Metoclopramide, better known as Primperan is a medication widely used to treat all types of nausea and vomiting since the 1980s. For a long period of time it was considered one of the safest drugs on the market.
However, Primperan is indicated for specific uses and should not be used without a doctor’s prescription, as many people usually do; In this article we explain why.
What is metoclopramide?
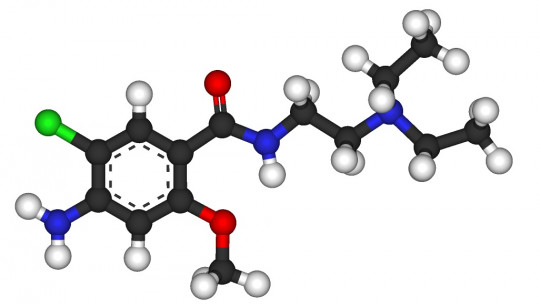
The generic name of Primperan is ‘metoclopramide’. Other less common trade names include Digespar, Clopan, Metoclox, Bitecain, Aeroflat, Novomit and Rilaquin.
The main effect of metoclopramide is antiemetic : acts as an antagonist of dopamine D2 receptors and serotonergic 5-HT3 receptors, reducing the likelihood that the user will vomit.
Furthermore, the Primperan relaxes the digestive tract , increases the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter and expands gastric contractions. For this reason, it is classified within the group of prokinetic medications, which facilitate intestinal transit.
Metoclopramide is administered orally. Its effects last approximately 6 hours, and its maximum potency occurs between half an hour and two hours after taking it.
What is Primperan used for?
Metoclopramide is often used to treat any type of nausea; However, in recent years scientific studies have specified the main indications of this medicine
1. Nausea induced by chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Primperan is usually prescribed to prevent the onset or reduce the intensity of nausea and vomiting that occur during chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments for cancer.
The use of antiemetic medications also serves to prevent the development of anticipatory nausea and vomiting , which take place when the body associates the therapy with the appearance of these symptoms. It may also happen that nausea is caused by the smell or taste of foods consumed after these treatments.
2. Postoperative treatments
Metoclopramide is indicated in people who experience nausea and vomiting as a result of surgical operations It is also used to treat the decrease in the speed of intestinal transit that occurs after some interventions, especially in the digestive system.
3. Vomiting caused by migraine
Nausea and vomiting induced by acute migraine They are frequently treated with Primperan. It is also usually combined with migraine analgesic medications such as paracetamol because metoclopramide facilitates its absorption, increasing its effectiveness.
If it is used to treat migraines, it is advisable to take Primperan in small doses since increasing them does not enhance the effects but does increase the likelihood of developing side effects, especially drowsiness and akathisia (physical restlessness).
4. Digestive and stomach disorders
Primperan can be effective to relieve symptoms of various gastrointestinal disorders Particularly noteworthy is chronic heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux, a disease in which fluid from the stomach rises into the esophagus, irritating it and causing symptoms such as cough and difficulty swallowing.
Also used to treat gastroparesis , that is, the decrease in the ability to empty the stomach. Specifically, it seems useful for diabetic gastroparesis; In this disorder, the high glucose levels typical of diabetes damage the nerves of the stomach and cause it to empty more slowly.
When using Primperan to treat digestive problems, extreme caution should be taken due to the possible side effects of continued consumption.
Side and adverse effects
The greatest risk of taking Primperan is the development of dyskinesia a disorder in which involuntary movements of the facial muscles occur, such as chewing, clenching the lips, wrinkling the eyebrows, or blinking.
It is not recommended to take metoclopramide for more than three months because the longer it is consumed, the more likely it is that dyskinesia will occur and that it will persist after stopping consumption; This phenomenon is known as ‘tardive dyskinesia’.
There is also a risk of agranulocytosis, a disorder consisting of a severe reduction in the number of white blood cells, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome which includes fever, delirium, and respiratory, circulatory, and digestive disorders.
In addition to the above, serious adverse effects of Primperan include depression, agitation or akathisia, heart rhythm disturbances, muscle stiffness, and vision problems. It is recommended to consult a doctor if these symptoms appear.
Among the most common and benign side effects we find fatigue, drowsiness, weakness, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, constipation, frequent urination, breast growth, decreased sexual function and disappearance of menstruation.
Contraindications and warnings
The likelihood of adverse effects occurring is greater in children. Therefore, it is the habitual use of Primperan in children is especially discouraged , reducing its applications in these cases to postoperative treatments and chemotherapy. Under no circumstances should metoclopramide be administered to children under one year of age.
The First may worsen symptoms of Parkinson’s disease , since it has an antidopamine effect and the symptoms of this disorder are due to low levels of dopamine. Something similar happens with depression, in which the function of this neurotransmitter is also altered.
People diagnosed with restless legs syndrome, hyperprolactinemia, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder are also not recommended to take Primperan.
Metoclopramide interacts with a number of medications, including sedatives, insulin, aspirin, antihistamines, levodopa, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and antipsychotics such as haloperidol.
Taking Primperan during pregnancy It seems quite safe, except in the last trimester, when the risk of extrapyramidal syndrome in the baby increases. Metoclopramide is excreted in breast milk, so it should not be taken during breast-feeding.