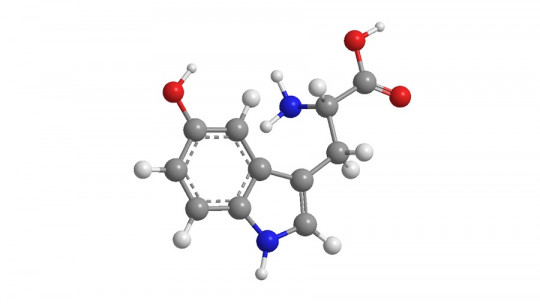
He tryptophan (L-tryptophan) is an essential amino acid found in different foods, for example, turkey. Its molecular formula is C11H12N2O2, and within the human body it fulfills many functions.
In this article We will review its characteristics, its functions and the foods that contain it
Characteristics of tryptophan
As mentioned, tryptophan is an essential amino acid. But what does this mean? Well then The body itself cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained through food Luckily, tryptophan is found in a wide variety of foods, including meats, nuts, eggs, and dairy products.
The body uses tryptophan to synthesize proteins, the B vitamin niacin and the chemicals serotonin and melatonin. However, in order to acquire serotonin thanks to niacin, it is necessary to also consume iron, riboflavin and vitamin B6.
A good dietary supplement
In recent years, This amino acid has begun to be marketed as a dietary supplement for its supposed benefits for mood In any case, regarding this type of products, it has not been shown that they significantly affect tryptophan levels in the blood. Therefore, its results are more than questioned.
However, some studies claim that tryptophan supplements could be effective as a sleep remedy and as an antidepressant. These results are associated with its role as a serotonin and melatonin synthesizer.
Excessive stimulation of serotonin on the postsynaptic 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors at the central and peripheral level can have negative consequences for the body. This is known as serotonin syndrome and can be fatal. Although this syndrome can be caused by taking medications (for example, Prozac) or the use of drugs (for example, LSD, MDMA, methylphenidate, bath salts…), it is unlikely to occur due to the consumption of tryptophan supplements. However, when combining different substances, special care must be taken.
Is it possible to consume a lot of tryptophan through food?
Tryptophan is necessary for life, but Some studies indicate that consuming too much can be counterproductive to health For example, because it causes a decrease in life expectancy, organ damage and increased insulin resistance.
Features
Next we are going to learn what the main functions of tryptophan are. This amino acid is closely linked to the proper functioning of the brain and our neurons.
1. The role of this amino acid in the brain
The blood-brain barrier determines which substances found in the blood can reach the brain. At least nine amino acids, including tryptophan, compete with each other to access the same carrier that transports them across this barrier.
Amino acids that are present in greater quantities in the blood are more likely to pass the barrier. In most foods, tryptophan is found in small quantities, so it has serious difficulties passing the blood-brain barrier. However, It is possible to increase the possibility of crossing the barrier if it is consumed together with carbohydrates The latter cause the release of insulin, which reduces the amount of other amino acids in the blood without affecting tryptophan levels.
2. The role of tryptophan in the synthesis of serotonin
Serotonin is a chemical substance with which neurons communicate, that is, a neurotransmitter. Although many think that serotonin is only found in the brain, the Central Nervous System (CNS) only contains 5% of 5-HT. It is in the small intestine where the rest is produced. This serotonin never reaches the brain, as it has other functions, such as regulating the state of contraction of the smooth muscles of blood vessels.
In the brain, serotonin is essential. Once tryptophan reaches the brain, it is converted into serotonin As a neurotransmitter, serotonin plays an important role in memory, regulating mood and appetite. Low levels of this neurotransmitter are associated with different pathologies (depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, etc.).
3. Its influence on sleep cycles
After being converted into serotonin, the body can use this chemical to produce the hormone melatonin In this sense, tryptophan helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, because melatonin regulates the biological clock. The amount of melatonin produced is determined by the light in the environment: during the day, melatonin levels decrease. However, during the night, they increase.
Melatonin supplements help improve sleep problems, such as those caused by jetlag.
4. The role of tryptophan in the production of niacin
The body can transform tryptophan into niacin, also known as vitamin B3 which is essential for converting food into energy and maintaining a healthy nervous system.
Another important vitamin, which helps convert tryptophan to serotonin, is vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 deficiency can cause confusion, depression, memory loss, a faster rate of brain degeneration, difficulty paying attention, fatigue, and insomnia.