When we talk about artificial intelligence, what do we mean? Experts in this matter have various points of view on the matter, but one of the most shared arguments is that a computer can be considered intelligent when it is capable of thinking like a human being.
Checking to what extent a machine “thinks” is complicated. Before we can make machines think, we should first understand how we think, an issue that remains a great mystery today.
Be that as it may, of all the ways to check if a machine has artificial intelligence, the Turing test It is surely the most famous. Next we are going to discover what it consists of and what its implications have been.
What is the Turing test?
The Turing test is a method of inquiry in artificial intelligence (AI) to determine whether or not a computer is capable of thinking like a human being This test is named in honor of its author, Alan Turing (1912-1954), one of the most famous experts in theoretical computer science, cryptanalysis, theoretical biology and mathematics. Turing proposed that to say that a computer has true intelligence, it must being able to imitate the responses that a human would give to specific conditions.
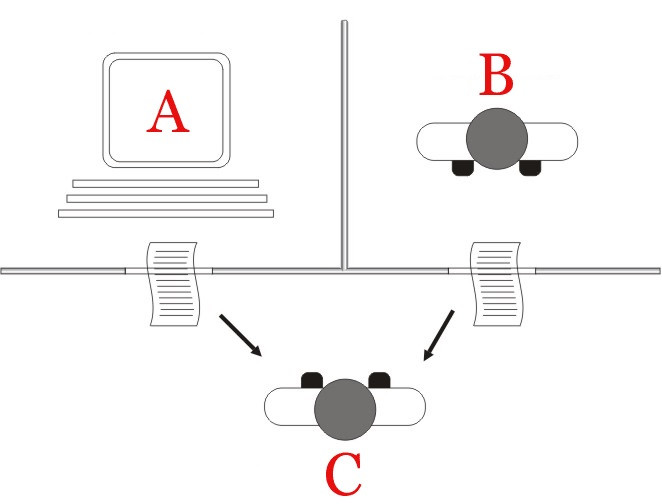
The original Turing test required three separate terminals. One terminal would be operated by a computer, while the other two would be operated by humans. During the test, One of the humans is tasked with asking questions, while the other human and the computer must answer them
The questions will be on a specific topic, using a specific format and context. After having done the questioning, the human asking the questions must decide which respondent was the human being and which was the computer.
The test is repeated as many times as you want. If the interrogator is wrong more than half of the time in deciding who the machine is, the computer is considered to have artificial intelligence given that he has behaved in such a human way that he has sown doubt in those who asked the questions.
History of the test
As we have mentioned, this test is named after its inventor, Alan Turing. This English mathematician was a pioneer in computing and machine learning research during the 1940s and 1950s. Turing introduced this test in his 1950 work called “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” when he worked at the University of Manchester. Without Alan Turing and his particular proposal, current AI programs such as chatbots and office assistants would be science fiction
His article began: “I propose to consider the question, Can machines think?” This question was accompanied by a peculiar hypothetical exercise: The Imitation Game. In its original conception, it did not involve a computer but three human participants in three separate rooms, connected to each other by a screen and a keyboard. In one room there was a man, in another a woman, and in another was the person who was going to serve as judge, of irrelevant gender. The woman had to try to convince the judge that she was the man.
After explaining this exercise with humans, Turing proposed it again, but this time putting a computer as a participant whose mission was to convince the judge that it was not a computer, but a human being. The task of the interrogator is to decide who is the Artificial Intelligence and who is the human being, as we have commented in the previous section.
Since the Turing test was conceptualized, it has been used countless times, being used as a useful tool to determine that a computer or cybernetic program has artificial intelligence. We have some resonant examples with the program ELIZA (1966), by Joseph Weizenbaum, capable of impersonating a psychotherapist and PARRY (1972) developed by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby who pretended to be a person with paranoid schizophrenia.
Limitations of the test when studying artificial intelligence
The Turing test is not infallible The main criticism of it has to do with the way it has been traditionally applied, usually in the form of very limited interrogation so that the computer, with the technology available at the time, could exhibit human-like intelligence.
Many of the occasions in which the test has been applied, the questions asked of the computers were closed , the kind that are answered with a “yes” or “no”. Sometimes these questions were so simple for the computer programs to answer that they could hardly be taken as a demonstration of their AI.
On the other hand, when the Turing test was applied with open or conversational questions, the response of the computer programs could become very chaotic. Although computer programs are more intelligent today, it is worth saying that depending on what open questions they make, they answer in a way that makes it obvious for their flesh-and-blood interlocutor to discover that they are talking to a machine.
For many researchers, the question of whether a computer is capable of passing the Turing test or not no longer matters today. Instead of focusing on how you can convince someone that they are humans instead of computer programs, the important thing would be to see how to make human-machine interaction more intuitive and efficient. For example, using a conversational interface.
Alternatives to this test
Since Turing lived, the world of computing and computing has evolved greatly. Today there are many alternatives to the original Turing test, which allow us to determine more clearly what an AI is. Between them we have:
1. Reverse Turing test
In this case, it is the human being who tries to convince the computer that it is not another computer. We have an example of this in the popular CAPTCHA very common on web pages where you have to enter a password.
2. Total Turing Test
Here the interrogator can test perceptual skills in addition to checking the ability of the interrogated subject to manipulate objects.
3. Minimum Intelligent Signal Test (MIST)
This would be the most minimalist version of the Turing test, in which Only closed true/false or yes/no questions are asked
4. The Marcus Test
This test is very interesting. Allows you to evaluate to what extent is a computer program capable of “watching” a television show and understanding it checking it by asking questions about its plot or characters.
5. The Lovelace Test 2.0
This test is made to detect artificial intelligence through his ability to create art
- Related article: “Ada Lovelace: biography of this mathematician and programming pioneer”
6. Winograd Schema Challenge
Multiple answer questions are asked in a specific format.
How is the Turing test currently used?
Despite there being variations of the Turing test, its original version is still used today We have an example of this with the Loebner Prize, a competition held annually since 1990 in which an award is given to those computers that manage to convince the jury that awards it that they are human, using the Turing test to define it. The competition follows the standard rules of the Turing test.
In a competition organized by the University of Reading to commemorate the 60th anniversary of Turing’s death in 2014, a chatbot called Eugen Goostman who pretended to be a 13-year-old boy managed to pass the Turing test, fooling 33% of the judges. .
In 2018, Google Duplex managed to book an appointment over the phone with a hair salon while a crowd of 7,000 people watched. The receptionist didn’t know she wasn’t having a conversation with a real human being This is considered by some to be one of the most recent and interesting cases of passing the Turing test, despite the fact that it does not follow the original format proposed by Alan Turing.
We have another case with GPT-3, a natural language processing model that some consider has the greatest probability of passing the test in its original format. However, despite its extremely advanced abilities, many have criticized this technology because it can be easily tricked by asking meaningless questions and cause it to have problems passing the Turing test.
Although there is debate about the relevance of the Turing test to determine that a computer program has intelligence, this test continues to be used today and widely commented on from a philosophical point of view to discuss and research AI. As artificial intelligence advances and there is a better understanding of how the human brain works, The Turing test will continue to be used as a tool to establish when a machine is capable of thinking like a human being