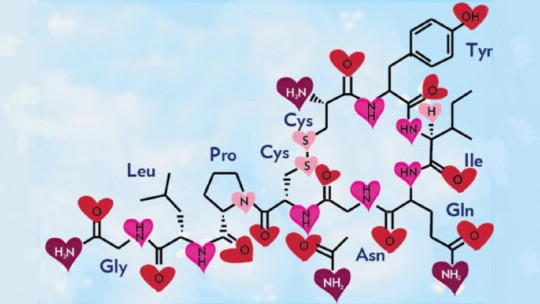
The oxytocin It is one of those substances that make the areas of study of neuroscience and biology more interesting.
The reason is that oxytocin is closely related to emotional ties of all kinds, both those that are as strong as those experienced by couples of lovers and the more diffuse ones, such as those that unite a person with their community of friends and neighbors. .
Oxytocin is, therefore, a small piece of body chemistry that allows us to scientifically explain sensations as intense and inexplicable as those related to love. This is what makes many people try to understand how it works to get an idea about the nature of what they feel when they see a certain person, when they hug someone, or when they kiss.
What is oxytocin?
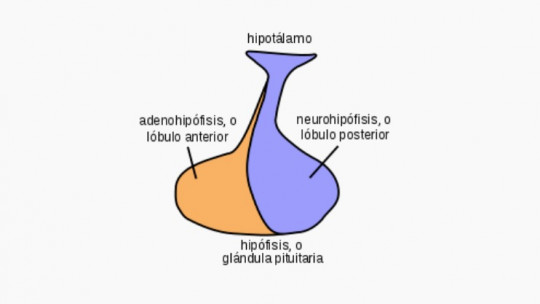
But let’s start with the basics. What is oxytocin? It is basically a substance produced by our own body, specifically, in a structure of the brain called the hypothalamus and in other organs distributed throughout the body. In terms of its function, oxytocin is tremendously versatile, and can act as a hormone and as a neurotransmitter.
As a hormone, travels through the blood to reach different tissues and organs of the human body and cause them to react in a certain way following protocols designed by thousands of years of evolution and that have to do with our way of adjusting to different situations in the best possible way.
As a neurotransmitter, oxytocin travels between the small spaces in which communication between neurons is established (the so-called synaptic spaces) and therefore plays a role in the transmission of electrical signals throughout the nervous system including the brain.
Functions of this hormone
However, one of its most significant specific functions has to do with love and affection. Oxytocin participates in this aspect of our life as a hormone and also as a neurotransmitter.
1. Linked to love
It is frequently said that Oxytocin is the substance responsible for the existence of love This is still a reductionist and somewhat risky conclusion, taking into account that there is no single conception of what love is and, in any case, many other substances intervene in the subjective experience related to affection and falling in love. Oxytocin, as with all neurotransmitters, never works alone: it is always embedded in a biochemical puzzle that shapes our mind and our actions.
However, it is true that there are some patterns in which the relationship between oxytocin and that whole set of experiences and processes that have to do with love and affection can be seen.
For example, Oxytocin levels increase when familiar faces have to be recognized They also increase when looking into the eyes of loved ones, have a role in remembering members of one’s own group, and are generally secreted in relatively large quantities in situations related to love and attachment. When we experience the sensation of sharing an intimate relationship with another person and when we feel that we are in an environment of trust, more oxytocin is secreted, as explained in the article on the chemistry of love.
In fact, it has been seen that people with chronic depression who are given an extra dose of oxytocin tend to pay more attention to happy faces than to sad ones.
2. Regulator of childbirth and motherhood
Oxytocin intervenes in other more varied processes. Etymologically, the word “oxytocin” means “rapid birth” in Greek. This is because, as a hormone, Oxytocin plays a very important role in childbirth and, by extension, in breastfeeding two fundamental processes in motherhood, as confirmed by the physiologist Henry Dale, who named this substance.
Specifically, oxytocin causes certain muscle fibers in the uterus to remain contracted during childbirth , and is also responsible for contractions occurring before birth. In addition, oxytocin has certain mechanical effects on the breasts, causing them to eject breast milk.
3. The role of this hormone in sexuality
During sexual intercourse, oxytocin levels in the blood are usually significantly higher than normal This reinforces the hypothesis that this hormone has an important role in the chemical and mechanical processes involved in sexuality.
It has been proven, for example, that oxytocin intervenes in the appearance of vaginal contractions that make it easier for the sperm to reach the egg. In the case of men, it produces contractions in the prostate and seminal vesicles. Furthermore, in both men and women Blood oxytocin levels peak during orgasm
4. Creating social links
As we have seen, Oxytocin is strongly associated with the generation of emotional bonds and not only those related to motherhood.
This is not coincidental. The fact of being able to count on the help and support of other people is one of the great evolutionary advantages that our species has had, and that is why it can be said that Oxytocin is part of that social glue that has benefited us so much If the fact of coming into contact with a person makes us secrete more oxytocin, in the long run we enter into a chemical and relational dynamic in which personal ties are very strong. In this way, the bond becomes very resistant and remains over time.