The brain is one of the most important organs for most living beings , since it is responsible for allowing the different systems to function and coordinate them with each other in order to achieve survival and adaptation to the environment. This organ has been studied for a long time, each of its nooks and crannies having been explored and analyzed countless times.
But although some might think that being something so analyzed, little can be discovered anymore, the truth is that there is still a lot we don’t know about it. In fact, even today, surprising discoveries continue to be made regarding the king organ that allow us to explore and understand to a greater extent how the brain works and how it is capable of generating so much variability in behaviors and skills.
An example of this occurred this year, in which A new type of nerve cell has been discovered: rose hip neurons of which we are going to talk briefly throughout this article.
What are rose hip neurons?
They are called rose hip neurons, rose hip neurons or rosehip neurons (their original name in English), a new type of neurons that has been recently found by an international team made up of experts from the University of Szeged and the Allen Institute for Brain Science
The discovery was reported and published this month of August, and was made accidentally while the brain tissues of two deceased subjects who had donated their bodies to science were being analyzed. Both centers discovered the presence of this type of neurons, later collaborating to study it: while the Hungarians analyzed their shape and properties, the Americans did the same with their genetics.
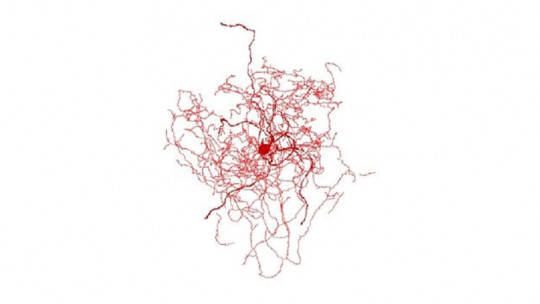
Rose hip neurons are a type of neuron that has been found in the first layer of the neocortex, in its most superficial area, and whose name comes mainly from its morphology (since it is reminiscent of said plant). They are characterized by being relatively small and having a large number of highly branched dendrites, although these branches are compacted. They also have axonal buttons shaped like a rosehip bulb. At the moment they have been found in the sensory cortex and they are relatively uncommon, making up only about 10% of layer I of the neocortex.
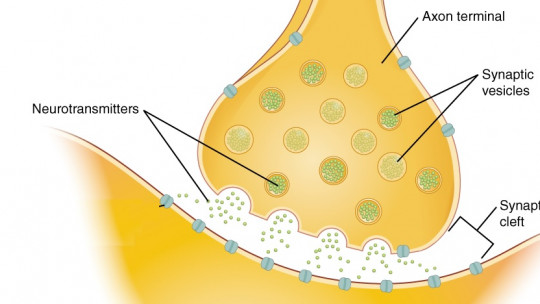
They are interneurons that have very specific connections with neurons located in the third layer of the cortex, and specifically it has been seen that they make a connection with the pyramidal cells. Furthermore, its connection is very precise, connecting only in specific parts of the pyramidal neurons. Likewise, it has been seen that they have an inhibitory behavior, being GABAergic neurons that probably control the transmission of information in a very specific way. At a genetic level, it has been observed that they have a genetic profile that has so far only been found in humans and that allows the activation of a series of very specific genes.
Its duties?
The discovery of rosehip neurons is extremely recent, and their exact function is not yet known. However, in the absence of further research, due to the areas in which they have been found and the connections they make with other neurons, it is possible to speculate and hypothesize about some possible functions
For example, the fact that their action is inhibitory and that they are GABAergic may suggest that they have the mission of very precisely controlling information, potentially generating greater control of the transmission of information in such a way that the unnecessary signs. The fact that they appear in the most external and phylogenetically most novel part of the brain may be linked to elements such as consciousness, higher cognitive functions or the precise processing of sensory information.
Only in humans?
One of the most surprising aspects of this type of neuron is the fact that its discovery has only occurred in human beings, not having them, for example, in the mouse samples that have been studied. This could be indicating the existence of a distinctive type of nerve cell in humans, something that according to experts could help explain the existence of cognitive differences between us and other animal species.
However, it must be taken into account that The fact that its existence is not documented in other beings does not imply that it does not exist , which may be because it has simply not yet been analyzed or discovered in them. After all, rose hip neurons have just been discovered in people: it would not be crazy if they had not been observed or had been overlooked in other species. It would be useful to assess, for example, whether animals with intelligent behaviors such as apes or dolphins possess them.
Future research avenues
The discovery of these neurons has implications of great relevance for humans, and It can help us explain aspects of our psyche that we still do not know
For example, the study of the brains of people with different neurological and psychiatric diseases is proposed in order to assess whether rose hip neurons are present in them or could have some type of alteration. Other possible avenues of research would be to explore whether there is some type of relationship between rosehip neurons and self-awareness, metacognition or higher mental abilities.