The human body is made up of 37 trillion cells which are the unit of life.
It is not surprising that we find great diversification among them to be able to carry out different functions, allowing them to complement each other and cover the vital needs of an organism, such as the maintenance of body structure, nutrition and respiration. It is estimated that there are about 200 types of cells that we can distinguish in the organism, some more studied than others.
Throughout this article we will talk about the main categories that group cell types according to their characteristics.
Why do these microscopic bodies matter?
Although our mental processes seem to arise from some hidden point in our head where the connection between the soul and the body is established, as the philosopher Descartes believed, the truth is that they are basically explained through the relationship between the human organism and the body. the environment in which it lives. That is why knowing the types of cells of which we are composed allows us helps us understand how we are and how we experience things.
As you can imagine, we will not talk about each of them, but we will make some general touches about some of them to get to know our body better.
Classifying cell types
Before starting, it would be ideal to group the cell types to better organize the topic. There are several criteria to distinguish different types of cells
In our case (human cells) we can classify them depending on the group of cells to which they belong, that is, in what type of tissue they can be found.
The human body is made up of four different types of tissue, thanks to which we are able to keep different environments relatively isolated from each other. What our body needs to function properly These fabric categories are as follows:
- Epithelial tissue: configures the superficial layers of the organism. In turn, it can be divided into coating and glandular.
- Conjunctive tissue: acts as a connection between tissues and makes up the structure of the body. Bone, cartilage and blood are the most specialized tissues of the connective tissue.
- Muscle tissue: as its name indicates, it is made up of the group of cells that make up the muscles.
- Nervous tissue: formed by all the elements that make up the nervous system.
1. Epithelial tissue cells
In this group we find the cells that are part of the most superficial layers of the organism. It is subdivided into two types that we will see below with their fundamental characteristics.
1.1. Covering fabric
They are the layers themselves that cover the organism.
1.2. glandular tissue
Groups of cells that share the function of generating and releasing substances.
2. Connective tissue cells
In this category we will find the types of cells that are part of the connecting and structural tissue of the body.
3. Muscle tissue cells
In this group we only find a single type of cell that structures the muscles, responsible for the mobility of the organism.
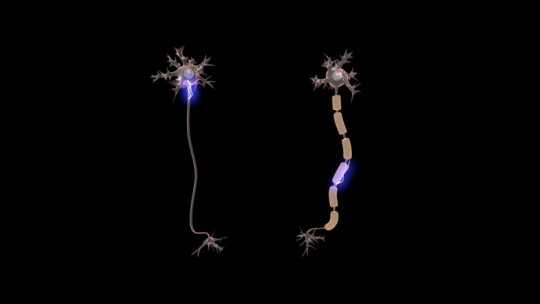
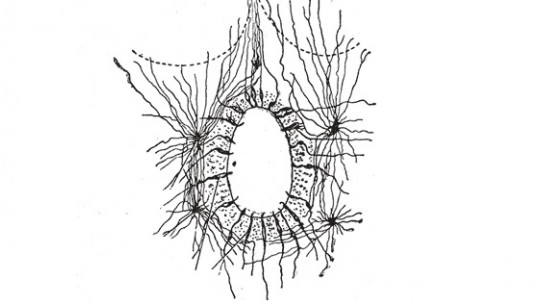
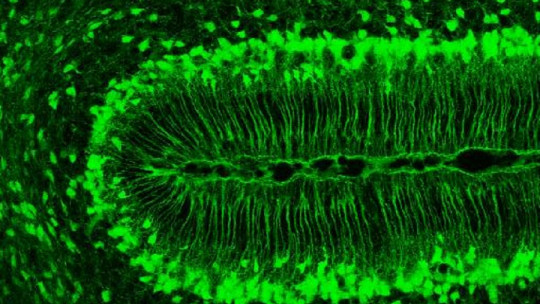
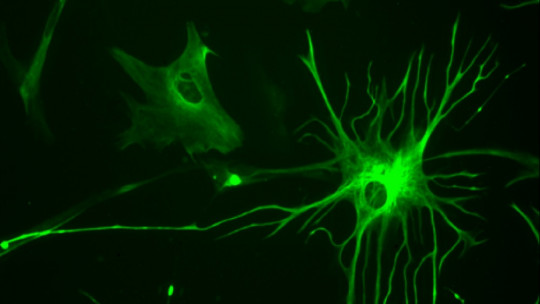
4. Nervous tissue cells
Finally, in this category are the cells that are part of the nervous system.