In daily life, human beings carry out a large number of behaviors and actions. We shower, go to work, talk and interact with others, walk, eat or go to bed. Most of these actions are carried out consciously and voluntarily However, our body does much more than that.
Regardless of our will, our body makes the heart beat constantly, maintains respiratory function, follows a long process to desire, digest and after digestion excrete food, regulates the sexual response or prepares us to react to dangers or stimuli. appetizing Regulation of basic bodily functions It is carried out by one of the parts of the brain known as the brainstem. Within this structure, there is another one known as the medulla oblongata and that has a very important role
What is the medulla oblongata?
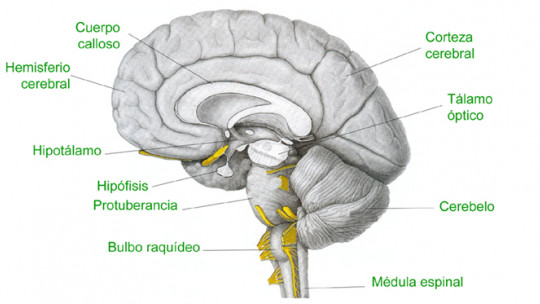
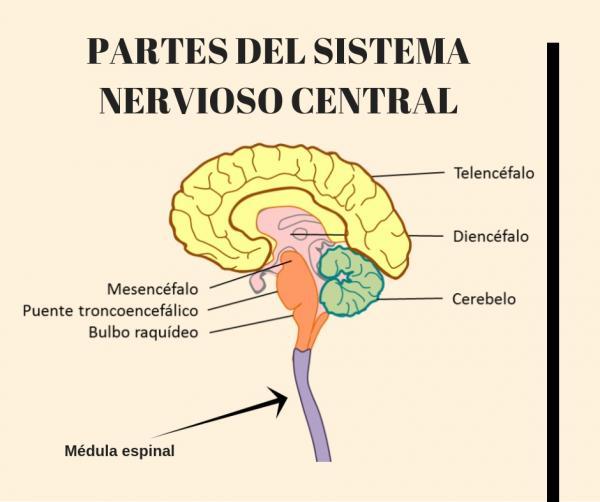
Also called myelencephalon, the medulla oblongata is a subcortical structure located in the lower part of the brain stem With a shape similar to a cone, it is the structure of the nervous system that connects the brain and the spinal cord (hence another of its names, medulla oblongata), bordering the decussation of the pyramidal bundles and the pons
In the medulla oblongata can be found both motor and sensory nerve connections, passing through it the different nervous tracts. It is a neurovegetative nucleus, responsible for the maintenance and functioning of the organs in an automated way and outside of consciousness. It also maintains vital signs, so problems that compromise its functioning lead to brain death. It is therefore an area of great importance for the survival of human beings.
Parts and anatomical configuration
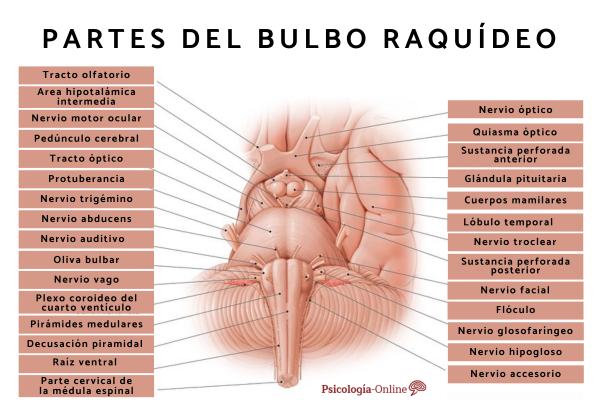
When talking about the medulla oblongata we are talking about a structure that is not homogeneous in its composition and function On the contrary, this structure is made up of different nuclei, some of the best-known nervous tracts beginning in them, and these parts of the medulla oblongata have different functions.
The medulla oblongata is generally considered to be mainly divisible into three parts: pyramids and their pyramidal decussation, lemnisci and lemniscal decussation and lower olive complex Below we can observe some of the most relevant structures of each of these brain nuclei, in addition to other nuclei of interest in the medulla oblongata.
1. Bulbar pyramids and pyramidal decussation
Named for their shape, the bundles of nerve fibers that connect the cortex with the medulla and the spine are located in the pyramids of the medulla oblongata. So that, It is in this area where the brain connects with the rest of the body sending motor information to muscle fibers distributed throughout the body.
In pyramidal decussation, the nerve fibers of the pyramids decussate, that is, they mostly change sides, with the fibers of the left pyramid being on the right and vice versa. Specifically, in this area the motor pathways are especially decussated.
2. Lemnisci and lemniscal decussation
The lemnisci are bundles of nerve fibers whose function, as in the case of the pyramids, is to transmit information between the brain, specifically the thalamus, and the spinal cord. In this case, however, The information they carry is mainly sensory
As in the case of the decussation of the pyramids, the fiber bundles of the lemnisci decussate following the same process in this case for sensory information.
3. Olive grove complex
The olivary complex is a structure located in the brain stem, being part in the pons and part in the medulla oblongata The region present in the medulla connects with the cerebellum, being linked to the control of motor skills. It has also been linked to vision.
Other relevant nuclei and tracts
These are other structures that are also found within the medulla oblongata.
Ambiguous nucleus
The vagus, accessory and glossopharyngeal nerves begin in this structure. These nerves participate in the control of feeding and digestion, controlling the muscles of the pharynx and larynx. So, they are the ones who They allow us to swallow and allow food to move through the digestive tract
Nucleus of the solitary tract
This is the part of the medulla oblongata that regulates the sensitivity of the viscera, intervening in the same way in cardiorespiratory function. Likewise, the facial-lateral part also participates in the perception of taste, a process that takes place exclusively inside the skull.
Dorsal nucleus of the vagus
This nucleus, through which the vagus nerve passes, is linked to digestion, controlling the production and emission of gastric flows. It is, therefore, part of a network of neural networks involved in the enteric nervous system framed partly in the peripheral nervous system.
trigeminal nucleus
In this location we can find the trigeminal nerve, which is of special relevance when it comes to transmit pain, temperature and touch information It is an area in which neuronal cells accumulate to process information at a very basic level; Other brain structures will be in charge of continuing to work from this information when the nerve cells transmit the signal to the higher area.
What does he participate in? Functions of the medulla oblongata
The correct functioning of the medulla oblongata is vital for human beings. Literally, since the destruction or cessation of operation of this area causes death.
To understand why it is so important, it is necessary that we consider some of the main functions of this structure, as well as take into account that since it is located at the base of the brain, a large part of the vertically arranged neural networks pass through this structure of the central nervous system.
Transmits information from the spinal cord to the brain and vice versa
Being the part of the nervous system that connects the brain and spinal cord, one of the main functions of the medulla oblongata is to serve as a link between the brain and/or cerebellum and spinal cord Thus, it is responsible for transmitting both sensory and motor nervous information from the rest of the body.
Control of heart rate and blood pressure
The medulla oblongata keeps us alive, since it has the important function of control vital and unconscious elements such as heartbeat and blood pressure Thus, it is responsible for maintaining heart rate and regulating vasoconstriction.
Regulation of breathing
Breathing is one of the basic functions that allows life, since we need the presence of a constant supply of oxygen for the functioning of the different organs. The medulla oblongata manages control of respiratory function maintaining it at all times.
It is a process that, precisely because of its importance, cannot depend on our ability to manage the focus of attention, which is reflected, for example, in the fact that we never forget to breathe, no matter how complex the task we are performing. or even if we sleep. In general, the medulla oblongata is useful precisely because of the hierarchy of tasks that it allows us to establish and thanks to which we make more optimal use of the resources of the nervous system.
Participates in nutrition and digestion
Control of involuntary muscles, such as those that push food through the digestive tract When we eat, it depends on a part of the bulbar complex. In addition to muscular control, the functioning of the digestive system is also linked to the medulla oblongata as it regulates the emission of gastric flows This means that it is a structure of the brain that helps maintain ideal chemical balances in the body.