What is known as syndrome Wolf-Hirschhorn, also called Pitt syndrome is a rare medical condition caused by genetics that produces a wide variety of both physical and psychological symptoms.
In this article we will review the basic information of what is known about this genetic disease, as well as the type of treatments that are normally recommended in these cases.
What is Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome?
Pitt syndrome, or Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, is a serious pathology that It is expressed from birth and that it is associated with a whole set of very varied signs and symptoms.
More in detail, it is a condition that produces significant malformations in the head, as well as developmental delays
It is a rare disease, and it is estimated that it appears in approximately one in every 50,000 births, being much more common in girls than in boys. In fact, it is twice as likely to appear in girls
Symptoms
This is a list of the main symptoms associated with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.
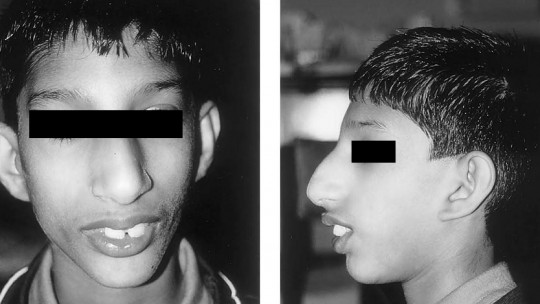
1. Typical facial phenotype
People with this genetic disease usually present characteristic facial features and relatively easy to recognize. The bridge of the nose is flat and very wide, while the forehead is high.
Furthermore, the difference between the mouth and nose is very short, the eyes are usually strikingly large, and the mouth creates an “inverted smile,” with the corners facing downward. Cleft lip also occurs more frequently than normal.
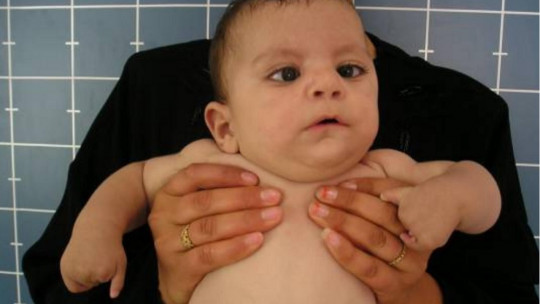
2. Microcephaly
Another characteristic symptom is microcephaly, that is, the fact that skull capacity is significantly less than expected for the person’s age range. This causes the brain to not develop as it should.
3. Intellectual disability
Both due to skull malformations and abnormal development of the nervous system, people with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome They usually experience a clear intellectual disability
4. Stunting
In general, the evolution and maturation of children’s bodies occurs very slowly in practically all aspects.
5. Seizures
Complications in the functioning of the nervous system make seizures not rare These episodes can be very dangerous.
6. Problems in speech development
In cases in which the intellectual disability is severe, the communication initiatives presented by these people are limited to a small repertoire of sounds.
Causes
Although it is a genetic disease, little is known about its specific causes (DNA and its expression being so complex), it is believed that it is triggered by loss of genetic information from a part of chromosome 4 (the short arm of this one).
It must be taken into account that the type and amount of genotype information that is lost varies depending on the case, which is why there are different degrees of severity that may occur. This explains the variability in life expectancy experienced by boys and girls born with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.
Forecast
Most fetuses or babies with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome die before birth or before reaching their first birthday, since the medical complications associated with this condition can be very severe. Especially convulsive crises, heart disease and other medical problems that frequently appear in these cases, such as kidney diseases, are very damaging.
However, there are many cases of moderate severity in which the first year of life is exceeded or childhood is even completed, reaching adolescence. In these young people, the most characteristic symptoms are those related to their cognitive abilities, which are usually less developed than expected. Despite this, physical symptoms do not completely disappear
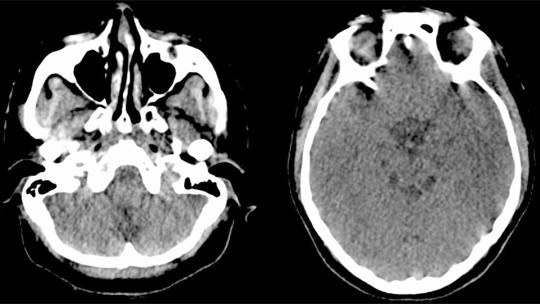
Diagnosis
The use of ultrasound makes it possible to diagnose cases of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome before birth, since it is expressed through malformations and developmental delays. However, it is also true that sometimes an incorrect diagnostic category is used, confusing diseases. After delivery, evaluation is much easier.
Treatment
Being a genetic disease, Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome has no cure, since its causes are deeply rooted in the genomic information available in each cell.
Thus, the type of medical and psychoeducational interventions are aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the pathology and to promote the autonomy of these people.
Specifically, the use of antiepileptic drugs is very common to control the appearance of seizures as much as possible, as well as surgical interventions in cases of microcephaly or to correct facial malformations.
In addition, educational support is also often widely used, especially to help with communication skills.