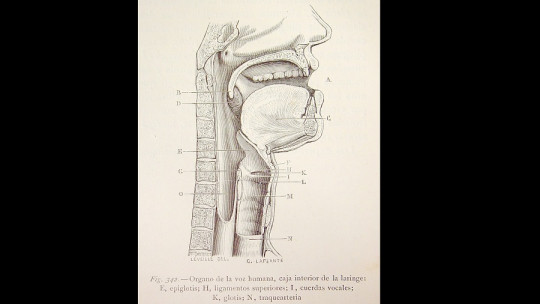
The glottis is an opening located in the middle-upper part of the larynx of variable size and narrow, which is delimited by the vocal cords, four folds of smooth muscle tissue that are located on each side of the space.
Beyond its technical terminological definition, today we are going to discover that the glottis, despite its anecdotal nature, is an essential structure for the formation of sound: that is, human speech, among many other functions.
Although other living beings can emit complex and developed sounds with different intentions (such as elephants, birds or primates), we are the only species that has generated a complex language, on which we have based our society and interactions during day to day life. . What would become of us without the laryngeal structures that give us the ability to speak?
Each small part of our organism has an essential function for what today describes us both as a species and as autonomous individuals. Therefore, in this article we will see the functions and characteristics of the glottis
What is the glottis?
According to the Royal Spanish Academy of Language (RAE), the glottis is defined as “anterior orifice or opening of the larynx.” Of course, this cold conglomeration of words does not do justice to the functionality and essential work of this space. Before entering fully into the structure that concerns us today, It is necessary to talk about the already named larynx, the place where it is located Go for it.
The importance of the larynx
The larynx, defined as a tubular organ composed of nine pieces of cartilage, is a muscle-cartilaginous structure adapted to the phonation or voice emission needs of the human being Due to its structural complexity (which would require a space by itself to be described), we are going to divide the laryngeal structure into three parts in a simple way.
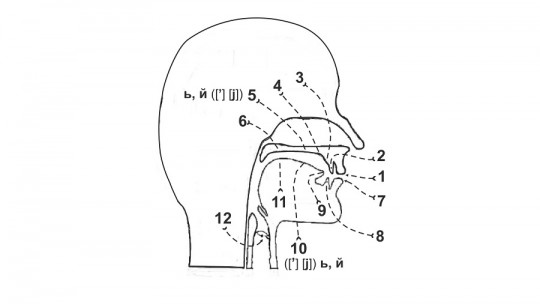
The subglottis or infraglottic level is the space below the vocal folds At this level, the larynx joins the trachea. The glottal level (the glottis itself) is the triangular space that remains when the vocal folds are open. The supraglottis or the supraglottic level is the space located above the vocal folds, or in other words, the laryngeal vestibule.
Once we have briefly described the morphology of this complicated tubular organ, we are going to limit ourselves to quickly listing its multiple functions:
These are some of the essential functions of the larynx, but we certainly have not covered them all. Without a doubt, it is a multifaceted structure, since It protects us from the entry of foreign substances or food into the upper respiratory tract but also allows us to communicate with each other and with the environment that surrounds us.
Morphology and function of the glottis
Once the laryngeal function has been defined, let’s return to the structure that concerns us here. The word “glottis” comes from the Latin “glossa,” which means tongue. Only with the linguistic dissection of the term can we already guess where the shots are going to go.
From a physiological point of view, this space is defined as the middle part of the larynx, where the vocal cords are located It should be noted that the anterior two-thirds of the glottis make up the “ligamentous or membranous glottis”; while the posterior third makes up the “cartilaginous glottis”.
To understand the space that separates the vocal cords, it is also necessary to describe them above. The vocal fold is formed thanks to the presence of a structure called the vocal ligament which runs from the ventral surface of the arytenoid cartilage to the dorsal surface of the thyroid cartilage and, over it, the vocal muscle and the laryngeal mucosa fall like a tent, which finally constitutes the vocal membranous folds.
It should be noted that between the lower vocal folds there is a hollow opening: the glottis. This space is divided into two according to its functionality:
As far as diction is concerned, without wanting to go into the production of sound due to the complexity that this process entails, we will limit ourselves to saying that Sounds that only involve the glottis are called glottal Many languages on different continents present this glottal stop, that is, a voiceless consonant resulting from the interruption of pulmonary air flow in the glottis.
Thus, we can conclude that the glottis has various functions: first, it allows the passage of air to the lungs (which is said quickly), but at the same time, this air flow makes the vocal cords vibrate, which causes sounds. The space of the vocal glottis is essential for speech
Finally, this portion of the laryngeal lumen also helps prevent the passage of food into the upper respiratory tract, especially at the time of swallowing. This last function is closely related to the structure above it, the epiglottis, which we reserve for another opportunity.
Diseases associated with this part of the body
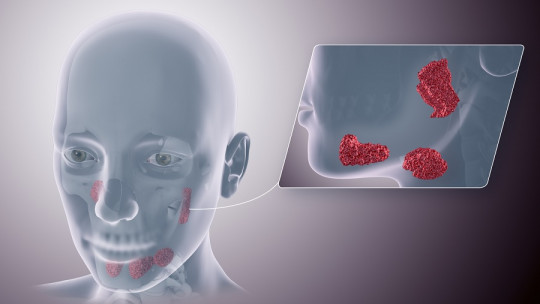
Glottis cancer, also called laryngeal, throat or vocal cord cancer, is one of the most serious diseases associated with this part of the body According to the American Cancer Society, the appearance of these tumor processes in the tissue surrounding the glottis generates hoarseness, dysphonia or changes in the voice, which allows their early detection in many cases.
Like most cancers associated with the neck and upper and lower respiratory tract, glottic cancer is positively correlated with tobacco consumption, and to a lesser extent, alcohol.
Despite this being the most relevant condition, there are genetic disorders that can promote the formation of glottic tumor, such as Falconi anemia or dyskeratosis congenita
Finally, there are also biases in terms of gender and age: men are up to four times more likely to suffer from laryngeal cancer, and more than half of the patients are 65 years old or older.
Another pathology that affects the glottis is inflammation of its surrounding tissue from an allergic reaction, which makes it impossible for air to pass and ends up causing the patient to die from asphyxiation. This is a medical emergency, and if the inflammation does not subside with the application of corticosteroids and other medications, a tracheotomy is necessary to allow air to pass to the lungs.
Summary
As we have seen, despite its morphological simplicity (since it is a hole, no more, no less), the glottis is essential for both speech and breathing in human beings and life itself. Different functions are collected in this space: from the passage of air to the lungs, through the protection of the upper airways against external agents and food, to the production of sounds and the miracle of speech in human beings.
These types of spaces reveal the exquisiteness of the human body: every small hole, every nook, every tissue and even every cellular body has a specific and essential function for our body. Of course, there is no doubt that our body is a true work of evolutionary engineering.