It is already known to all that the different regions of the brain, although their functioning requires coordinated action with the rest of the brain, tend to specialize in some functions.
This article aims to show the importance of the functioning of the nucleus accumbens a part of the brain not well known by the majority of the population, but of great relevance for human beings due to its participation in the brain reward system and the integration of motivation and action.
Where is the nucleus accumbens?
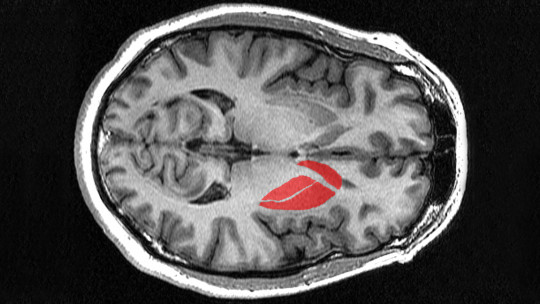
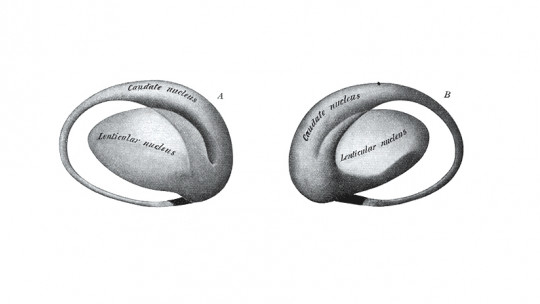
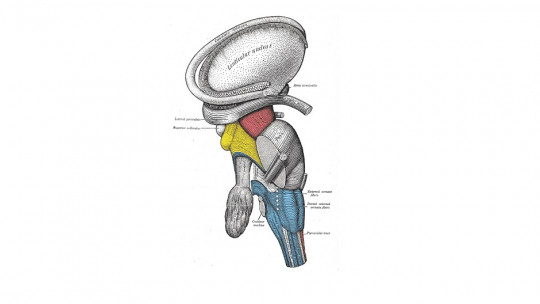
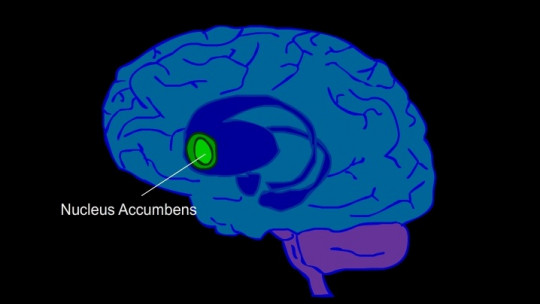
The nucleus accumbens is a subcortical brain structure, located at the point where the caudate nucleus and putamen meet the septum. This nucleus is part of the ventral area of the striatum being one of the nuclei that make up the basal ganglia.
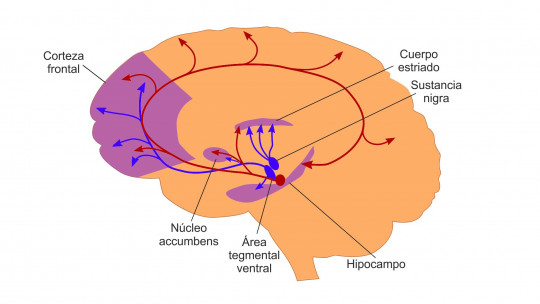
The nucleus accumbens is also part of the brain reward circuit, having a great influence when it comes to integrating cognitive, motivational and motor aspects, and being one of the main nuclei that allows will to be translated into action, allowing the performance of behaviors. pleasure seeking.
Parts of this structure
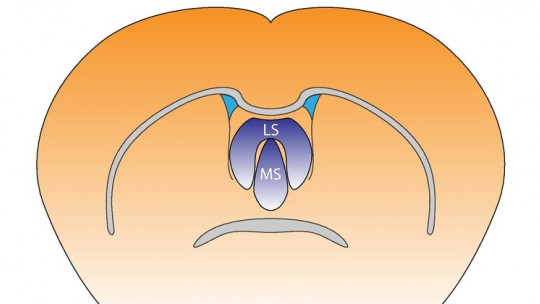
The nucleus accumbens has traditionally been divided into two sections, central zone and cortex, due to its different connections with other brain areas and its greater connection to the emotional or motor aspects.
1. Shell
This part of the nucleus accumbens is characterized by its high number of connections with the limbic system and the hippocampus, receiving both dopamine, serotonin and glutamate from various brain areas.
It is therefore the part most linked to emotions of this structure. It also has many connections coming from the front, sending the nucleus accumbens the collected information to the thalamus and receiving back to the central area of the nucleus accumbens.
2. Central zone (Core)
The central area of the nucleus accumbens has functions mainly linked to motor skills, being connected to the basal ganglia, the substantia nigra and the motor cortex. ANDThis area is activated to a large extent when performing actions with emotional meaning directed at a specific goal.
Principal functions
The location of this structure and the connections it maintains with different brain areas makes the nucleus accumbens a structure of great importance. However, to be able to see the importance of this structure and its implications, it is necessary to visualize in a more direct way what processes it participates in.
Although many of them are shared by the rest of the basal ganglia, Some of these processes in which the nucleus accumbens has a special participation are the following:
1. Emotion-motivation-action integration
One of the main functions of the nucleus accumbens is to transmit information about the subject’s motivation and translate it into a motor action in order to meet the organism’s objectives. This integration comes from its connections with both the prefrontal and the basal ganglia. Thus, it allows us to carry out instrumental behaviors, directed towards a specific goal.
In a certain sense, this function of the cerebral amygdala has to do with a very important type of memory: emotional memory. This capacity is on the border between mental processes linked to emotion and higher psychological processes, since on the one hand it works with emotions and on the other it influences decision making and the creation of concepts.
2. Influences behavioral planning
The connections of the nucleus accumbens with the frontal lobe have allowed us to see how this structure has participation in the ideation and planning of behavior being, as we have said, an important point of integration between the motivational aspects of behavior and its implementation.
3. Assessment of the situation
The participation of this structure is also given an evaluative level, at Integrate emotional information with adaptive assessment that makes the front. In this way, it is possible to associate a stimulus with a subjective evaluation through a process that also has to do with emotional memory.
4. Role in addiction
The nucleus accumbens plays an important role in the addictive process, since it is linked to reward experimentation. This brain nucleus is part of the mesolimbic pathway, forming part of the brain reward center. Specifically, it is in this area where stimulant drugs act, producing an increase in brain dopamine levels.
5. Obtaining pleasure
Although it is not the only brain structure linked to the experience of pleasure, the nucleus accumbens does maintain a close connection with its achievement. And different experiments have shown that although its inhibition does not eliminate the desire to obtain a reinforcer, it does produce a decrease or suppression of the behaviors necessary to obtain the object of desire. The observed data show that The participation of the nucleus accumbens occurs in addictive processes, as well as in food and sex
6. Learning and memory
The previous points mentioned show that the nucleus accumbens It has great relevance when establishing automation and learning of behaviors aimed at obtaining a reward. It also participates in the habituation process.
7. Aggression and risky behavior
Hyperactivity in the nucleus accumbens can cause aggressive behavior Given a very high presence of dopamine and other alterations that make behavioral inhibition difficult, it can lead to the search for personal satisfaction without assessing the risks.
In fact, studies carried out on people who have psychopathy seem to indicate that these people have, among other alterations, a severe imbalance in the nucleus accumbens, suffering from hyperreactivity to dopamine that could induce them to seek their own reward with indifference to the consequences for themselves. the others.