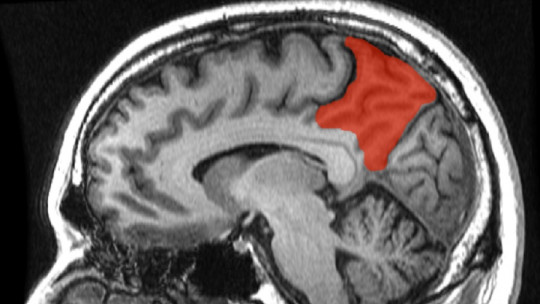
He parietal lobe located under the cranial bone that gives it its name and between the frontal and occipital lobes, is one of the most important brain structures both due to its size and the processes in which it participates.
In fact, it is so crucial when it comes to successfully carrying out various mental processes that it is practically impossible to talk about this part of the brain as if it were a “simple” piece of our nervous system or a structure that performs a single characteristic function.
Next We will see what the characteristics of the parietal lobe are and what processes it participates in
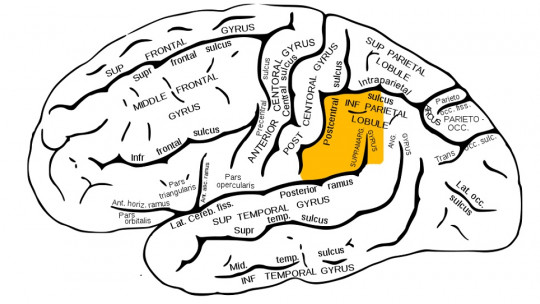
What is the parietal lobe?
This part of the brain is an area of the cerebral cortex that is located just behind the frontal lobe: both lobes are separated by the so-called central sulcus. However, The parietal lobe works together with that and the rest of the lobes of the brain since it includes a large association area, which can be seen as a center in which many types of information are mixed to generate a unit.
Although the parietal lobe is more specialized in certain brain functions than others, one of its main characteristics is that integrates data from different sources For example, it mixes data related to what is seen and those that tell us about what is heard, and makes a complete perceptual experience appear.
Likewise, in this area of the cerebral cortex there are many memories that, once “stored” by the hippocampus, move until they are fixed in the neural networks of this lobe. Memories include all the sensory information that comes to us from the outside world, but also the feelings and emotions linked to that piece of memory. That is, both perceptual processes and the regulation of moods flow into the parietal lobe.
So, if a single word has to be chosen to define the function of the parietal lobe, this should be “integration” a concept that refers to the functions of many other parts of the brain.
Functions of this area of the brain
There are many and varied functions carried out by the neuronal networks of the parietal lobe but in summary it can be said that it plays an important role especially in three kinds of processes: the integration and processing of sensory information coming from different “channels”, the processing of symbolic information (which includes the related to language and its use) and the processing of numerical information, something basic to be able to count and perform mathematical operations.
1. Sensory integration
One of the largest association areas of the brain is included in the parietal lobe, which means that information from all areas of the body are combined in this area to result in information that is more than the sum of its parts. Therefore, the creation of abstract concepts occurs in part thanks to the parietal lobe, thanks to which we are able to generate, for example, the idea of what a dog is, with its associated movement, touch and smell.
But in the parietal lobe not only do data about the world around us and what lives in it come together, but also information about how we relate to that world in real time For example, it is in the parietal lobe where the data coming from the muscles of the body are united, thanks to which we get an idea about the physical position and posture in which we find ourselves. The same goes for touch. In short, the parietal lobe is responsible for somesthetic processing, that is, the sensory ability to recognize bodily sensations.
Similarly, the parietal lobe works together with the frontal lobe to provide a feedback about how the voluntary movements we are carrying out are going, in order to be able to correct them immediately in the event that unforeseen events are detected.
As a curiosity, this function includes graphesthesia, which is the ability to recognize letters and words when an element touches the skin, tracing their shape.
2. Processing of symbolic-analytical information
Another of the great functions of the parietal lobe is to work with symbols and arithmetic The mathematical function is carried out together with the previous one, since it is from the analysis of what is sensory perceived that a sequence of units can be imagined with which to work mathematically.
Since the parietal lobe is a place where many mental processes mix, it makes possible the abstract thinking necessary to think in symbols.
In this sense, the location of the parietal lobe is very relevant in this sense, given that It is in a central position where it can receive input from all parts of the central nervous system This allows it to integrate information from very varied places, thus participating in the appearance of the global experience that appears in our consciousness.
Lesions in the parietal lobe
As often happens in psychobiology, part of the functions of a brain structure tell us about the functions they perform. In the case of the parietal lobe, These lesions speak about the multiplicity of tasks performed by groups of neurons of this part of the brain.
Lesion in the left parietal lobe
An injury to the parietal lobe of the left hemisphere can result in the appearance of Gerstmann Syndrome which includes symptoms such as acalculia (acquired inability to perform calculations), confusion of left and right, and difficulty when writing (agraphia).
Injury to the right parietal lobe
With the rest of the brain in good health, a lesion in the right parietal lobe can cause hemineglect that is, inability to pay attention to stimuli present on the left side of the body while the person is not aware of this problem (a phenomenon known as anosognosia).
People with hemineglect completely neglect one of the halves of their body, which means that they do not wash, dress or comb their hair, and in the same way they will act as if they were ignoring everything that happens on one of the sides of their body.
Injury to both parietal lobes
When the parietal lobes of the left and right hemisphere are injured, Balint Syndrome may appear This is a serious neurological disorder that mainly affects perception and psychomotor ability, and for which there is no cure, so treatment is based on the management of the symptoms they produce.
Among its symptoms is the inability to perceive images as a whole, that is, you see separate elements but you do not know how far they are from yourself or each other or the position they occupy. Similarly, difficulties appear in the coordination of eye movements (optic ataxia).
Concluding
The parietal lobe is characterized by the way it works together with many other areas of the brain offering them a space in which they can integrate their torrents of information with each other.
This, of course, does not mean that in this part of the cerebral cortex we cannot find more or less specialized areas, and in fact it has been seen that several of them are especially involved in vision and in the execution and monitoring of coordinated movements. with the posterior area of the frontal lobe.
However, by its very distributed nature, the brain functions from networks of neurons spread across many different places, and in this sense the parietal lobe is no exception. Consequently, these functions are very relative, and in reality they exist thanks to the joint work of several areas of the nervous system.
In conclusion, the parietal lobe works by coordinating with other areas of the cerebral cortex to ensure that the processes of perception, thought and movement can occur and be functional. To do this, it processes part of the information that comes from other regions of the brain, and sends the information to other networks of nerve cells so that they continue working on it.