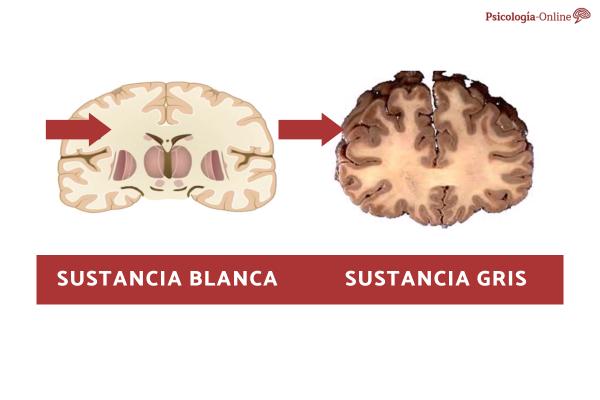
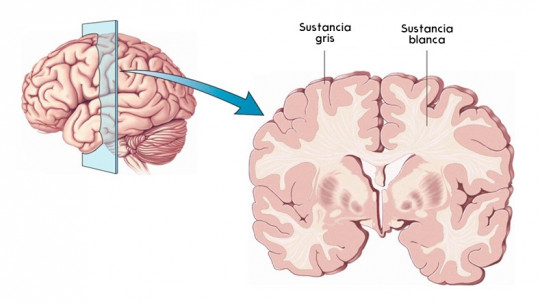
The human brain is a complex structure. If we look at it from the outside, we see a gelatinous mass of an approximately grayish color, with numerous protuberances, grooves and convolutions that cover its surface. Inside, however, a series of structures of a more whitish color can be seen.
This change in color is not accidental: the neurons that make up the brain have different parts with different functions, having delimited the existence of two types of matter or substances throughout the entire nervous system: the gray matter, in which we mainly find somas or nuclei of neurons, and the white matter, also called white matter
The white matter
The white matter is that part of the nervous system made up mainly of neuron axons, that is, the part of the neurons responsible for transmitting the information processed by the soma to the rest of the system. Although gray matter (also called gray matter) is especially visible in the cerebral cortex and inside the spinal cord, White matter can be found more easily in the internal structures of the brain and in the outermost part of the spinal cord
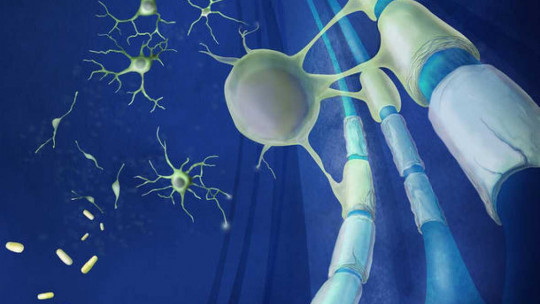
The whitish color of this substance is due to the presence of myelin, a substance that covers the axons of most neurons. The main function of this myelin is to accelerate the transmission of information This acceleration is due to the fact that, thanks to myelin, the information does not have to pass in a straight and continuous way through the axon, but rather it is done through small jumps between the myelin sheaths (this type is called saltatory transmission). Communication).
Basic functions
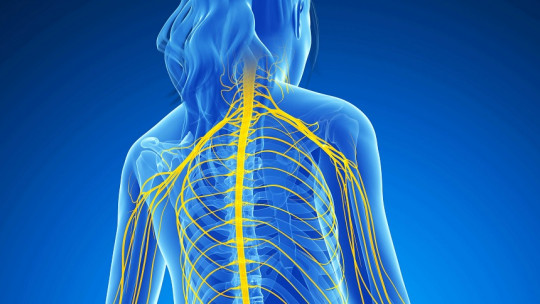
The main function of white matter is the correct transmission of brain information This substance has a great implication in allowing humans to transfer the electrochemical pulses emitted by the brain to the rest of the body. In this way we can consider that it coordinates communication between the different systems of the human body, both inside and outside the brain. Thanks to it, distant parts of the nervous system can maintain the contact necessary to work together.
That is why where there is white matter, the axons of neurons especially predominate, which means that These areas of the brain that are white are, in essence, neuronal highways communication areas between parts of the brain.
Other recently discovered features
Traditionally, it has been assumed that what we have seen is the main function of the white matter, believing it to be a passive element that was limited to transferring orders from the nucleus of the neuron to other cells. However, more recent research indicates that the white matter, apart from the mere transmission of information, It is related to different cognitive and emotional elements
This is because the connection and speed offered by the substance allows the construction of neural networks that can govern different processes. Specifically, it greatly affects memory and learning, as well as the management of cognitive resources and executive functions. In this way, it has been indicated that the white matter greatly affects the development and use of intelligence
Structure and internal configuration
As we have indicated, the white matter is predominantly made up of myelinated axons, which are the part of the neuron responsible for projecting the nervous impulse to relatively distant areas, with maximum speed and efficiency. This does not mean that somas or even axons without myelin cannot be found, but their proportion is much lower than that of the gray matter, which produces the visual effect that white predominates in those regions.
Apart from these components, It also contains a high number of glial cells, structures that support and maintain neurons Myelin is not the only substance associated with these glial cells, there is a wide variety of these that serve to keep neurons functioning correctly.
The brain tracts
Both inside and outside the central nervous system, white matter It is organized in the form of bundles of nerve fibers The so-called projection nerve tracts or fibers send the information processed by the gray matter to the different body regions located outside the brain. A second type of white matter fibers are association fibers that connect different brain regions of the same hemisphere The third and last type corresponds to the interhemispheric commissures, which connect structures from different hemispheres.
Within the brain there are a large number of structures made up mainly of white matter. One of the most visible and notable is the corpus callosum, one of the interhemispheric commissures, of great importance that unites the two cerebral hemispheres and transmits information between them.
When the white matter fails
As we already know, there are numerous disorders caused by damage to the structures of the brain, of a neurological nature. Taking into account that processing speed is largely due to the presence of myelin and the need for information to travel effectively and efficiently in order to coordinate our actions, The presence of damage to the white matter can cause disorders such as the following: Tiredness, psychomotor slowness, lack of coordination and muscle weakness, blurred vision, difficulty remembering, deficits in executive functions and intellectual abilities are some of the frequent symptoms of poor functioning of the white matter.
Some of the disorders that affect or are affected by the white matter are multiple sclerosis (in which an inflammation of the white matter occurs that produces demyelination of the neurons), Alzheimer’s and other dementias, ADHD (a smaller amount of white matter has been observed in subjects with this disorder) or dyslexia ( difficulties being linked to processing speed).