Warts are defined as skin growths that are usually round We all know this description widespread in the general population, since it is enough to pay attention to a specific area of our body to discover them. What not all people know is that these are skin lesions of viral origin.
That’s right, warts hold many more secrets than we might initially believe: they are infections of the skin and/or mucous membranes caused by the Papillomaviridae family of viruses, better known as human papillomaviruses (HPV).
There are more than 100 types of HPV, of which at least 14 are considered oncogenic (high-risk). This is not anecdotal data, since subtypes 16 and 18 are responsible for more than 70% of cervical cancer cases. Furthermore, more than 99% of cases of this type of cancer are correlated with genital HPV infection. Who would have thought that a lesion as harmless as a wart and such a lethal cancer would share a causal agent from the same family?
If you want to know more about types of warts its global impact, the process that underlies its formation and many other questions, continue reading.
Types of warts: a world beyond the pimple
Warts are lesions that have a variable and excrescent shape, usually with a globular shape They occur in different areas of the skin, so we will distinguish the type of wart according to its location on the patient’s body. The National Library of Medicine of the United States collects its classification :
At this point, it is necessary to clarify that We are dealing with benign cell proliferations, that is, non-cancerous They are a very common reason for visiting the doctor, since it is estimated that 0.8-22% of the adolescent population may experience them. Additionally, it is estimated that 10% of people on Earth have warts at some point in their lives. Below, we develop the most important types of warts one by one.
Of course, before doing so we must make a clarification. The types of human papillomaviruses are classified according to their differences in the viral DNA sequence and not according to their capsid-forming proteins (so we do not talk about serotypes). Therefore, we will use a nomenclature of “HPV X” to refer to each variant (for example HPV 16 or HPV 66), but we must not forget that we are always dealing with the same family of pathogens.
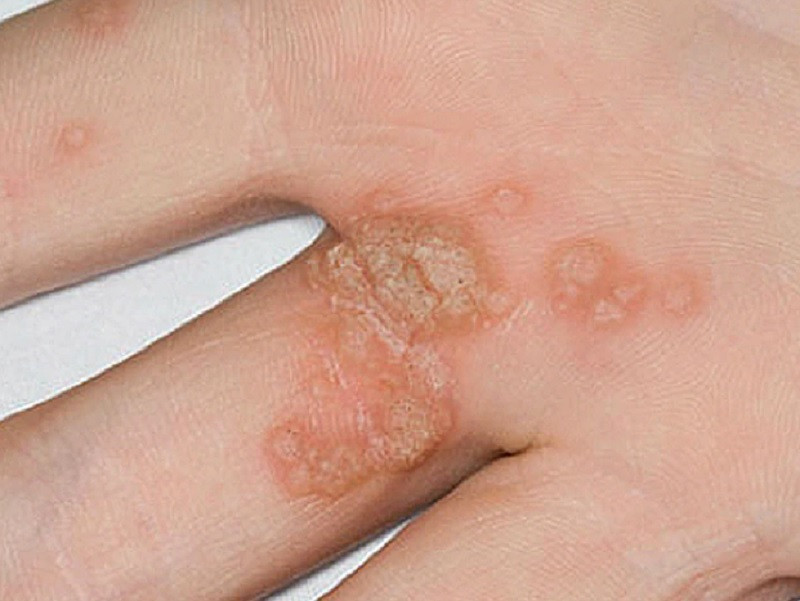
1. Common warts
Also known as verrucae vulgaris, These lesions are related to HPV types 2 and 4 infection , followed by other variants depending on the patient’s degree of immunosuppression. They are rounded papules with sharp edges, a rough surface and a grayish color. As we have already said before, they can appear in any area, but the skin area of the hands is usually their favorite place.
They usually present asymptomatically, as they do not usually cause pain , although sometimes they do cause discomfort in the patient if they are located in areas subject to weight forces (for example, in the lower part of the feet). Little more needs to be said, except that the appearance of multiple or large lesions is usually related to patients with a certain degree of immunodeficiency (for example, organ transplants and other pathologies).
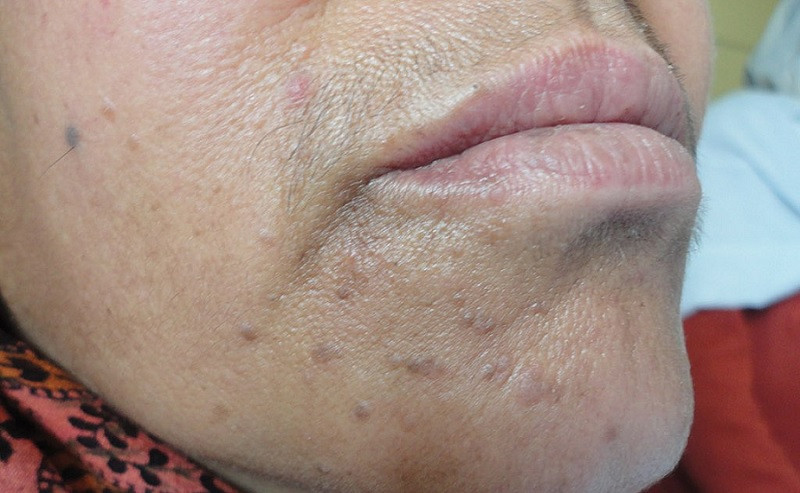
2. Flat warts
This somewhat less well-known variant of warty skin lesion is caused by HPV types 3 and 10, in addition to occasional appearances by HPVs 26, 29 and 41. They are soft, pink warts with a slightly scaly surface
Its location is usually the face, the anterior area of the legs and in scratching areas. For this reason, its nature is “autoinoculative”, that is, through physical contact with a sample infected by the virus.
Professional sources emphasize that, although they are harmless lesions that do not generate any symptoms, their treatment and removal is complex.
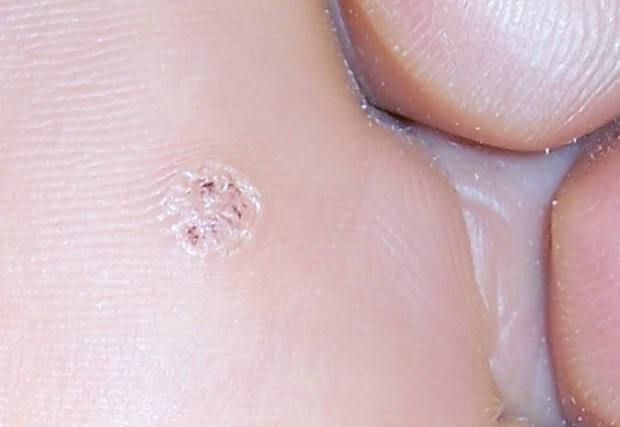
3. Palmoplantar warts
They are mainly caused by HPV type 1, followed by variants 2, 3, 4, 27 and 57. These are endophytic (i.e. growing inward) papules of a painful nature As their name indicates, they occur on the soles of the feet, so their shape is flattened by the weight of the body and they are surrounded by cornified epithelium.
Unfortunately, this variant can be very annoying for the patient, since tasks such as standing or walking can be made difficult by the appearance of these warts.
4. Genital warts
Be careful, we are entering swampy terrain. Just as the symptoms in the types of warts previously described ranged from harmless to slightly annoying, genital warts are a different matter. As we mentioned at the beginning, HPV types 16 and 18 are considered oncogenic, since cause more than 70% of cervical cancer cases in women
We go further, because in 2012 the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated a total of 528,000 new cases and 266,000 deaths from this worrying type of cancer. HPV is the cause of 12% of all female cancers in regions of the Global South. As if this were not enough, studies link these types of HPV with cancers of the vulva, penis, vagina and anus.
In any case, previously cited sources state that the majority of HPV infections of a genital nature are not very problematic, since In 90% of cases, they usually disappear on their own in less than two years without associated symptoms It is also worth noting that there are other HPV genital warts with a low tendency to form carcinogenic processes, such as types 6 and 11.
Even so, a persistent infection with the oncogenic HPVs mentioned above can cause the dreaded uterine cancer. Luckily, there are two vaccines (one bivalent and one tetravalent) that protect the general population against this type of pathogenic infection. This treatment appears in the vaccination schedules of many countries among boys and girls aged 9-14 years, before they begin to practice sexual activities (the method of contagion of this genital virus).
5. Other types and considerations
Although we have left out the types of mosaic, filiform and periungual warts, we have seen it as especially important to focus on the most common ones and the genital variant, since the rest have an anecdotal nature of moderate epidemiological interest.
If we want to make something clear, it is the multifaceted nature of human papillomaviruses, since according to their differences in the DNA sequence that makes them up , can cause disasters as astronomical as uterine cancer or a simple skin lesion without major importance. Although it may be a trivial issue, it is also important to note that these clinical manifestations occur twice as often in people of white ethnicity, and that the proportion of infection between men and women does not present significant differences.
Summary
As we have seen, warts are skin lesions that contain a much more complex world than one might initially expect.
Human papillomavirus types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 66 are carcinogenic to humans, while many others present with skin lesions that are relatively harmless to humans. the Porter. Finally, it is necessary to note that The prevalent HPV genotypes worldwide are: 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
If we want to make something clear with this numerical conglomerate, it is the following: the human papillomavirus family can present anything from a small skin wart to cervical cancer. We do not want to scare readers, but rather report the variation and epidemiological interest of this family of viruses.