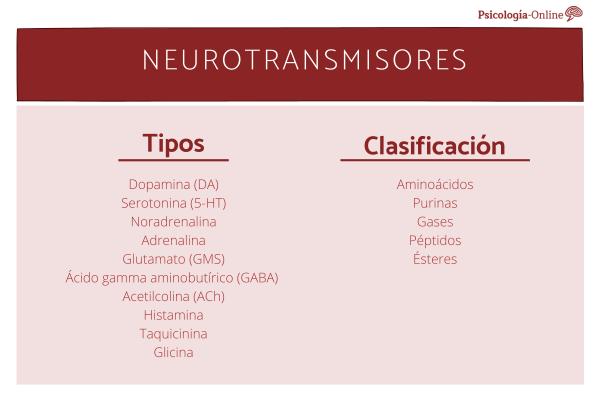
Serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, glutamate… They are some of the most well-known and popular neurotransmitters among those that run through the nervous system of our body, allowing neurons to communicate with each other. But are not the only ones.
And there are a large number of substances that are not often talked about and that nevertheless play an important role in our daily lives. One of them is anandamide which we are going to talk about throughout this article.
Anandamide: what is this substance?
Anandamide, also known as arachidonoylethanolamide or AEA, is one of the many chemical compounds that our body manufactures endogenously. It is an endogenous lipid with great affinity for cannabinoid receptors. In fact, it is considered one of the best-known eicosanoid endocannabinoids (derived from fatty acids) and the second one found in greatest quantity. Discovered in 1992, the name of this lipid derives from the Sanskrit word for happiness or bringer of peace, “ananda”, due to the effects and relaxation it generates, and is composed of arachidonic acid and ethanolamine.
Short-lived and easily degraded, anandamide It is a fragile molecule whose effects are short-lived in the human body This substance is linked, like the rest of the cannabinoids, to sedation, reduction of vomiting and hunger provocation, improvement of respiratory function and relaxation. as well as some problems with concentration, time perception and even memory.
It is a substance that is not produced in a particular region of the brain, but rather It is secreted by the membrane of neurons, and has been located in different regions of the body, both inside and outside the brain. Its presence is common in the thalamus, hippocampus, basal ganglia and cerebellum, as well as in the spleen and heart. Its receptors are therefore widely distributed, being linked to the G protein.
On the other hand, anandamide It can also be acquired through the consumption of different foods Some of its best-known natural sources are cocoa and chocolate, in fact anandamide being one of the main elements that makes it seem so pleasant to most people. Likewise, it is present in some fish and their eggs, or in sea urchins.
Anandamide synthesis and uptake
Anandamide is an endocannabinoid that originates in the membrane of neurons from the hydrolysis of its precursor, a phospholipid called N-arachidonoyl phosphatylethanolamine (or NAPE) derived from the archedonic acid found in said membrane. This synthesis occurs thanks to the enzyme phospholipase D, also joining ethanolamine to end up configuring anandamide. Anandamide is characterized by being generated only at the moment it is going to be released, unlike other neurotransmitters that are previously manufactured and stored until the moment of transmission. It is usually generated by the postsynaptic neuron, in a retrograde manner, generating stimulation or inhibition of the production of neurotransmitters in the presynaptic neuron.
At that moment, this substance is released into the synaptic space, to later be received by both neurons and glial cells. Once captured, it is degraded to ethanolamine and arachidonic acid, and is then reincorporated into the lipids of the membrane. This substance is therefore quickly metabolized by the body, disappearing in a short period of time.
Functions of anandamide
Anandamide is a very useful substance for our body, which has important roles in our brain and body functioning. Although many of them have already been mentioned above, we are going to look at them in greater depth. Among the many functions or roles of anandamide, the following stand out.
1. Homeostasis
As part of the endocannabinoid system, anandamide has a relevant role in maintaining body homeostasis, influencing and modulating nervous transmission and interacting with multiple systems and neurotransmitters. Among others, it can inhibit the synthesis of GABA and glutamate. It also participates in reducing eye pressure.
2. Modulates pain
Like the rest of cannabinoids, one of the main and most recognized functions of cannabinoids is to modulate and generate a decrease in the sensation of pain in the event of an injury having an analgesic effect.
3. They prevent cell proliferation
Another of the actions performed by anandamide, and which in fact continues to be investigated today and generating great interest, is the fact that its action prevents or reduces the cellular proliferation of cancer cells, causing the death of said cells. This has been especially investigated in melanomas
4. It has a neuroprotective effect
Cannabinoids also have a neuroprotective effect by having the ability to reduce the excitation of the nervous system, something that in turn has protective effects towards excitotoxicity
5. Stimulates hunger
Anandamide and the set of endocannabinoids alter and modulate diet, being in close interaction with leptin. While the second is one of the main hormones that regulates satiety, anandamide stimulates appetite and generates the search for food. Anandamide would generate an effect in the form of loss or decreased appetite If there is an increase in leptin, this leads to a reduction in anandamide levels in the hypothalamus.
6. It has antiemetic effect
As with cannabis, anandamide has an antiemetic effect. That is, it inhibits vomiting by interacting with serotonin.
7. Modulates sexual behavior
One of the interactions that anandamide has is with sex hormones Apparently, in this sense, anandamide has a biphasic response: small amounts stimulate sexual activity, while high doses inhibit it.
8. It influences pregnancy
Some studies associate anandamide with a very relevant role in generating implantation of the embryo in the epithelium of the uterus
9. Participate in motivation
In experiments with mice, it was observed that anandamide apparently contributes to motivation and decision-making, accelerating it and generating greater capacity for action and reaction in order to seek solutions.
10. A role in learning and memory
The functioning of anandamide in the brain has also been seen related to learning and memory capacity, frequently found associated with areas that manage memory, such as the hippocampus. In principle, it facilitates the creation of new brain connections and the elimination of old ones. However, some animal models seem to indicate that it can cause memory problems.
11. Linking with feelings of relaxation and happiness
The name of this substance, as we said at the beginning of the article, is linked to the idea of peace, relaxation and happiness. It is associated with pleasure. It also generates a distortion of temporal perception.