Pneumonia and bronchitis are both respiratory diseases that, to a certain extent, are related, which is why it is quite common for people to confuse both conditions.
Although both are caused by some type of infectious agent that has entered the respiratory system, their symptoms and severity are very different, and one is potentially more deadly.
Next we will discover the differences between pneumonia and bronchitis in addition to briefly seeing what causes them and to what extent one can be considered a much more serious medical condition than the other.
The main differences between pneumonia and bronchitis
Both bronchitis and pneumonia are infectious diseases which affect the respiratory system, which is why it is quite common for both to be confused in popular language. Added to this, both diseases increase their prevalence when the cold months approach, since it is during the winter that our defenses are low, making us more prone to suffering from infectious diseases.
But although they affect the respiratory tract in one way or another, they are actually very different diseases, not only because of the specific symptoms but also because of their severity. Bronchitis is a milder inflammation of the bronchi than pneumonia, which is an infection of the lung with accumulation of fluid and infected secretions in the alveolus.
Bronchitis
As its name suggests, bronchitis is a disease in which the main affected area is the bronchial tree It is an inflammation of the bronchi that can be caused by bacteria, viruses or other irritating agents, although normally the infectious component is viral.
Among the symptoms of bronchitis we find appearance of mucus, persistent cough, difficulty breathing, some fatigue and pressure in the chest area These symptoms can be more intense and long-lasting, which is why we are talking about acute bronchitis, a condition that is highly contagious. If the symptoms last for a long time, the condition is considered to have become chronic.
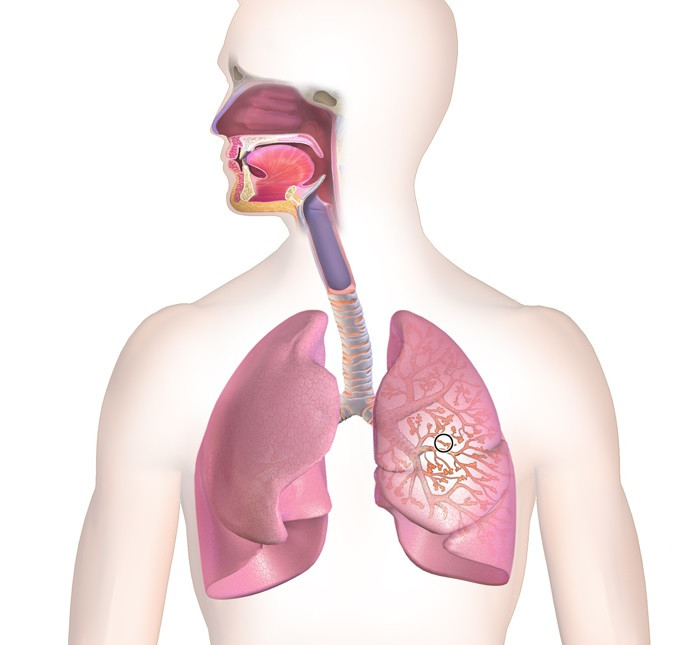
pneumonia
Pneumonia, also known as pneumonia, are infections in which very intense inflammation of the lung tissue occurs. These inflammations arise as a kind of defense mechanism of the respiratory system in the presence of a harmful agent, which is usually a bacteria, mostly a pneumococcus (commonly Streptococcus pneumoniae). Pneumonia can also be caused by fungi and viruses, as would be the case of pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2
Among the most common symptoms of pneumonia we find high fever, acute cough, phlegm and expectoration, pain in the chest and sides, a feeling of suffocation, and muscle and bone pain (dyspnea). Some of these symptoms coincide with those of the flu and bronchitis and, in fact, there are cases of these two diseases that worsen and evolve into a case of pneumonia.
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection much more serious than bronchitis, since it can be fatal in people at risk Its mortality rate is between 1 and 2% in normal patients, while it rises to 8% in hospitalized patients and 30% in those admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). It is especially dangerous in children, the elderly and those affected by asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), kidney failure, diabetes mellitus, heart disease and cancer.
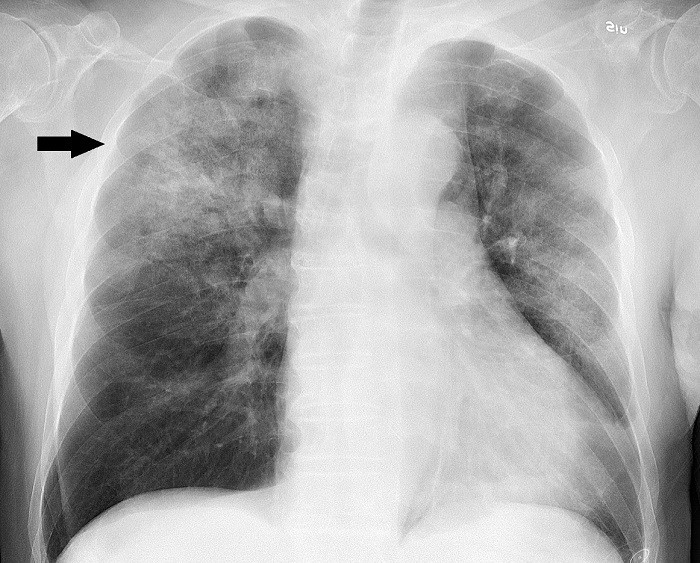
Aspects that differentiate these two diseases
Once we have seen the characteristics of both diseases we can comment on their main differences.
To begin with, we have different symptoms and severity. Bronchitis brings with it symptoms that, although unpleasant and annoying, such as persistent cough, are not particularly serious and is rarely fatal.
On the other hand, pneumonia involves greater damage, having more serious symptoms such as muscle and bone pain, a feeling of shortness of breath, high fevers, and in people at risk it can be fatal.
Another difference is their etiopathogenesis, that is, what causes them. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tree, usually caused by a virus, while pneumonia is an infection of the lung tissue usually caused by bacteria, although fungi and viruses can also be involved. It should also be said that bronchitis can also be caused by irritants such as smoke and bacteria.
As a result of its different origin, it is common for antibiotics to be administered to treat pneumonia, as long as it is known that the specific case is caused by a bacteria. On the other hand, in the case of bronchitis, these types of drugs are not usually so necessary and are only administered if it is certain that the specific case is a bacterial infection.
Prevention and treatment
The best way to prevent both diseases is to avoid bad habits, especially smoking Added to this, if you are a person at risk, it is advisable to receive the flu virus vaccine annually, which is especially recommended for people over 65 years of age, chronically ill patients, and immunosuppressed patients. You should also avoid exposing yourself to the cold since it is a factor that can lower our defenses and it is advisable to wear a mask in seasons when there is a special incidence of respiratory diseases.
Most acute infectious diseases can be diagnosed and managed by primary care physicians, to which it is advisable to go if you suspect you are suffering from bronchitis or pneumonia. In both cases, self-medication should be avoided, consulting the doctor first and seeing what the appropriate treatment to follow is. If the symptoms are more serious, of greater intensity and duration, you can go to a specialist.
If the symptoms that predominate are from the upper airway, that is, nose, ears and/or pharynx, the patient should see an otorhinolaryngologist. On the other hand, if the symptoms that predominate are from the trachea and chest pain is present, there is difficulty breathing and blood is coughed up, you should go to a pulmonologist.