It’s summer and one of the greatest pleasures at this time is to immerse ourselves in the peace and calm of the sea or the pool. Although humans are not marine animals, we certainly miss being able to submerge when the colder months arrive.
This calm when submerged in cold waters has an evolutionary reason and we share it with other animals, especially mammals. This phenomenon is the immersion reflex of mammals and it turns out to be essential for the survival of many marine animals.
Next we are going to learn what awakens this reflex, what changes at an organic level it implies and how diving training influences its appearance.
Mammalian Dip Reflex: Definition
Sea or pool water gives us peace. It is by entering that cold water that we begin to feel deep calm. This sensation is ancestral and has a very important evolutionary origin shared with the rest of the mammalian species. It is called the mammalian diving reflex and Just immerse yourself in cold water or splash it on your face to start activating pleasant sensations
Although this reflex is a very striking link with other mammalian species, it is especially present in aquatic mammals, such as seals, otters or dolphins, in which its appearance is a fundamental condition for their survival. In human beings it occurs in a very weakened form, but it still involves a whole series of changes at an organic level that mean that we can spend longer than expected submerged in water, whether fresh or salty.
Although it is called a mammal, it also seems to manifest itself in marine animals such as penguins, which has led to the assumption that Its true origin would be in a common ancestor between birds and mammals It would be a mechanism that demonstrates the theory that birds and mammals come from the same ancestor and that it must have lived in water.
How does it manifest?
The mammalian dive reflex It occurs as long as it comes into contact with water that is at a low temperature, normally less than 21ºC The lower the temperature the effect will be greater.
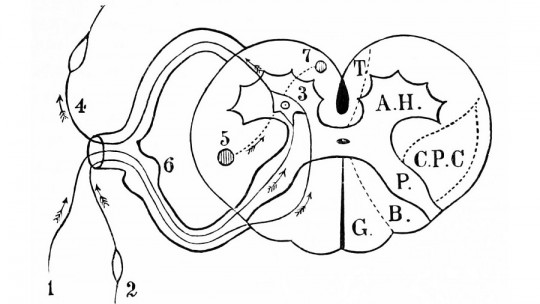
Also It is necessary that, for this mechanism to be activated, the water hits the face , since that is where the trigeminal nerve is located, made up of the ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular nerves. These are three nerve branches that can only be found on the face and, when activated, initiate the reflex, which involves the following processes following the same order.
1. Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a decrease in heart rate When we are diving it is necessary that we reduce oxygen consumption and, for this reason, the heart begins to reduce its beats per minute between 10 and 25%.
This phenomenon depends directly on the temperature, meaning that the lower it is, the fewer beats are made. There have been cases of people who have only made between 15 and 5 beats per minute, something very low considering that the normal rate is 60 or more.
2. Peripheral vasoconstriction
Peripheral vasoconstriction or redistribution of blood involves taking it to more important organs , like the brain and the heart. Blood capillaries are selectively closed, while those of major vital organs are kept open.
The first capillaries to contract are those of the toes and hands, and then give way to the feet and hands as they extend. Finally, those in the arms and legs contract, cutting off blood circulation and leaving more blood flow to the heart and brain.
This minimizes possible damage caused by low temperatures and increases survival in the event of prolonged oxygen deprivation. The adrenaline hormone plays a major role in this process and it is the reason why, when we wash our face with very cold water, we wake up faster.
3. Introduction of blood plasma
Blood plasma is introduced into the lungs and other parts of the rib cage, causing the alveoli to fill with this plasma, which is reabsorbed when it is released into a pressurized environment. This way, The organs in this region are prevented from being crushed by high aquatic pressures
Blood plasma is also produced within the lungs. When diving at shallow depths, in a more mechanical way, part of the blood is introduced into the lung alveoli. This protects them by increasing resistance against pressure.
This phase of the immersion reflex has been observed in humans, as would be the case of the freediver Martin Stepanek, during apneas greater than 90 meters deep. In this way, people can survive longer without oxygen under cold water than on land
4. Contraction of the spleen
The spleen is an organ located behind and to the left of the stomach, whose main function is the reserve of white and red blood cells. This organ contracts when the mammalian dive reflex occurs, causing it to release part of its blood cells into the blood, increasing its capacity to transport oxygen. Thanks to this, temporarily increases hematocrit by 6% and hemoglobin by 3%
It has been seen that in trained people, such as the Ama, Japanese and Korean divers who are dedicated to collecting pearls, the increases in these cells are around 10%, percentages close to what happens to marine animals like seals.
Conclusion
The immersion reflex of mammals is a mechanism that human beings possess, ancestral evidence that we have a common ancestor between birds and other mammals that must have lived in aquatic environments. Thanks to this reflection, we can survive submerged for a more or less long period of time trainable as would be the case of the Japanese and Korean ama or, also, the Bajau of the Philippines, populations dedicated to underwater fishing.
Although human beings cannot be considered marine animals, the truth is that we can train our ability to dive. We can be submerged for 10 minutes and there are even cases of people who have exceeded 24 minutes or more. Not only can you last a long time underwater, but you can reach depths close to 300 meters.