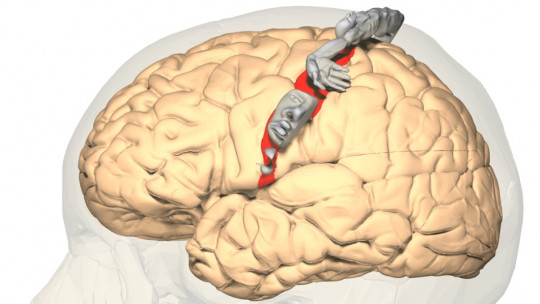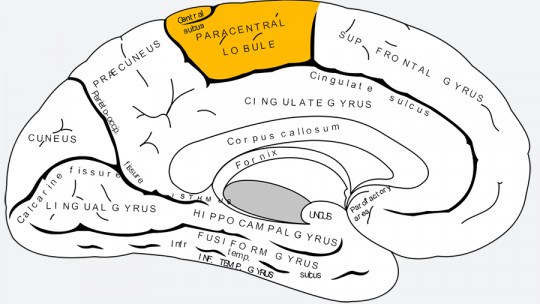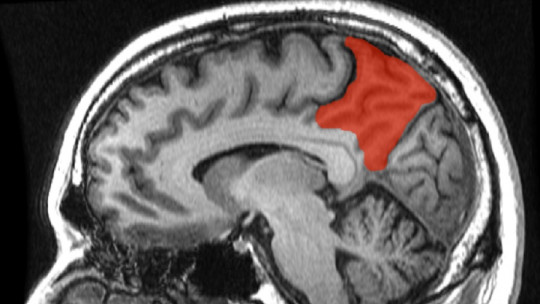
The human brain is a complex and fascinating organ. Each cerebral hemisphere is made up of several lobes.
And in the superior parietal lobe, hidden between layers of nerve fibers, we can find the precuneus, a region unique for its characteristics and for the functions that have been attributed to it as the main brain coordination center, as well as for participating in the processes of self-awareness. .
In this article we explain what the precuña is what is its structure and where it is located, what are its main functions and what role does it play in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Precuña: definition, structure and location
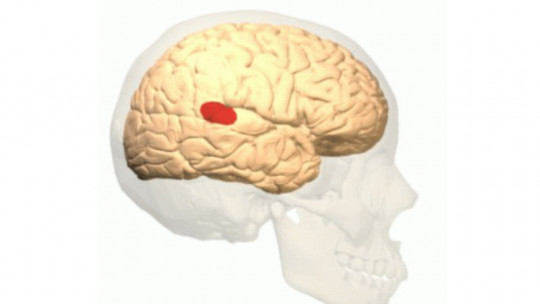
The precuneus or precuneus is a region located in the superior parietal lobe, hidden in the longitudinal fissure of the brain, between both hemispheres. It borders in front with the marginal branch of the cingulate sulcus, in the posterior part with the parieto-occipital sulcus and, below, with the subparietal sulcus.
The precuneus has also sometimes been described as the medial area of the superior parietal cortex. In cytoarchitectural terms, corresponds to Brodmann area 7 a subdivision of the parietal region of the cortex.
In addition, it has a complex cortical organization in the form of columns and is one of the brain regions that takes the longest to complete its myelination (a process by which axons are covered with myelin to, among other things, improve the speed of impulse transmission. nervous). Its morphology shows individual variations, both in its shape and longitudinal size.
In addition, The precuneus has numerous neuronal connections ; At the cortical level, it connects with sensorimotor areas, with areas linked to executive functions, memory and motor planning, and with the primary visual cortex; and at the subcortical level, it has important connections with the thalamic nuclei and the brain stem.
The precunea is a structure that has developed more in humans than in animals, since at an evolutionary level there has been a considerable increase in the size (in shape and surface) of the parietal and frontal lobes of the human cerebral cortex with respect to the rest. of the animal kingdom, with what this implies regarding the development of higher cognitive functions. Therefore it is, a structure that has sparked great interest in the neuroscientific community despite being anatomically so “elusive” (due to its location).
Features
The precuña is one of the main areas of regulation and integration of our brain and acts as a kind of orchestra conductor through which many of the necessary signals pass for this organ to function as an integrated whole.
Below are the different functions attributed to the precuña:
Autobiographical information (episodic memory)
The precunea works in connection with the left prefrontal cortex, involved in processes that have to do with episodic memory and autobiographical memories. In this sense, it participates in aspects such as attention, the recovery of episodic memory, working memory or conscious perception processes.
1. Visuospatial processing
Another key function in which the precuneus has been suggested to be involved is visuospatial processing; This area would participate in the management of spatial attention, when there are movements and, also, when images are generated
It is also believed to be responsible for motor coordination in divided attention processes; that is, when it is required to shift attention to different places or spatial locations (e.g. when writing a text or drawing a painting). Furthermore, the precuneus would be activated, together with the premotor cortex, in mental operations that require visuospatial processing.
2. Self-awareness
Various investigations have linked the precuña with processes in which self-awareness intervenes; In this sense, this brain region would have a relevant role in the integration of our perception of ourselves, in a network of spatial, temporal and social relationships. The precuña would be responsible for generating that feeling of continuity between brain, body and environment.
In functional imaging studies it has been observed that This brain structure analyzes and interprets the “intention” of others regarding ourselves ; That is, it would act as a mechanism for analyzing other people’s judgments that require adequate interpretation in order to act accordingly (e.g. with empathy).
3. Conscious perception
In addition to having a relevant role in self-awareness processes, it has been suggested that the precuneus could be, together with the posterior cingulate cortex, relevant to the processing and conscious perception of information
It has been observed that during wakefulness brain glucose metabolism increases significantly, contrary to what happens when under the influence of anesthesia. Furthermore, during slow wave sleep and rapid eye movement sleep or REM sleep, the precuneus would be practically deactivated.
On the other hand, it is believed that the cognitive functions related to this brain region could contribute to integrating internal information (that comes from the brain and our body) with environmental or external information; In this way, the precunea would have an essential role in the processes that generate consciousness and the mind in general.
4. Integrating core
There are more and more studies that support the role of the precunea as neural networks integrative center of the brain, due to its high centrality in the cortical network of this organ and its numerous and powerful connections with prefrontal areas in charge of executive functions such as planning, supervision and decision making.
The prewedge in Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease, in its early phase, It begins with metabolic problems in the area of the medial parietal lobes It seems that the enlargement of these brain regions is what confers a certain vulnerability to the subsequent neurodegeneration suffered by these patients.
Various studies have suggested that there may be a relationship between the precunea and the development of this serious disease. As we have mentioned previously, the precunea has evolved differently in humans than in animals: the main difference with respect to other primates, for example, is that this structure has particularly high metabolic levels.
Apparently, The precunea has higher levels of metabolic expenditure than would be appropriate for its size, which also happens with its thermal values. The curious thing is that Alzheimer’s begins with metabolic problems precisely in the deep medial parietal area, where the precuneus is located. And a hallmark of Alzheimer’s is the phosphorylation of tau proteins, which occurs in hibernating mammals in response to temperature changes.
What neuroscientists suggest is that a pathology as common and characteristic of humans as Alzheimer’s would be associated with areas of the brain that also have a specific morphology in humans. And what is questioned is whether the increase in the complexity of these brain areas could have led to an increase, likewise, in the biological complexity that, secondarily, could cause an increase in the metabolic load, oxidative stress and the cellular problems that predispose a person to suffer from Alzheimer’s disease.
However, research is currently continuing on the possible link between the precunea and other similar structures with the development of this and other neurodegenerative diseases, with the aim of finding new drugs and therapeutic targets that cure or, at least, slow their progression.