Researchers, with current knowledge, have managed to calculate that the human body houses about 30 trillion cells. Without a doubt, each tissue has its particularities and, for example, 84% of this cellular volume in our species corresponds to red blood cells, which transport oxygen in the blood. Yes, as strange as it may seem, many experts consider blood to be a type of connective tissue that is fluid in nature.
Human beings are 50% proteins, since these represent half of our dry tissue and, as you can imagine, the biological system that makes up us cannot be conceived without tissue as a basic level of organization beyond the cell. It’s all about perspective but, in short, without tissue organization we are nothing.
This entire introduction goes to underline the diversity and importance of tissues in our body. We all know what nervous or muscular tissue is due to its clear functionality, but, What comes to mind if we name you the term “mesothelium”? If the answer is nothing, don’t worry, because here we tell you everything you need to know about him.
What is the mesothelium?
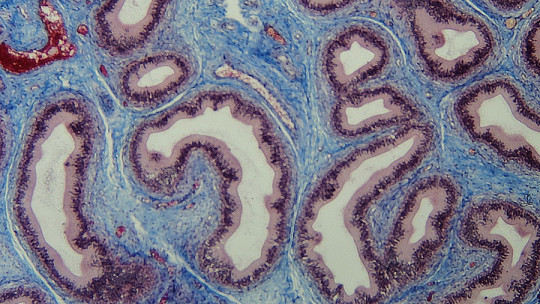
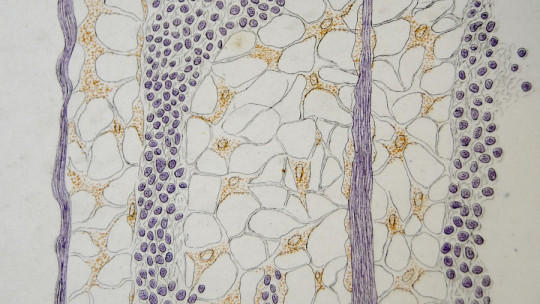
We start directly. From a physiological point of view, the mesothelium is defined as a type of simple squamous epithelium that rests on a basal lamina supported by connective tissue We dissect each of these terms:
That makes it clearer, right? We are talking about a really simple type of tissue: a single layer of flattened cells. To locate this curious tissue, we must emphasize that it is the outermost layer of the peritoneum but what is this?
The peritoneum is the serous layer that lines the inside of the abdominal cavity, that is, the “hollow space” in which all our organs are housed. This is made up of two layers and, between them, there is a space (peritoneal cavity) that contains about 50 milliliters of lubricating liquid that allows them to slide against each other. It is the most extensive serous membrane in the body because, in addition to lining the peritoneal cavity, it also shelters our intestines. It is estimated that, for this reason, it occupies 40-50% of the total skin surface.
The mesothelial cell
We have already described the general shape of the mesothelium and its location, which is why we only have to pay special attention to its basic functional unit, the mesothelial cell, to complete the panorama of this unique tissue. Go for it.
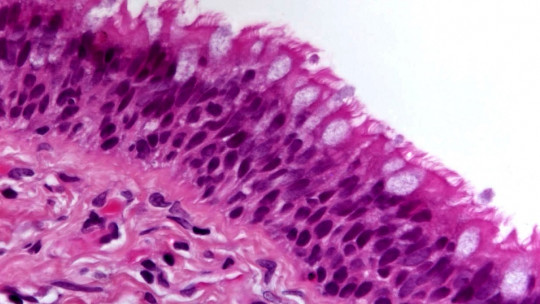
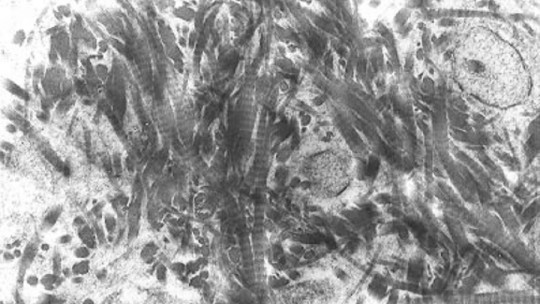
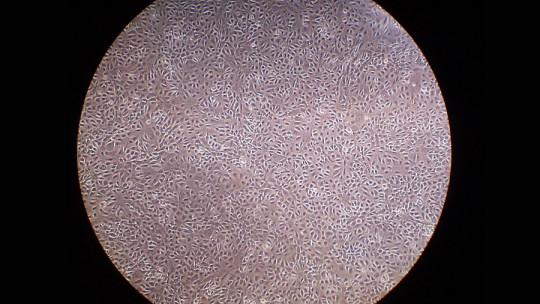
The mesothelial cell is of the flat epithelial type, of mesenchymal origin (loose connective tissue of embryonic origin) that lines the serous cavities These cells form a monolayer with a polygonal mosaic appearance in which certain microvilli emerge. The proteins and serous fluids that are trapped between these microvilli provide a low-friction surface, which is an excellent contact zone between organs. On the other hand, these cells rest on a basement membrane (MB) that offers little resistance to the passage of molecules less than 30,000 daltons.
Finally, it should be noted that mesothelial cells are very reactive This means that they change appearance easily. For example, when they are at rest they are observed in well-organized groups of different volumes, with a high nucleus:cytoplasm ratio. On the other hand, as they are activated they increase in size, forming irregular cytoplasmic protrusions and greater vacuolization. Unfortunately, this plasticity can be a problem: we will have to talk about cancer in future lines.
Functions of the mesothelium
The main purpose of mesothelial cells (and therefore of the mesothelium) is create a layer of lubricating fluid that is released between coating layers producing a slippery, non-adhesive surface.
In addition to this, the mesothelium also represents the transport and movement of particles and cells between cavities, among which are leukocytes, involved in the immune response as inflammatory mediators. In short, it is a “passage” tissue that allows movement between organs and the transport of various substances and cellular bodies essential for the physiological well-being of the organism.
Mesothelioma, a cancer of the mesothelium
Like virtually all cells in the body that grow and replace themselves, The mesothelium is a potential candidate for cancer events After all, cancer is nothing more than a mutation in a cell that causes it to divide uncontrollably and not respond to normal periods of apoptosis (cell death), giving rise to the feared malignant tumor.
Mesothelioma can be divided into various categories depending on the location affected. Among them, we find the following.
1. Pleural mesothelioma
It affects the tissue that surrounds the lungs, that is, it develops in the chest cavity It can cause chest pain, painful cough, difficulty breathing, unusual lumps under the skin of the chest, and unexplained weight loss, among many other things.
2. Peritoneal mesothelioma
As its name indicates, affects the tissue of the abdomen (peritoneum) It causes abdominal bloating, pain in the abdomen, nausea and weight loss without apparent cause. Unfortunately, both types of mesothelioma are extremely aggressive and carry a non-negligible fatality rate.
3. Other types of mesothelioma
There are more types of mesothelioma depending on the tissue they affect, for example, pericardial mesothelioma grows in the tissue surrounding the heart, causing breathing problems and oppression. On the other hand, mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis affects the lining of the testicles. Basically, Any mesothelial lining is susceptible to the appearance of a malignant tumor although not all mesothelial tumors automatically translate into cancer.
Distribution and epidemiology of mesotheliomas
Mesothelioma appears in approximately 1-2 patients per million people per year. Unfortunately, people who work in the construction sector (especially if they are in contact with asbestos) are up to 40 times more likely to develop it. This very aggressive type of cancer kills about 5,000 people a year in Europe and 3,000 in the US a year.
The typical mesothelioma patient is a 60-year-old man who has been working in this type of industry for at least 30 years It is shocking to know that, in most cases, it usually takes 20 to 40 years after exposure to asbestos (in vinyl, cars and construction materials) until cancer develops.
For this reason, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended that all countries in the world stop using this material in the field of construction. Unfortunately, in 2010 this organization estimated that, despite global bans, 125 million people around the globe are still in close contact with asbestos. In addition to mesothelioma, this material also causes asbestosis (scarring lesions in the lung and pleura) and lung cancer in addition to possible metastases derived from these types of malignant tumors.
Summary
As you have seen, the mesothelium is a very simple structure that has many secrets to unravel. To understand ourselves (and in a more familiar final note), we can say that it is a simple layer that allows the sliding between organs and the transport of substances, from proteins to specialized immune bodies, passing through many other cell types.
Mesotheliomas are a type of malignant tumor that is very rare in the general population but, unfortunately, they occur almost only in people who have worked on construction sites in contact with asbestos. If you have a history of working/physical work and notice strange lumps in any soft part of your body, abdominal swelling and continuous coughing, go to the doctor immediately.