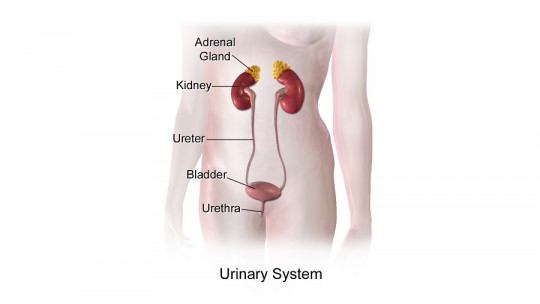
Monurol is one of the most used medications to treat urinary tract infections , which includes the bladder, kidneys, urethra, and ureters. Some of the most common are cystitis, pyelonephritis or urethritis, to name a few.
They are generally caused by bacteria traveling from the urethra to the bladder, and are more common in women than men (because the urethra is shorter in them). They are also common in elderly people and in people with different diseases like diabetes.
Thanks to its bactericidal properties, Monurol is an effective medication to treat these infections. We will see below what Monurol is, how it acts within the body, how it should be administered, and finally, its contraindications and side effects.
What is Monurol and what is it for?
Monurol is an antibiotic type medication. As such, it is used to treat urinary tract infections (known as “UTIs” for short). This drug It is made up of a chemical substance with anti-infective properties called “phosphonic acid” From the latter, one more substance is derived, “formocin trometamol”. Formocin trometamol is precisely the active ingredient of Monurol.
What fosfomycin does is block the development of bacteria by slowing or preventing the synthesis of one of the enzymes essential for their growth. It specifically blocks the growth of bacteria that cause the most common UTIs. Thus, Monurol has a bactericidal property, which helps relieve uncomplicated urine infections, such as cystitis and urethritis
This drug is useful for treating uncomplicated bacterial infections, which are those caused by bacteria sensitive to the active ingredient. That is, in the case of serious infections (caused by bacteria highly resistant to formocin trometamol), Monurol will not be an effective medication, or the doses will have to be adjusted according to the severity of the infection.
For example, this may be the case of infections that occur in older adults or also in patients who spend a lot of time in bed. In the same sense, Monurol not effective for treating infections not caused by bacteria but by viruses (like the flu).
Presentation and recommended doses
Monurol is sold in sachets that contain a water-soluble granule. Its concentration can be 2 or 3 grams and it is quickly absorbed. To encourage this, it is recommended not to take monurol with food, or to take it a couple of hours after the last meal. It can also be taken one hour before eating and It is recommended to take it after emptying the bladder Otherwise, the absorption of Monurol inside our body becomes slower.
On the other hand, the recommended dose for adults who suffer from mild infections is usually a single dose (only one sachet). The decision whether to take Monurol 3g or Monurol 2g depends largely on the severity of the infection.
For older adults, or in the case of people with serious infections, the general recommendation is to take two doses (2 sachets) throughout the same day. Again, according to the severity of the infection, Monurol 3g or Monurol 2g can be administered.
Once administered, Monurol is expected to have the expected effects within two to three days The latter also depends on the person’s clinical history (for example, whether he has had recurrent infections or inflammations in the period before taking Monurol). In fact, it is common for the treatment to take a few days longer to take effect when there has previously been some inflammation.
Contraindications
Monurol is contraindicated in the case of people who have the following conditions:
Side effects
As with all medications, Monurol produces some adverse effects. These are mild and moderate effects, among which are nausea, burning sensation in the chest and diarrhea On very few occasions, cases of anaphylaxis have been reported, specifically due to allergy to the active ingredient.
Special medical monitoring is also necessary when it comes to people with diabetes, due to the high sucrose content contained in this medication. If you have ingested a dose greater than the recommended one, it is important to drink water, since fosfomycin trometamol is expelled through urine.