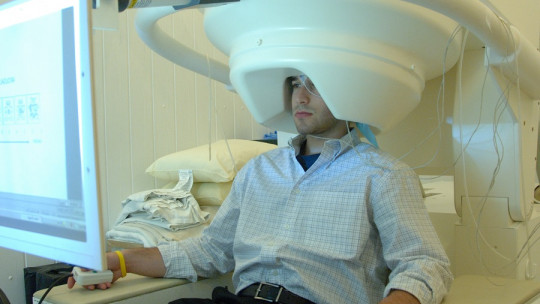
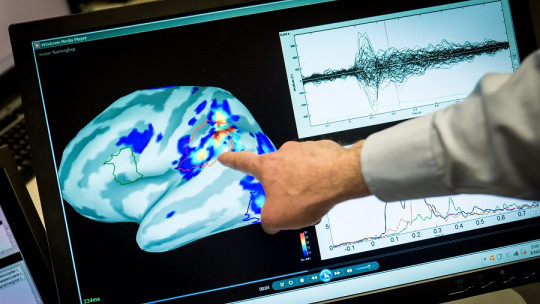
In recent years, scientific and technological advances have been very helpful in the development of novel techniques to explore human psychophysiology A very significant field that advances at the speed of light is neuroscience. Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) is currently being looked at; a revolutionary technique capable of influencing brain activity without invasive interventions or surgical procedures.
The discoveries around tACS promise that it will be a pioneer for the improvement of cognitive functions, the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders and the general enhancement of the human brain. This works by using low-intensity electrical currents with the aim of modifying the electrical activity of specific regions of the brain. By applying electrical impulses, we seek to modulate neuronal excitability and enhance synaptic connections.
Throughout this article, we will explore in detail the fundamentals, applications and future prospects of transcranial alternating current stimulation. We will emphasize understanding why this technique has captured the attention of scientists, doctors and specialists around the world transforming the way of studying and understanding the human brain and its functioning.
What is transcranial alternating current stimulation?
Transcranial stimulation with alternating current was born as a product between two relatively differentiated fields of study: neuroscience and electricity. To understand how this technique works, it is important to first know its scientific foundations.
Transcranial alternating current stimulation is based on the idea that electrical currents have an effect on neuronal excitability The human brain is a highly electrochemical organ, in which electrical signals play a fundamental role in communication between brain cells. Through the application of electrical currents through electrodes placed on the scalp, it is possible to modify the electrical activity of specific regions of the brain.
It is important to keep in mind that transcranial stimulation with alternating current focuses on specific and localized regions of the brain, allowing selective stimulation of brain areas related to cognitive, motor or emotional functions. The precision of stimulation depends on the location and configuration of the electrodes, as well as the intensity and duration of the applied current.
One of the most interesting points of study of transcranial stimulation with alternating current is its ability to influence brain plasticity Brain plasticity has been defined as the brain’s ability to change, adapting its structures to new information, stimulation or skills. By modulating neuronal excitability, tACS allows the formation and strengthening of synaptic connections to be promoted, and can have beneficial effects on different brain functions and the brain’s ability to adapt to them.

What applications does tACS have?
As discussed throughout the article, transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) has aroused great interest in the field of neuroscience and medicine due to its diversity of applications and potential.
Next, we will explore some of the areas of research and practical applications in which this technique is used It is important to keep in mind that research in the field of tACS is constantly evolving, exploring new areas and expanding therapeutic possibilities, so these applications may change over time.
1. Neurorehabilitation
Transcranial stimulation with alternating current has shown promising results in neurological rehabilitation. It has been used as a component in treatment to improve motor function in people with stroke, spinal cord injuries, or neurodegenerative diseases. By modulating neuronal excitability, this technique can help restore or enhance neuronal connections involved in motor function promoting the recovery and rehabilitation of patients.
2. Neuropsychiatric disorders
Transcranial alternating current stimulation has also been investigated as a therapeutic option for neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and schizophrenia. Studies have shown that it has positive effects on the reduction of depressive symptoms, improvements in concentration and attention, as well as the modulation of brain activity associated with schizophrenia.
3. Improved cognitive performance
Another field of application of tACS is the improvement of cognitive performance in healthy individuals. The ability it has to enhance memory, attention, information processing and other cognitive functions is currently being investigated Although the results are varied and more research is still needed, many scientists question its application in areas far from the clinic, such as education or personal development.
4. Pain control
Transcranial alternating current stimulation has also been studied as a possible option for the management of chronic pain. By modulating neuronal excitability in brain areas related to pain perception, a reduction in symptoms has been observed in certain patients. However, it is important to note that this application requires careful evaluation and supervision by medical professionals.
Benefits and limitations
As presented, transcranial stimulation with alternating current is presented as a promising methodology in the study and understanding of the human mind, but like any scientific perspective, it also has its limitations. Next, we will review some benefits and limitations associated with tACS.
1. Benefits:
Let’s look at the positive aspects:
1.1. Non-invasive
One of the main advantages of tACS is its ability to be non-invasive in the brains of the people on whom it is used. It does not require surgery or invasive procedures, making it safer and less traumatic for patients
1.2. Low cost and accessibility
Compared to other brain stimulation techniques, tACS is presented as relatively inexpensive and more accessible to people from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
1.3. Therapeutic potential
The main benefit is the therapeutic potential that it has in various neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions Studies have shown improvements in motor function, reduction of depressive symptoms, and modulation of brain activity associated with disorders such as schizophrenia.
2. Limitations:
Let’s look at the negative aspects:
2.1. Side effects and safety
Although transcranial alternating current stimulation is generally safe, Temporary side effects such as discomfort, headache, or scalp irritation may occur Additionally, more extensive research is still needed to better understand the possible long-term effects.
2.2. Individuality of response
The response to transcranial alternating current stimulation can vary widely between individuals. Some people may experience significant benefits, while others may not respond in the same way. The effectiveness of the technique may depend on various factors, such as the location of the electrodes, the intensity of the current, and individual characteristics of the brain.
23. Need for more research
Although transcranial alternating current stimulation shows promise, more rigorous research is still needed to better understand its mechanisms of action, establish standardized protocols and determine the specific conditions under which it can be most effective
The future of transcranial alternating current stimulation
The future of transcranial stimulation with alternating current looks promising, with advances in personalization, technological development, expansion of application areas and integration with other techniques. These perspectives open a wide range of opportunities to improve our understanding of the human brain and find new ways to treat neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. However, it is important to continue researching and conducting rigorous studies to ensure the safety and effectiveness of this technique for the benefit of human health.
The wide application possibilities of transcranial alternating current stimulation appear exciting As research and technology continue to advance, it is expected that this technique will evolve and be applied in new fields. Below and as a conclusion, we will explore some future perspectives of transcranial alternating current stimulation.
With greater understanding of the mechanisms of action and better characterization of individual responses, it is hoped that transcranial alternating current stimulation can be personalized and adapted to the needs of each individual. This will allow a more precise and effective approach in the treatment of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders.
As research progresses, it is expected that more sophisticated and precise transcranial alternating current stimulation devices will be developed. This includes improving electrodes, optimizing stimulation settings, and implementing brain imaging techniques to guide stimulation delivery.
As more scientific evidence accumulates, transcranial alternating current stimulation may find new applications in fields such as improving learning and memory, treating sleep disorders, and rehabilitating other neurological disorders
Transcranial alternating current stimulation can be combined with other brain stimulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation, for synergistic results. This integration of techniques could open new therapeutic possibilities and enhance the effects of non-invasive brain stimulation.