to be palliative and aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life It is not uncommon for some type of drainage or diversion of cerebrospinal fluid to be performed to avoid possible hydrocephalus and accumulations.
Treatment with the parents and the child’s environment is also of great importance, requiring psychoeducation and counseling in the face of the difficult situation that this disorder entails, as well as the risks that the baby will face. Attending support groups can also be very useful, as well as psychotherapy in order to combat beliefs, fears and emotional alterations generated by the diagnosis (and in some cases may experience disorders such as depression).
In cases where there is survival, the baby will need different supports and aids. The use of physical therapy, speech therapy, training in basic daily living skills, special education, and other professional care may be required.