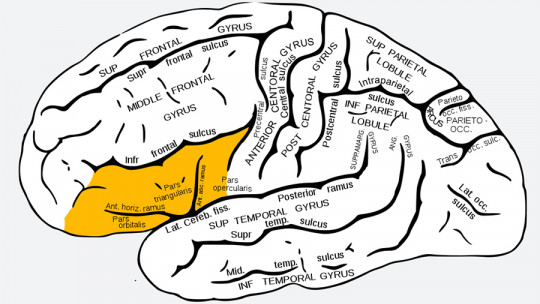
The frontal lobe, an integral part of the human brain, plays a crucial role in various cognitive and behavioral functions. Located in the anterior part of the brain, this component is essential for decision making, planning, impulse control, working memory and emotional regulation. Its proper development is essential for healthy brain functioning throughout life.
In terms of decision making, the frontal lobe coordinates the evaluation of information, allowing for informed and rational choices. Furthermore, working memory, an essential component of cognition, resides in this lobe, enabling the temporary retention of relevant information. The ability to plan and organize also finds its basis in the frontal lobe, facilitating the execution of complex tasks.
Emotional regulation is another critical function; the frontal lobe facilitates the management of emotional responses, influencing effective adaptation to challenging emotional situations. Proper development of the frontal lobe during childhood and adolescence lays the foundation for higher cognitive abilities in adulthood.
Understanding these fundamentals is essential to evaluate how social media can impact the frontal lobe, as its influence could have significant repercussions on the cognitive and emotional functions of individuals. Therefore, in this article we will focus on understanding the specific impact that social networks can have on the frontal lobe and its development.
Effects of social media on the frontal lobe
The massive influence of social media on contemporary society raises questions about its influence on the development of the frontal lobe, a key component of the human brain. Numerous studies suggest that constant exposure to digital platforms may have implications for the cognitive and emotional functions associated with this lobe.
1. Additional cognitive load
Non-stop information and overexposure to visual and auditory stimuli on social media can trigger additional cognitive load. Constant multitasking, characteristic of online interaction, can overload the frontal lobe, negatively affecting working memory and the ability to concentrate. Research indicates that reliance on social media may be associated with a decrease in sustained attention, which could compromise informed decision making.
2. Emotional control
Additionally, digital stress stemming from social comparison and pressure to maintain an online presence can negatively impact emotional control. The need for validation through likes and comments can create a dynamic that influences self-esteem and emotional well-being, areas where the frontal lobe plays a fundamental role.
3. Negative and positive balance
Although some studies warn of possible adverse effects, it is also essential to recognize that social media is not inherently harmful. They offer benefits such as facilitating communication and social connection However, it is crucial to balance these positive aspects with awareness of the potential negative impacts on frontal lobe development.
Potential benefits
Despite the potential negative effects, it is crucial to recognize the potential benefits that social media can bring to cognitive and social development, partly offsetting concerns about the frontal lobe.
1. Global connection and communication
In the social sphere, networks offer a unique platform for global connection. They facilitate interaction with people of diverse cultures and perspectives, promoting a broader understanding of the world. The ability to share experiences, ideas and knowledge can enrich the social and emotional development of individuals, fostering empathy and tolerance.
2. Creative expression and identity construction
Additionally, social media provides opportunities for creative expression and identity construction. Visual and content platforms allow users to develop artistic skills, tell stories and find like-minded communities. This creative process can have a positive impact on emotional well-being and contribute to the development of self-esteem.
3. Accessibility of information and resources
Access to instant information and educational resources through digital platforms also stands out as a significant benefit. The possibility of learning and sharing knowledge quickly and efficiently can enhance critical thinking and the acquisition of skills relevant to the digital age.
Moderating factors
The complexity of the impact of social media on frontal lobe development is influenced by various moderating factors that can modulate both the positive and negative effects of digital interaction.
1. Family context
The family context plays a crucial role. Parental guidance, open communication about responsible network use, and active supervision can mitigate potential risks. An environment that promotes offline connection and family activities can counteract digital isolation, contributing to a more balanced development of the frontal lobe.
2. Frequency and nature of interaction in networks
The frequency and nature of interaction on social networks are also determining factors Conscious use, limiting time spent on digital platforms and encouraging a variety of activities, can reduce cognitive load and promote a healthy balance.
3. Individual predisposition and personality
Individual predisposition and personal characteristics are also key factors. Emotional resilience, self-awareness, and self-regulation skills can modulate the frontal lobe response to online social pressure.
In conclusion, the impact of social media on frontal lobe development is a complex interaction of positive and negative factors. While there is concern about the associated cognitive and emotional burden, social and educational benefits are also recognized.
The key lies in conscious and balanced use, with special attention to moderating factors such as family environment, time management and individual characteristics. Addressing these considerations can lead to healthier harnessing of social media in human development.