As a result of the increase in awareness about issues related to discrimination against women, in recent years, some theories have emerged that explain the ways in which sexist violence is carried out.
In this article we will see one of the most popular lately, the pyramid of sexist violence, sometimes called the iceberg of gender violence You will also find a summary of what it proposes and its limitations and problems.
What is the pyramid of sexist violence?
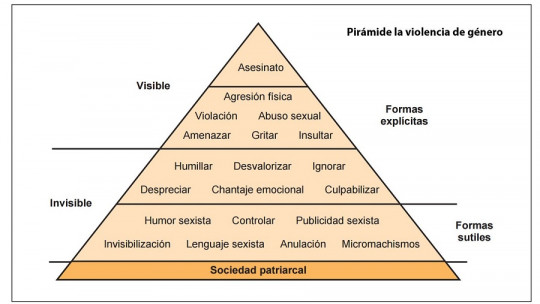
Social dynamics are always complicated to understand, and that is why, when it comes to understanding their nature, graphic representations are often used to simplify it. This is an example of how, using a triangular figure, an attempt is made to capture the different levels of aggression and violence.
The pyramid of sexist violence, sometimes simply called the pyramid of violence, is a graphic representation in which A relationship is established between extreme physical violence and other more subtle forms of violence, of a more symbolic and structural nature (that is, it involves the functioning of the entire society).
Furthermore, it is normally applied to the explanation of sexist violence against women, although sometimes it is also adapted to include violence and aggression that has to do with discrimination based on gender identity and sexual orientation, or even with racism and xenophobia. .
It is a very widespread concept based on a graph in which a triangle is seen with several staggered levels, in the lower part of which there are abstract and social phenomena that promote unequal dynamics and the imposition of power of some over others, and in the upper ones there is the definitive and concrete expression of that power over the other: physical violence and murder
The levels of violence
In summary, these are the levels of violence presented in the pyramid, ordered from bottom to top. However, as there are variants of this graphical representation, some intermediate elements may appear in different categories than those that appear here. For example, sexist jokes can appear both at the level of micro-machismo and at the level of harmful verbal expressions.
1. Attitudes and beliefs
At this level, beliefs are represented that legitimize certain forms of inequality and discrimination at the expense of the rights of some groups.
2. Microaggressions or micromachismos
These are actions (including speech) that they accept as good the situation of inferiority of women or of some historically discriminated minority
3. Harmful verbal expressions
These are verbalizations in which there is already an intention to denigrate or harm someone because of their social status. Also includes threats, defamation, insults …
4. Physical attacks
As its name indicates, this part of the violence pyramid includes attacks that compromise the physical integrity of people. It can occur through beatings and beatings, even rape.
5. Murder
In the last category, the attacked person is definitively annulled by murder; whoever perpetrates the attack kills her.
Its influences: the iceberg of the unconscious and the triangle of violence
The pyramid of sexist violence is not part of a sociological or psychological theory developed in detail by researchers, but rather is part of the memes spread on the internet and propaganda pieces to raise awareness. Therefore, is not included in a scientific theory but rather represents a theory in the broadest and most general sense of the word: explanations for a phenomenon that do not have to be empirically tested or have strong theoretical support.
Perhaps for this reason, the pyramid of sexist violence borrows explanatory elements that already existed before.
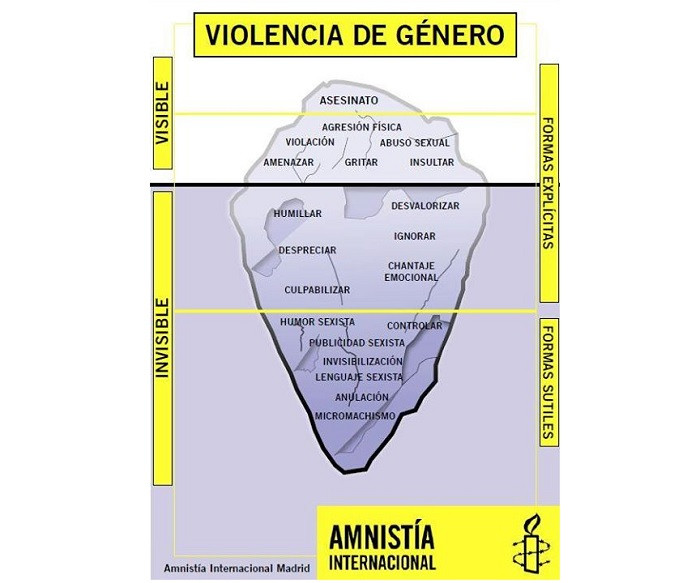
For example, Amnesty International published a variant of the pyramid titled “The iceberg of gender violence” in infographic format, which establishes a division between the visible and invisible part of this phenomenon, on the one hand, and the explicit forms and subtle ones, on the other. This representation necessarily makes one think of the psychological instances proposed by Sigmund Freud, although in this case all the elements are part of the social sphere, and not of what hypothetically occurs in the mind of each individual.
On the other hand, another influence of the pyramid of violence is the triangle of violence by sociologist Johan Galtung This researcher established a relationship between direct violence, cultural violence, and structural violence. Let’s see what each one consists of.
Direct violence
This type of violence generates objective damage to one or more individuals. That is, easily visible in specific acts, and unequivocally indicates the existence of a conflict
Cultural violence
It belongs to the psychological and attitudinal propensities of people, which are socially disseminated and reproduced in a given culture.
Structural violence
Structural violence is that which is explained not through psychological constructs, but through social, political and economic dynamics. That is to say, material provisions that generate imbalances and power asymmetries For example, a parliament in which women are practically not represented can be defined by some theorists as structural violence.
Problems and limitations
The main problem with the violence pyramid is ambiguity, since it is usually simply presented in the form of an infographic without further explanation.
This means that sometimes it can be understood as a way of classifying forms of violence, going from the most concrete to the most abstract, and other times, as a model that explains how violence increases in intensity. On this last case, a causal relationship is established from the lowest to the highest layers a relationship that does not have scientific studies to support it.
On the other hand, the definition of violence as something so diffuse that it is distributed throughout society generates many problems in delimiting the scope of these phenomena.








