The complexity of the human brain is manifested in an intricate network of neural communication. At the heart of this network lie neurotransmitters, small molecules responsible for transmitting signals between brain cells. These chemical messengers play a crucial role in regulating essential brain functions, from mood to memory. In this article, we will further explore brain neurotransmitters and their functions, shedding light on the intricate chemical ballet that underpins our mental experience.
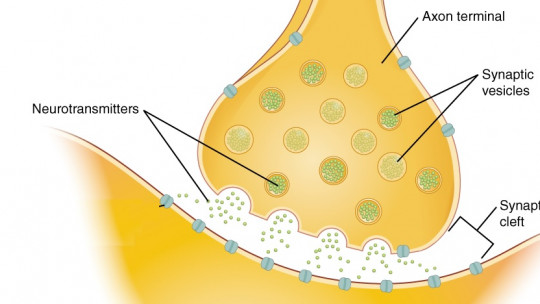
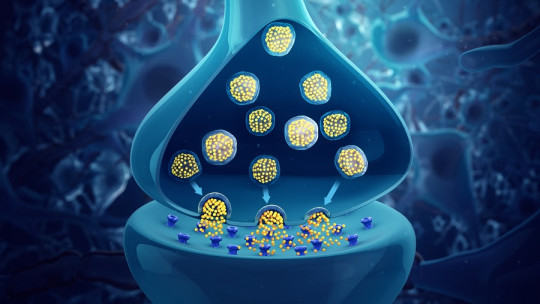
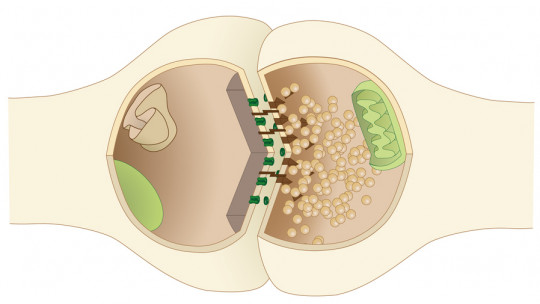
The central nervous system uses neurotransmitters to facilitate communication between neurons When a neuron, or nerve cell, receives an electrical signal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters at the synapse, the gap between neurons. This is where these tiny chemical messengers come into action, transmitting the signal from one cell to another.
The functioning of neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter can have excitatory or inhibitory effects on the recipient cell, determining whether the electrical signal is transmitted or stopped. This delicate dance of excitation and inhibition is essential for regulating neural activity and ultimately influencing our cognitive and emotional functions.
1. Dopamine: The Messenger of Pleasure and Motivation.
Dopamine, known as the “pleasure neurotransmitter,” plays a crucial role in the experience of reward and motivation. It is released in moments of pleasure and reinforces behaviors associated with gratification. Additionally, dopamine is involved in motor coordination and mood regulation. Imbalances in dopamine levels are associated with disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, among others.
2. Serotonin: The Key to Emotional Balance
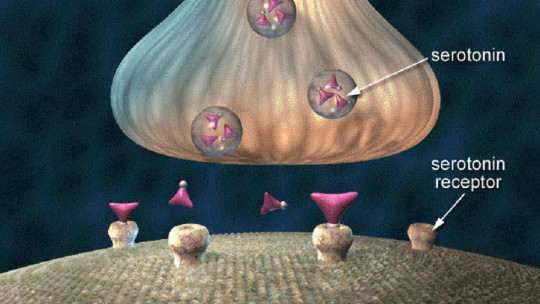
Serotonin, often called the “happiness neurotransmitter,” plays a crucial role in emotional balance. Contributes to the regulation of mood, sleep and appetite. Low levels of serotonin are linked to mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety. Common antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), seek to increase levels of this neurotransmitter to relieve symptoms.
3. Norepinephrine: Mobilizing the Body and Mind
Noradrenaline, also known as norepinephrine, plays a crucial role in the “fight or flight” response. This neurotransmitter prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate and blood pressure. In addition to its role in the stress response, norepinephrine contributes to attention and concentration. Imbalances in this system can influence disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
4. GABA: Calm in the Middle of Neuronal Chaos
Gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA, is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Its essential function is to counteract neuronal excitation, inducing relaxation and reducing brain activity. Medications that enhance the action of GABA, such as benzodiazepines, are used to treat anxiety disorders and sleep disorders.
5. Glutamate: The Driving Force of Learning and Memory
Contrary to GABA, glutamate It is the most abundant and excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain It plays a fundamental role in learning and memory by strengthening synaptic connections. However, high levels of glutamate can be toxic to neurons, and its dysfunction has been associated with neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s.
6. Endorphins: Natural Painkillers for the Body
Endogenous endorphins and morphines are neurotransmitters that act as natural analgesics and generators of well-being. They are released in response to stress and exercise, providing pain relief and a feeling of euphoria. This endorphin system has been harnessed for centuries through activities such as exercise, sports, and meditation to improve mental well-being.
Recommendation to strengthen brain chemical balance
It is important to mention some recommendations to promote healthy habits that reinforce the balanced functioning of these chemicals in the brain. Balanced diet, adequate sleep hygiene, sport and/or physical activity, brain gymnastics or cognitive training exercises, reading different types of literature, playing musical instruments, doing new activities every day, and avoiding the consumption of SPA (psychoactive substances). These are some of the experts’ recommendations to strengthen neuronal functioning.
By taking these recommendations into account, we are generating new neuronal connections that form a cognitive reserve, which is related to preserving the functioning of neurons and cognitive processes for longer.
Conclusions: The Delicate Balance of Brain Chemistry
In conclusion, neurotransmitters are the invisible architects of our mental experience. Its delicate balance is crucial for optimal brain function, and imbalances can lead to a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders. Understanding these chemical messengers not only sheds light on the complexity of the brain, but also opens new avenues for addressing and treating mental health challenges. Ultimately, the symphonic dance of neurotransmitters orchestrates the symphony of our mind, shaping who we are and how we experience, interpret, and respond to the world around us.