Fat in the abdominal area is more difficult to eliminate than other fats. Let’s see why and if this can really be combated.
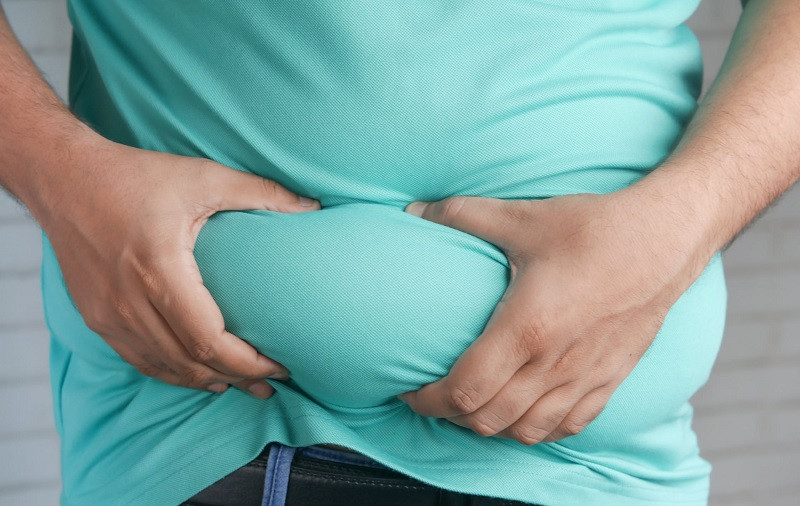
As we age, both men and women begin to accumulate fat in the abdomen. This fat, apart from causing us psychological discomfort because we do not look good, is also difficult to eliminate, which can generate frustration. Accumulated abdominal fat seems impossible to lose despite nutritional and sports efforts. But… Why does the belly resist diet and exercise? Is there an effective way to combat this fat?
In this article we will talk about fat in general and the process by which it is eliminated, explaining the reasons why it is more difficult to remove fat from the abdominal area in particular, and how we can try to lose it in a healthy way.
How does our body accumulate fat?
The first thing to explain is that when we use the word fat we are referring to the fat present in our body, since in biochemistry it is used as a general term to designate various types of lipids. Specifically, we use it to refer to acylglycerides These are molecules formed by one, two or three fatty acids linked to a glycerin molecule, forming monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides respectively.
There are cells in our body, adipocytes, which are responsible for storing fatty acids, forming adipose tissue. This process, through which we store energy, is part of metabolism. Our body breaks down what we eat into small parts to later use to rebuild cells and tissues. Through this fragmentation it obtains energy for all its processes.

The fat accumulated in adipocytes does not come directly from the fat that is ingested , but from excess energy. Our body also transforms sugars into fatty acids, therefore, even if we do not eat any fat, we can accumulate it. Fat gain is determined by the energy contribution of each food: fats provide nine calories per gram, double the contribution of carbohydrates and protein (which is four calories per gram), which is why it is important to moderate the intake. consumption of fats, but do not avoid it, since lipids are essential constituents of our cells.
Functions of fats
The first function of adipose (fat) tissue is to provide energy during fasting periods When we go long hours without eating food, adipose tissue, through lipolysis, releases fatty acids to provide energy to the rest of the body. It is thanks to the release of fatty acids that we lose weight when we are on a diet.
Adipose tissue also It has a valuable function of protection against cold and supports and protects the organs like kidneys and heart.
What is abdominal fat?
Fat can accumulate in different parts of the body and does not have the same characteristics The layer of fat that is located just under the skin is what we know as subcutaneous fat and although it poses aesthetic problems for some, it is not dangerous to health.
Visceral fat is located in the abdominal cavity and surrounds your internal organs (intestines, liver, kidneys, etc.). It presents a semi-liquid state and an excess is related to the risk of suffering from different pathologies, frequently: type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, respiratory problems and abnormal cholesterol.
Why do we accumulate abdominal fat?
As we have seen before, you have to know what type of abdominal fat we are talking about. You have to try to distinguish it, usually a little tummy, a waist circumference of less than 89 centimeters (in women) and a normal body mass index, They do not indicate any health problem and it would be subcutaneous fat Although, only a medical exam can truly determine the type of fat we are accumulating.
Regardless of their origin, there are several factors that can promote fat deposits, and the difficulty in combating it. Whatever its origin, there are several factors that intervene in its presence and the difficulty of getting rid of it.
1. Hormonal imbalance
Hormones have been pointed out by different specialists as the main responsible for abdominal fat
For men, as the years go by, their testosterone levels decrease. Testosterone, in addition to increasing metabolism thanks to the maintenance of muscle mass and increased energy, also slows down the expansion of adipocytes. Therefore, it is easier over the years to gain volume in the abdominal area.
Young women, for reasons related to motherhood, accumulate fat in the hips and thighs But with the arrival of menopause and premenopause, eggs stop being released and the body produces fewer female hormones. Changes in estrogen levels are responsible for fat redistribution. However, this redistribution is intended to protect the loss of bone density. Although for some it is a problem, it is nature’s way of protecting us.
Sagging is characteristic of aging by decreasing the production of different skin proteins, such as collagen and elastin. Flaccidity can give the sensation of abdominal overweight.
2. Genetic origin
Excessive insulin secretion could also produce a metabolic imbalance and promote the accumulation of fat in the abdomen. Insulin manages blood glucose levels and inhibits the lipolysis process , preventing the release of fatty acids. People who have a family history of diabetes are more likely to gain fat.
3. The diet
A high-calorie diet, rich in fat and processed foods (cookies, sugary drinks, etc.) can increase the work of the liver and directly impact the increase in abdominal fat in addition to general excess weight.
Alcohol is also associated with the risk of gaining volume in the belly. This is due to its caloric density, one glass contains approximately 240 calories, more than 10% of the daily needs of an average adult.
- You may be interested: “Eating psychology: definition and applications”
4. Stress
Cortisol is known as the wake-up hormone, but also as the stress hormone s. According to several studies, this hormone encourages fat to accumulate in the abdomen instead of being distributed throughout other areas of the body.
- Related article: “The 5 phases of stress (and how to combat them)”
How to lose abdominal fat?
To lose fat the most important thing is to eat a balanced diet. It’s not just about eating vegetables and low-calorie foods to lose weight, it’s about adapting intake to expenditure. Furthermore, it is more interesting to reduce quantities than to restrict foods such as carbohydrates, since these provide energy, and without energy we move less and as a consequence we spend less.
As for the abs, fat loss cannot be done locally But maintaining a balanced diet and working the core area can help you get a marked belly.
Visceral fat loss responds to the same strategies as subcutaneous fat.
1. Healthy diet
Increase the amount of low calorie density products, this means they provide few calories per volume. Vegetables, fruits and cereals can be your great allies. Accompanying your meals with a salad or a portion of vegetables will increase your feeling of satiety during the day and will make you eat less at each meal. But don’t just eat a salad. Proteins and carbohydrates are also essential for the functioning of your body.
2. Avoid sugary drinks
One of the easiest high-calorie-dense foods to avoid is sugary drinks, and They can be easily replaced with water or zero drinks
3. Measure portions
It is important to control what we eat, but also the quantities.
4. Perform physical activity
Moderate activity of at least half an hour a day, 5 days a week is recommended.
Studies have shown that Walking 10,000 steps or 15,000 steps a day promotes fat loss , but above all they prevent recovery after considerable weight loss. Getting a step counter and including this habit in your daily life can be a very effective strategy to gain health and fight against a sedentary lifestyle.
However, a recent study carried out by Australian researchers demonstrated one of the reasons for the accumulation of abdominal fat, apart from the genetic and age-related reasons mentioned above.
Abdominal fat becomes resistant to the release of fatty acids when practicing intermittent fasting , that is, by subjecting our body to long periods without food intake. According to this study, it seems that periods of restriction will activate a signaling pathway so that this fat becomes resistant. It would be like a message from the body to the fat saying “stay here because we are going to need you later.”
Therefore, the fasting strategy, although it may have other benefits, does not seem the most appropriate if what you want is to lose that annoying belly.