Among the clinical conditions associated with different alterations in cognitive activity is organic brain syndrome. Although it is a term it has fallen into disuse within some contexts; This is a category especially used to relate psychiatric manifestations with the functioning of organic structures.
In this article we will see what organic brain syndrome is by what other names it is known and what mental and physiological states it refers to.
What is organic brain syndrome?
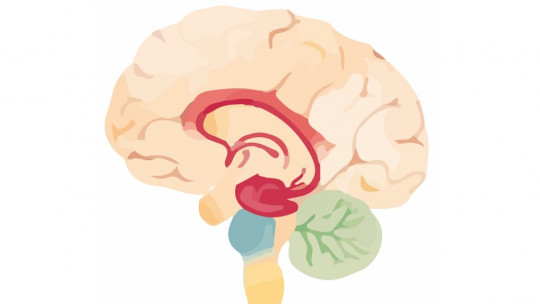
Organic Brain Syndrome is also known by the following names: organic brain disease, organic brain disorder, an organic mental syndrome or organic mental disorder. It is characterized by being a condition whose cause is related to the physiological structure more than with pure mental activity (which is why it is known as an “organic” syndrome).
It is not a specific diagnostic criterion, but rather a general classification, which encompasses a set of clinical manifestations whose common characteristic is that they are caused by or related to physical structures.
In other words, there are medical conditions that directly alter the physiological activity of the nervous system. This alteration can become visible in behavior, mood or subjective and cognitive experiences (such as thoughts, beliefs, perceptions, sensations, etc.).
In some cases, this causes clinically significant distress, so a psychiatric diagnosis may be sought. With the intention of make an evaluation and intervention that takes into account the physiological elements that may be behind the behaviors or cognitive activity causing said discomfort, the category of organic brain syndrome was created. However, and although it is a concept that has been very common within psychiatric clinics, it has currently been subject to some modifications.
Types and causes
Two main types of organic brain syndrome have been recognized, which They are mainly distinguished by the time of appearance
1. Acute
It means that it is a recently appeared mental state. It may be caused due to intoxication or overdose of psychoactive substances, infections and medical illnesses that affect the nervous system. They are usually temporary episodes, although they can occur on different occasions. For example, it may be the case of delirium.
2. Chronic
These are the manifestations that are maintained in the long term. This is usually the case of chronic dependence on psychoactive substances such as drugs or alcohol, whose toxic effects on brain structures can significantly modify neuronal and cognitive functions. In addition may be the case of neurodegenerative disorders different types of dementia or can occur as a result of cardiovascular accidents.
Origin of the concept and associated symptoms
In the context of modern psychiatry, the term “Organic Brain Syndrome” (and its synonyms) was used to differentiate between purely mental etiology, and etiology was clearly related to physiological functioning. However, with subsequent knowledge and theories about the functioning of the human mind and its relationship with both brain structures, This distinction has been increasingly disregarded
In the words of Ganguli, Black, Blazer, et al. (2011) the term “organic” suggested that there was a known brain structure that caused some manifestations. This structure was different from another, which was called “functional” and encompassed all manifestations that had a purely mental etiology.
But, with the development and transformations of cognitive science and neuroscience, psychiatry has rejected the false disconnection between organic and non-organic functional structures, which ultimately translated into a distinction between mental manifestations and those of the brain. Currently, psychiatry maintains that the brain (the organic structures) is actually the basis of mental or functional structures
However, the term Organic Brain Syndrome continues to be used as a way to describe states of consciousness and their relationship with different physiological elements and causes. As with medical categories, the latter facilitates communication between experts, especially those who have been trained in the psychiatric tradition where the category of “Organic Brain Syndrome” allowed different investigations and clinical approaches to be carried out
For example, the journal Rheumatology (cited in Sciencedirect, 2018), in its sixth version defines Organic Brain Syndrome as a state of brain dysfunction associated with disturbances in consciousness, cognition, affect, or mood ; caused by behavior during drug withdrawal; due to infections or metabolic causes.
Suggestions from the Neurocognitive Disorders Working Group
For its part, the neurocognitive disorders working group of the American Psychological Association, which was formed to form the fifth version of its Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, has accepted the use of the term “neurocognitive” to refer to clinical manifestations. where the mind acts as a result of alterations in the brain. Thus, the classification of “Neurocognitive disorders associated with medical causes” arises (for example, post-operative neurocognitive dysfunction).
Broadly speaking, the manifestations that are included in this category. They are visible in complex attention, learning and memory executive functions, language, visual-constructive perception and social cognition).