When we think of neurotransmitters, names like serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, glutamate, GABA or acetylcholine usually come to mind. Histamine and melatonin are also widely known.
However, there are many other substances that act as neurotransmitters and that have great relevance in our functioning as human beings. Among them we can find a type of neuropeptide that was not identified until 1998: hypocretins or orexins In this article we are going to briefly introduce what they are and some of the multiple functions in which they participate.
What is a hypocretin?
Hypocretins or orexins are peptides, small molecules composed of chains of amino acids that are found in large quantities in most animals. These are substances discovered relatively recently (specifically in 1998) and which have been proven to have a great influence on a wide variety of functions. The fact that it can be called in two ways is due to the fact that this neurotransmission system was discovered practically simultaneously by two different research teams, with the correspondence between them being observed later.
Within the hypocretins we can mainly find two neuropeptides, hypocretins 1 and 2 (or orexins A and B), which have their corresponding receptors in the membranes of some of the cells of the nervous system.
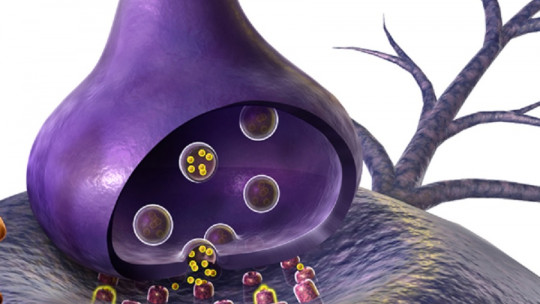
As with other hormones such as dopamine, the neurons that synthesize and use this type of neurotransmitter They make up a system, called the hypocretinergic system
Although the location of the neurons of this system occurs only in the posterior hypothalamus, the hypocretinergic system has a broad effect on the entire brain since the neurons that originate from it have a large number of connections with various areas of this set of organs. Among them, those existing with the limbic system stand out, with hypocretin being closely related to emotional processes. It is also linked to the ascending reticular system, being very relevant in processes such as sleep and wakefulness.
Functions of these peptides
Although relatively little known by most of the population, hypocretins play a very important role in a large number of functions and processes relevant to our behavior. Let’s see what they are.
1. Regulation of emotions and mood
One of the best-known functions of hypocretins has to do with emotion and mood. And it has been proven that there are dense connections of hypocretinergic neurons between the hypothalamus and the limbic system Although it does not generate emotions itself, this neurotransmitter acts to maximize the emotional experience.
In this sense, the presence of hypocretin seems to be linked to the experience of emotions that represent a surge of energy, whether positive such as joy or more negative ones such as anger. Likewise, a decrease in the level of these neurotransmitters has been observed in depressed or stressed patients.
2. Regulation of sleep/wake cycles
Wakefulness and sleep are also largely mediated by hypocretins or orexins, specifically affecting the activation of the wakefulness system and the maintenance of the wakeful state This is in turn involved in the capacity for attention and the use of energy and physical and mental resources.
A lower concentration than necessary will generate alterations in said maintenance, this factor being linked to the disorder known as narcolepsy (in fact it is one of the possible biological explanations for the disorder).
3. Forgetting and remembering: hypocretin in memory
Another of the multiple tasks associated with hypocretins is found in memory. Specifically, in experiments carried out with rodents it is observed that blocking the receptors of this type of peptides generate the disappearance of aversive memories That is, hypocretins help us consolidate and maintain unpleasant memories in memory (an aspect that, although experientially may seem aversive, is functionally useful by allowing us to distance ourselves from the source of said stimulation).
4. Learning
Directly derived from the previous point we can consider that hypocretins have a very important role in establishing learning and conditioning especially with regard to learning done from fear.
5. Intake
Another of the basic functions in which hypocretins participate is ingestion. It has been observed that these molecules have a relevant role in explaining why we look for food and have the desire to eat The synthesis of hypocretins is activated by the action of ghrelin and inhibited by leptin, which are known for their action in generating hunger or satiety, respectively. It is also suspected that it is their actions that generate a link between food and sleep.
6. Gratification and pleasure
Orexin or hypocretin is strongly linked to emotions and the feeling of pleasure, as well as the desire to achieve it. This is what happens with the numerous existing addictions, both at the level of drugs and at the level of sex or food
Disorders to which they are linked
As we have said, hypocretins have multiple functions of great relevance to humans. Therefore, dysfunction of the hypocretinergic system can have relevant consequences for our behavior, There is a certain link between the action of this neurotransmitter and some disorders Some of them are the following.
1. Narcolepsy
One of the main investigations related to hypocretins has to do with their effect on circadian rhythms and wakefulness. The reduction or insufficient presence of hypocretins makes it difficult to stay awake, a deficiency of these substances having been related to the origin of narcolepsy (although much more research is required on this matter).
2. Addictions
Another of the great investigations that has been carried out reflects that hypocretins are related to addiction and relapses. The hypocretins They are linked to craving and motivation to obtain the elements that make us feel pleasure and well-being, being a biological substrate that has a certain influence when it comes to facilitating the possibility of relapses into addictions.
3. Depression
Different investigations seem to reflect that the presence of a high level of hypocretins corresponds to energetic moods, which could be used in the future to make drugs against passivity and lack of energy typical of depression.
4. Anxiety and stress-related disorders
Likewise, it has been observed that hypocretins are related to encoding and maintenance of aversive memories and the regulation of fear High levels make it difficult to extinguish fear, for example, in a phobia or post-traumatic stress disorder.