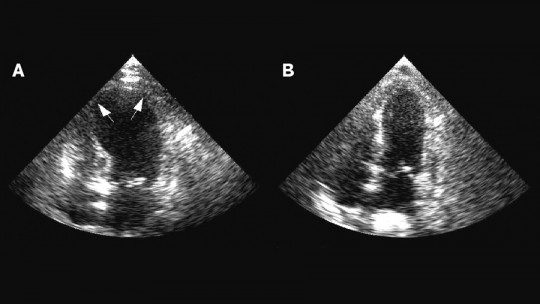
Alterations in the rhythm and frequency with which the heart pumps blood, whether due to excess, deficiency or irregularity, are known as arrhythmias. Although in many cases these abnormalities are not serious or produce symptoms, in others they increase the risk of cardiac problems such as heart attacks or sudden stops.
In this article we will detail What types of arrhythmia exist and what are the causes, symptoms and severity from each of them. It is worth keeping in mind that some types of arrhythmia can pose a health risk even when they do not produce symptoms.
What are arrhythmias?
“Arrhythmia” is the name given to heart rhythm and rate disorders These alterations may consist of an increase, decrease or irregularity in the speed of the heartbeat.
We speak of tachycardia when the heart rhythm and/or frequency increases significantly (more than 100 beats per minute in adults), while if a slowdown occurs (less than 60 beats per minute) we will be dealing with a case of bradycardia.
Its severity varies: while some arrhythmias are harmless, others can be a symptom of larger circulatory problems or even pose a short-term health risk, increasing the probability of suffer heart attacks or cardiac arrests
If the problems are severe, treatment for arrhythmias usually consists of anticoagulant or beta-blocking medications, cardiac surgery, or, in cases of bradycardia, the implantation of a pacemaker. Each of the different types of arrhythmia is treated differently, since the alterations can be opposite to each other.
Causes of these alterations
Arrhythmias are due to alterations in the electrical impulses of the heart. These abnormalities can be caused by the appearance of supplementary electrical signals, the blockage or delay of electrical conduction, or the propagation of these impulses through inappropriate pathways.
Although they can occur at any age, arrhythmias are more common in elderly people In many cases they are influenced by congenital problems in the morphology of the heart or diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism or heart failure.
The most common causes of tachycardia They are the consumption and abuse of medications and stimulant substances, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, cocaine, alcohol and caffeine. Continued stress also favors the appearance of tachycardias. As for bradycardia, it usually occurs as a consequence of atrioventricular or heart blocks.
Symptoms and signs
In many cases, arrhythmias do not produce detectable symptoms or signs, beyond the alteration in heart rhythm or rate. Even asymptomatic arrhythmias can predispose to the appearance of heart problems and accidents, for example through the formation of clots that make it difficult to transport blood to the heart.
People with arrhythmia often notice palpitations or pauses between each heartbeat. These may be more or less frequent and occur continuously or intermittently.
In more severe cases of arrhythmia, there may be symptoms such as fainting or syncope , difficulties breathing, sweating, paleness, feelings of dizziness and lightheadedness or pain in the chest. Likewise, the more severe the arrhythmia, the greater the probability of cardiac arrest, heart attack or sudden death.
Types of arrhythmia and their severity
There are four main types of arrhythmia Each of them is made up of a series of alterations of varying severity.
1. Extrasystoles
Extrasystoles consist of extra beats arising from electrical impulses that propagate inappropriately to the entire heart. Is about premature ventricular contractions followed by a compensatory pause
This type of arrhythmia is the most common of all and is not usually dangerous, so it generally does not require treatment. Normally extrasystoles are asymptomatic, although people who suffer from them may notice agitation in the chest or the sensation that the heart is skipping some beats.
2. Supraventricular arrhythmias
This type of arrhythmia is characterized by the appearance of tachycardia in the atria of the heart or in the atrioventricular node, which, as its name indicates, is located between the ventricles and the atria.
Among supraventricular arrhythmias, the most common subtype is atrial fibrillations , rapid and irregular contractions to which severe severity is attributed since they indicate that the heart is not pumping blood correctly. They predispose to the appearance of episodes of heart failure and strokes.
3. Ventricular arrhythmias
Ventricular arrhythmias cause approximately 80% of all deaths from sudden heart failure so they are considered a severe form of this disorder and usually warrant medical intervention, especially when the episodes last for a long time.
Among the factors that cause the appearance of ventricular arrhythmias are the presence of heart disease, the weakening of your muscles and the fact that you have previously suffered heart attacks.
4. Bradyarrhythmias
These arrhythmias consist of bradycardias, that is, a slowing of the heart rate or rhythm. When they are intense, blood does not reach the brain in the necessary quantity, so it can cause dizziness and even syncope. In general we can say that its severity is less than that of ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias
Some of the most common causes of bradyarrhythmia are aging, hypothyroidism, heart attacks or the use of drugs such as beta blockers. However, some people, especially if they are in good physical shape, usually have a heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute; In these cases bradycardia is not a problem.