Hypothyroidism is a disorder of the endocrine system specifically the thyroid gland, which is less active than normal, hindering the correct development of different functions of the human body.
There are multiple causes that can lead to hypothyroidism, giving rise to different symptoms and signs that you must know how to detect as soon as possible in order to go to health professionals as soon as possible.
In this article we will see what hypothyroidism is what this pathology consists of, what causes it, what risk factors increase the probability of its appearance and what treatment is the most appropriate.
What is the thyroid?
The thyroid is a gland of the endocrine system, that is, it produces hormones, specifically, thyroid hormones. It is located in the neck, just above the collarbone and is responsible for controlling many of the body’s functions such as metabolism, sexual development, growth, heart rate and even, in young children, brain development.
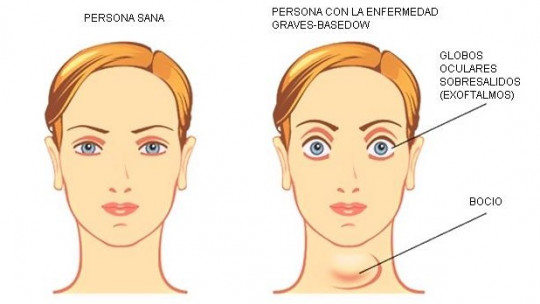
Given all the functions in which it participates, the effects that can occur if its functioning is altered are many: appearance of goiter due to an enlargement of the gland; hyperthyroidism, when more thyroid hormone is generated than necessary; hypothyroidism if less thyroid hormone is produced than the body needs; thyroid cancer; nodules when we see lumps in the thyroid and thyroiditis when the thyroid swells.
For this reason It will be necessary to evaluate and control possible deregulations to avoid alterations in the subject There are different ways to proceed depending on the impact. Let’s see what exactly hypothyroidism consists of.
What is hypothyroidism?
As we have already mentioned, hypothyroidism is a health disorder based on insufficient production of thyroid hormones, linked to a reduction in the activity of the thyroid gland
In these circumstances, the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), produced by the anterior pituitary and responsible for regulating the levels of thyroxine (a type of thyroid hormone) in the blood, begins to increase its concentration to try to make the thyroid gland increase its activity. In the case of hypothyroidism we will see how this attempt at regulation by the body does not achieve the desired effect.
Causes of hypothyroidism
There are various causes that can lead to a lower performance of the thyroid gland or a deficiency of this hormone. One of the most common is the appearance of Hashimoto’s disease which is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys the thyroid.
Other causes are: thyroiditis (which causes swelling of the thyroid gland); removal of the thyroid gland; congenital hypothyroidism, which is observed from birth; radiation treatments; thyroid cancer; the side effects of taking some medications; a deficiency of the hormone TSH; and on some less frequent occasions we can also observe a dysregulation of the iodine consumed.
Factors that increase the risk of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, as well as other conditions linked to the thyroid, It is seen more in women, especially from 50-60 years of age Frequently related to Hashimoto’s disease. You are also more likely to develop hypothyroidism if you have previously had thyroid problems or have undergone surgery or radiotherapy of this gland.
As with other pathologies, having a family history of this condition increases the risk of developing it. In addition, Being pregnant or having recently given birth also means a greater probability of developing the condition
Finally, there are some pathologies or alterations that are related to a greater risk of hypothyroidism: autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus; genetic alterations such as Turner syndrome where the lack of an X chromosome is detected in women; type 1 or insulin-dependent diabetes, related to difficulties for glucose to enter the cells or anemia due to lack of red blood cells.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
There are multiple and diverse symptoms that a subject with hypothyroidism can show; As we already know, this hormone participates in different functions, many of them essential. The development of the condition is progressive; In this way, we may not see serious problems at first, but they may lead to greater damage if not treated.
In the first stage of the pathology it is common to observe that the subject feels more tired and that his weight increases inexplicably When these symptoms begin, we may not give them importance, since we tend to link them with other causes such as leading a stressful life, which makes us feel tired, or simply age.

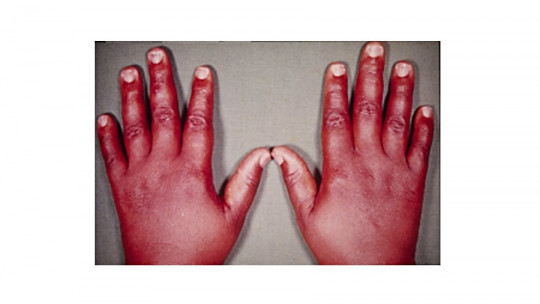
Other symptoms or signs that we can identify in patients with low thyroid activation are: increased feeling of cold, constipation, pain and stiffness in the joints and muscles, more swollen face, breathing problems when we sleep (snoring) increased blood cholesterol level, irregularities in menstruation or heavier bleeding, thinning and loss of hair, dry skin, sweating less, fertility problems in women, decreased heart rate, depression, memory problems or goiter, enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Another condition that hypothyroidism can also cause and that we must keep in mind is the alteration of the growth and development of the baby. It has been seen that mothers who do not treat their thyroid problem may have children who show delays and psychomotor problems during childhood.
How is the diagnosis of hypothyroidism made?
To make a correct diagnosis of hypothyroidism and know what the cause is to proceed with appropriate treatment; The doctor will take into account different variables. In the same way, what happens with any other pathology, First, the professional usually asks the subject different questions to find out their medical history if you have a family history of hypothyroidism, if you have had thyroid problems before or if you take any type of medication or have had any surgery.
Apart from the clinical history, it is also common to ask about the patient’s current condition, whether they notice any type of symptoms or have any sensations other than usual. For example, If you feel more tired, notice that you have gained weight or that your hair is falling out more, as we have already seen, are usually the first consequences that are detected from this affectation. In women, a sign that is also easy to identify is irregular menstruation or an increase in the amount of bleeding.
Another procedure that can help with the evaluation consists of performing a physical examination where the doctor palpates the patient’s neck, place where the thyroid gland is located. The purpose is to know the size of the gland, its consistency, the sensitivity it shows, as well as detect irregularities, asymmetries or nodules that it may present. For the examination to be correct, it is necessary to palpate gently and carefully, since if we press excessively it will be more difficult to appreciate the alterations.
Likewise, another useful medical test to contrast the information already obtained and know if the patient’s symptoms or signs are due to hypothyroidism is blood test As we already mentioned, a decrease in thyroxine (T4) produces an increase in the hormone TSH. Thus, if we detect a lower concentration of T4 or an increase in the level of TSH in the blood, it is likely due to a decrease in the activation of the gland.
We can also check the level of antibodies in the blood, specifically antithyroglobulin and antithyroid peroxidase, which are those that increase when the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
Finally, it is possible to perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland to identify any type of irregularity or a reactive iodine absorption test to check the functioning of the thyroid.
Treatment
The main treatment for hypothyroidism is take a medication that has the function of compensating for thyroid hormone deficiency According to the results obtained in the evaluation, the professional will set the dose and adjust it depending on the hormone levels observed in the following blood tests. Once the dose is established, the subject’s condition will usually be monitored with a blood test every year in case the dose needs to be changed.
Normally, the condition is chronic, requiring lifelong medication, although if the doctor’s instructions are correctly followed, the symptoms can be controlled without problem. It is especially important that we adjust and monitor the dose at the time of pregnancy, since low levels of the hormone can affect the baby. If hypothyroidism is observed in newborns, it is essential to start treatment as soon as possible to avoid problems in development.