Let’s think for a moment about a human brain. It is a structure of great complexity in which the existence of two clearly differentiated parts is perceived, the two cerebral hemispheres.
We also know that each of these hemispheres has some more specialized functions in different aspects, for example, speech being found in the left hemisphere (generally) or having seen that while the right hemisphere is more holistic or global, the left one is more logical and analytical. However, these two hemispheres are not loose and separated from each other, but at some point in the anatomy of the brain it is possible to find a point of union. This junction point is the so-called corpus callosum
What is the corpus callosum?
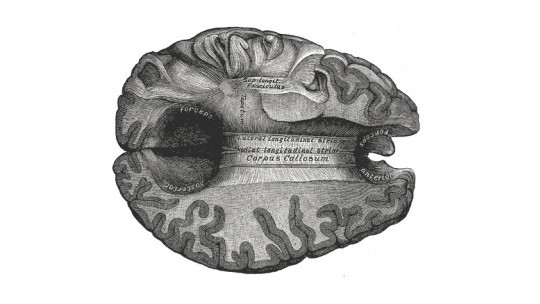
The main set of nerve fibers that joins both cerebral hemispheres is called the corpus callosum. This structure is mainly formed by neuronal axons covered with myelin, making them part of the white matter of the brain. Within the white matter, the corpus callosum is considered an interhemispheric commissure, since it connects and exchanges information between structures of the different hemispheres. In the human brain there are other interhemispheric commissures, but they are much smaller than the corpus callosum.
This structure is located in the midline of the brain, located at the bottom of the interhemispheric fissure, and is mostly hidden from external observation as it is partially covered by the cortex. It is shaped like a leaf or a comma, having different parts that connect different parts of the brain to each other
The areas connected by this structure of the brain are mostly cortical areas, although with some exceptions. Generally the subcortical structures communicated with other structures and commissures.
Parts of the corpus callosum
Although the corpus callosum is considered a single structure, it has traditionally been divided into several parts. Specifically, The corpus callosum could be divided into the following four sections
1. Beak or rostrum
Located in the lower front part of the corpus callosum, it is the most anterior part of this structure. It arises from the lamina terminalis and is connected to the optic chiasm.
2. Genu or knee
This is the part of the corpus callosum that curves towards the interior of the brain, first heading towards the frontal lobes to form forceps minor. The fibers of this part of the corpus callosum They connect the prefrontal cortices of the two hemispheres, allowing their information to be integrated
3. Body
After the genu or knee, is the body, which ends up thickening at the back. Connects with the septum and trine this in turn being an important connection structure between regions of the brain, such as the thalamus, the hippocampus and other areas of the limbic system.
4. Splenium or labrum
The most posterior and final part of the corpus callosum is formed by the fibers of which it consists that end up associating with other projection and associative fibers. It connects with the occipital lobe to form the forceps major, and also It is linked to the lateral ventricle to the point of forming one of its inferior walls It also connects with the pineal gland and the habenular commissure (which connects the habenular nuclei of both hemispheres).
Functions of this part of the brain
The main function of the corpus callosum is to transmit information from one hemisphere to the other, allowing interhemispheric communication. In this way, the fact that the functions of each of the hemispheres are partly different does not prevent them from acting as an integrated whole, allowing the precise execution of the different processes and actions carried out by the human being.
In this sense also It is linked to learning and information processing, by uniting and acting as a link between the different brain nuclei. On the other hand, if, for example, a part of one cerebral hemisphere is injured, thanks to the corpus callosum the opposite hemisphere can take care of those functions that are left unattended.
Furthermore, some studies show that apart from this function the corpus callosum It also influences vision, specifically eye movement, as information about the eye muscles is transmitted through it. It is natural, since coordination between the two hemibodies, in this case the eyes, is crucial in eye movements.
What happens when it is sectioned?
The corpus callosum is an important structure when it comes to integrating the information received and processed by both cerebral hemispheres. Although the absence of connection between hemispheres at the level of the corpus callosum does not imply a complete loss of functionality (since Although it is the main interhemispheric commissure, it is not the only one ), the total or partial disconnection of the cerebral hemispheres can represent a significant handicap when carrying out various activities.
Among other things, this kind of disconnection between parts of the brain can lead to what is known as callosal disconnection syndrome
In this syndrome, it has been seen how patients with a split brain (that is, who present a disconnection between both hemispheres) have shown difficulties such as lack of coordination, repetition or perseveration when carrying out sequenced activities such as combing one’s hair, feeding oneself or dressing oneself, sometimes performing the same action twice due to lack of motor integration.
Also greatly hinders learning and retaining new information by not being able to coordinate information correctly (although it does not make it impossible, it requires a much greater effort than usual), as well as it can cause alexia (inability to read) and agraphia (inability to write).
In addition, significant alterations can occur at a sensory level. For example, it has been shown that Later lesions of the corpus callosum can cause severe difficulties in making discriminations between somatic stimuli, causing somatic agnosias or lack of recognition from tactile stimuli. Memory and language problems are also common.
Callosotomy: when sectioning the corpus callosum can be good
Despite the disadvantages that may arise from performing this type of surgical intervention, In the presence of some very serious disorders, the division of the corpus callosum or callosotomy has been evaluated and successfully applied for medical purposes, as a lesser evil.
The most typical example is resistant epilepsy, in which sectioning parts of the corpus callosum is used as a method of reducing severe epileptic seizures, preventing epileptoid impulses from traveling from one hemisphere to another. Despite the problems it can cause in itself, callosotomy increases the quality of life of these patients, because the difficulties it can cause are less than those caused by continued seizures, thereby reducing the risk of death and quality of life can improve.
On the other hand, over time it is possible that the brain reorganizes to allow mental processes to be carried out that during the first weeks after the operation seemed eliminated or seriously damaged, although recovery is usually not complete.
Conditions that affect the corpus callosum
It has been previously indicated that the division of the corpus callosum can have limiting effects, although sometimes its section may be considered in order to improve the symptoms of a disorder.
However, The corpus callosum being cut or damaged can occur accidentally or naturally, there are multiple diseases that can affect this area of the brain. Some of these alterations may occur from the following.
1. Traumatic brain injuries
In the event of a blow or trauma, the corpus callosum can be easily damaged due mainly to its great consistency and density. Generally a tearing of the substance occurs, or diffuse axonal damage as a consequence of the blow-counter blow against the bones of the skull. If we talk about effects focused on one point, the greatest affectation usually occurs in the splenium.
2. Strokes
Although it is not frequent due to the bilateral irrigation of the corpus callosum, it is possible to find cases in which hemorrhages or ischemia affect the white matter of the corpus callosum In this way, alterations in blood flow are capable of practically cutting off the communication between the two hemispheres that takes place in the corpus callosum, without the need for a solid element to come into contact with this part of the brain and break it.
3. Demyelinating disorders
Being a structure made up of white matter, covered with myelin, Disorders such as multiple sclerosis greatly affect the corpus callosum This type of disorder causes the messages sent by the brain to not be sent as efficiently or even cause many neurons to die, which in the corpus callosum causes the perceptions and functionalities of both hemispheres to not be easily integrated. In this way, mental processes that involve regions on both sides of the brain are greatly affected, or cannot be carried out at all.
4. Brain tumors
Although its compactness means that in general there are not many tumors that affect the corpus callosum some of great aggressiveness such as lymphoma or glioblastoma multiforme which is usually located in the white matter, if they can infiltrate, affect this specific structure and cause serious damage or “strangle” it due to the pressure exerted by the growth of the cancerous parts.
In the case of glioblastoma, it usually produces a typical butterfly-shaped pattern with greater involvement of the central area.
5. Malformations
Although not very frequent, it is possible to find malformations in some subjects that cause them, from birth, to have a smaller number of connections than usual. Other types of congenital malformations can cause easy rupture (and subsequent hemorrhage) of blood vessels in the brain, which can also affect the corpus callosum.