Embolic stroke, also known as cerebral embolism, is one of the major health complications that can occur affecting the functioning of the brain. This is a type of stroke that can cause permanent brain damage, induce a coma, or directly cause death.
Below we will see how a cerebral embolism occurs and what type of damage and disorders it can cause.
What is a cerebral embolism?
a cerebral embolism It is a type of heart attack, that is, a vascular disease in which the flow of blood is interrupted (in this case, blood that runs through the vessels of the brain), seriously compromising the survival of regions of the body irrigated by that duct and its branches due to the immediate lack of oxygen. In this way, a situation of asphyxiation occurs that affects an infarcted, or ischemic, area.
Specifically, what distinguishes cerebral embolism from other types of cerebral infarction is the way in which it occurs. the cessation of blood flow through the affected area In this disease, a body blocks the blood vessel for a time or permanently until it is removed by surgery.
The difference between a thrombus and an embolus
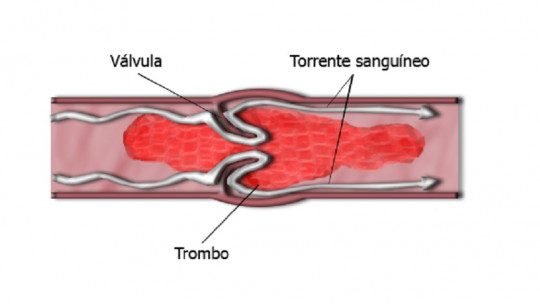
The obstructing element that causes a cerebral embolism is usually a clot that occurs due to a narrowing of a section of the blood vessel. It must be taken into account, however, that in ischemic accidents This obstructing body can be of two types: either a thrombus or an embolus
If it is a thrombus, this clot will not have left the wall of the blood vessel at any time, and will have been growing in size there. On the other hand, the embolus does not have a fixed position in the circulatory system, and It travels through the blood vessels until it becomes “locked in.” in one place and cause thrombosis.
So, while the thrombus affects the part of the body where it develops, the embolus can come from a distant area of the body and cause problems almost anywhere.
Regarding cerebral embolism, It is found within the ischemias known as embolic accidents while heart attacks caused by thrombi are thrombotic accidents.
Why does brain damage occur?
It must be taken into account that the brain is one of the most complex organs in the human body, but also one of the most delicate and energetically demanding.
Unlike other structures in the body, it needs constant blood flow to continue functioning; specifically, Every 100 grams of brain matter needs to receive about 50 ml every minute of properly oxygenated blood.
If this amount falls below 30 ml, an infarcted area may be generated due to lack of glucose and oxygen. In the case of cerebral embolism, the infarcted or ischemic area is dead cell tissue basically composed of neurons and glia.
Symptoms
The main long-term symptoms produced by this type of ischemic attack can be very varied, since there are many functions that depend on the proper functioning of the brain. However, short-term symptoms are easier to recognize ; They are the following, although the presence of just one does not mean that this is the cause, and they do not have to occur all at the same time:
Main types of cerebral embolism
Beyond the classification of ischemic events, differentiating between thrombotic and embolic accidents, the latter also present different sub-categories that allow us to better understand the characteristics of each case.
Fundamentally, these categories depend on the characteristics of the embolus that produces the risk situation. So, the main types of cerebral embolism They are the following.
1. Air plunger
In these cases, the plunger is an air bubble which acts by preventing the passage of blood.
2. Tissue embolus
In this type of stroke, the obstructing body is part of a tumor or groups of cancer cells.
3. Fat embolus
The plunger is made of fatty material that has accumulated forming a plaque in the blood vessel, and that has been traveling through the circulation after detaching itself from its original position.
4. Cardiac embolus
In this type of cerebral embolism, the embolus is a blood clot which has acquired a thick and pasty consistency.
Associated disorders and sequelae
Among the most common consequences of cerebral embolism are the following:
Emotion regulation disorders
People who have suffered a stroke may have greater difficulty repressing impulses, regulating complex emotional responses, or expressing the way they feel.
Language disorders
Language uses networks of distributed neurons by various parts of the brain, so it is easy for an ischemic attack to affect the biological functions that maintain it. For example, the appearance of aphasia is relatively common.
Paralysis
Stroke can cause parts of the body to become “disconnected” from the brain, causing the muscle fibers that move them to not be activated by the motor neurons that reach them.
Apraxias
Apraxias are disorders based on difficulty coordinating voluntary movements
Memory problems and amnesia
Amnesias, both retrograde and anterograde, are not rare. It may also occur that procedural memory, linked to the person’s intelligence, decreases.