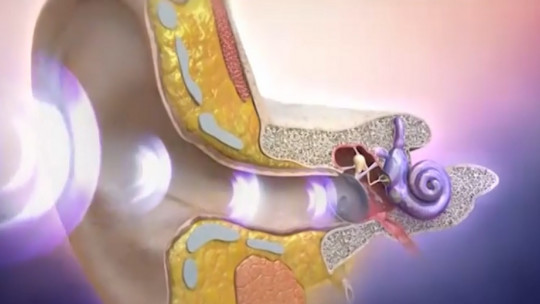
The human body is an organism made up of a large number of systems, whose coordinated management allows us to function correctly and to be able to survive and adapt to the environment. Among them we can find the nervous system, thanks to which the aforementioned coordination and management is possible, or systems as relevant as the auditory system, which in addition to the perception of sounds itself also has an effect on our orientation, balance and postural maintenance. .
However, there are various problems that can appear in these systems, which can significantly affect our quality of life. Fortunately, there are medical specialties focused on the relationship between the nervous and auditory-vestibular systems that allow us to detect and treat the different disorders and problems that may arise, highlighting the relatively recent neurotology
What is neurotology?
Neurotology or otoneurology is understood to be one of the branches of medicine which specializes in the study of the relationships between the auditory system and the nervous system. Is considered a subspecialization of the specialty of otorhinolaryngology, since we are mostly dealing with problems that originate in or affect the inner ear. However, it could also be a very specific subspecialty of neurology, since it is the connection with the nervous system that is explored.
In this way, neurotology is mainly responsible for the investigation, diagnosis and treatment of disorders in which an alteration occurs in the interaction between both systems. More specifically, the study of the human body from this subspecialization of medicine focuses on the inner ear, the vestibular system, the skull, and the facial, auditory, vestibular, vagus, spinal, lower and hypoglossal nerves, among others. .
These specialists They usually perform evaluations at both the otological and neurological levels to define and find the causes of disorders linked to dizziness, floating sensations and hearing loss. In general, these are hearing problems and problems linked to balance or body position derived from neurological impairment.
Required training
This medical field already had a powerful corpus of theoretical knowledge since the 20th century, but it was not until a few decades ago that it was established as a subspecialty. To become a neuro-otologist or otoneurologist we must have knowledge of both otorhinolaryngology and neurology.
To achieve this degree, it will first be necessary to have completed a degree in medicine, after which specialization in otorhinolaryngology is required (although the possibility of entering from neurology is not ruled out) and subsequently subspecializing in this field. We are before a prolonged and very exhaustive type of training regarding a very specific part of the body
Although it is already a subspecialization within neurotology, a more specific subbranch can also be found: otoneurosurgery. It may be necessary to perform some type of surgical intervention, requiring great preparation for it.
Common problems and illnesses
Neurotology is a medical discipline that deals with very diverse problems that can generate different levels of impairment and functional limitation to people who suffer from them, in some cases even putting their lives in danger. Within the set of these disorders, the following stand out.
1. Hearing loss and deafness
We call hearing loss a loss of hearing ability which, although not total, represents a loss of functionality and capacity of the person in their daily life. Deafness as such would be the total loss of hearing ability.
In both cases we are facing something distressing and that generates limitations in daily life, the causes of which must be carefully analyzed. An example of a disease that causes hearing loss is otosclerosis. Likewise, probably one of the best-known types of intervention that is performed by neurotology in this sense is the cochlear implant.
2. Vertigo
Probably one of the problems that neurotologists see most frequently is vertigo. The symptom is understood as such (since it is not a disorder in itself but rather it would indicate some type of affectation or alteration of the vestibular system) characterized by the presence of dizziness, balance and orientation problems discomfort, feeling that the world is rattling around us or even fainting.
3. Tinnitus and tinnitus
The frequent perception of ringing or ringing sounds coming from the ear and that tend to make hearing difficult are usually a reason for consultation, which neurotologists can examine to determine their causes.
4. Ménière’s disease
Ménière’s disease is a disorder characterized by balance and hearing problems which are caused by alterations in the labyrinth It is common for it to present with dizziness, tinnitus (continuous roaring noises) and feelings of discomfort, and the subject may become deaf. The specific causes are currently unknown and there is no cure as such, but it can be treated in such a way that it is controlled.
5. Facial paralysis
Although somewhat different from the previous ones, it is possible to find people who suffer from some type of facial paralysis associated with injury or impingement of any of the cranial nerves nerves that are also studied from neurotology.
6. Tumors
It is also possible that different types of tumors of different grades appear in the auditory pathways or in the nerves that connect them to the brain, or that some type of tumor presses on the nerve pathways in these areas. Neurotology can also help detect these neoplasms. An example is acoustic neuroma.
7. Malformations
In addition to all of the above, we can also find the presence of different types of malformation, both congenital and acquired (for example as a result of accidents).
Through neurotheology it is possible to observe the level of involvement of the auditory and vestibular systems and even correct through surgery some disorders and malformations that hinder its proper functioning.